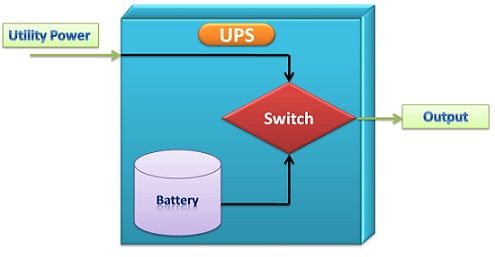
Definition: UPS is an acronym of Uninterruptible Power Supply, it is an electronic device which is used to supply power to other devices such as a computer, telecommunication equipment etc. in case of power outage.
The rectifier present in the UPS converts the AC power into DC, then the battery stores the DC power. This process continues when the AC power is on. When there is the power outage, the inverter converts the DC power into AC which is required for the functioning of the device.
We often rely on AC mains for running our domestic electronic devices such as fan, refrigerators, washing machine etc. For such devices, the effect of the power outage at any point of time might be insignificant, but for computer systems, communication equipment, medical equipment, the effect of instantaneous power cut is quite crucial.
Let’s take an example of a computer system, if we are working on it from a long time and we have a lot of unsaved work, then in case of instantaneous power cut, all the data will be lost. This can be big trouble for us if we do not give even the slightest thought to such problems.
Fortunately, we have UPS (Uninterruptible power supply) now. It will provide power to the device when external power is not available. We can easily save our work and properly shut down the system.
Significance of UPS (Uninterruptible power supply)
All our devices are dependent on AC mains power to process the inputs. But the AC mains may get sometimes fail due to the error in the circuit or short circuit of any network component. And after some time when the power is available, then it may have a slight variation in output voltage.
This leads to surges in the voltage and current, these distortions in the input voltage may lead to deterioration of the device. Electronic devices require constant supply until it gets switched off.
UPS (Uninterruptible power supply) plays a crucial role in providing constant power supply. The runtime of the UPS depends on the capacity of the battery it uses.
Types of UPS (Uninterruptible power supply)
There are three types of UPS available, and these are as follows:-
- Off-Line UPS or Standby UPS
- Line interactive UPS
- On-line UPS
Off-Line UPS or Standby UPS
The Off-line UPS consists of the battery, rectifier, inverter, EMI filter, Surge Suppressor and a transfer switch. When the AC input is fed into off-line UPS, then the surge suppressor or EMI filter removes the spikes and distortion due to the power surge. And the transfer switch connects the filter and switch path to the electronic device.

When the AC input is not available, then the transfer switches the device with the battery, rectifier and inverter path. In this condition, the AC input is converted into DC voltage first then battery is used for the storage of DC voltage and then whenever there is a requirement of AC power, the inverter converts the DC voltage into AC voltage.
Line Interactive UPS
The line interactive Ups is similar in construction as that of Standby Ups or off-line ups. The only difference between them is the Line Interactive consists of automatic voltage regulator along with EMI and RFI filter. The Automatic voltage regulator removes the fluctuation in the voltage along with suppressing surges in the voltage.

On-line UPS
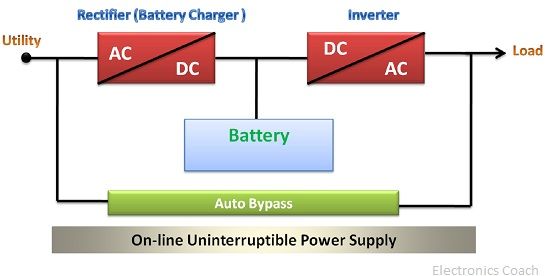
An on-line UPS (Uninterruptible power supply), consist of a battery, battery charger and inverter. The on-line ups is also termed as double conversion system.
In the above types of the primary source of power is AC mains, while in case of on-line ups the primary source of power is inverter present in the UPS.
In the above block diagram of on-line ups, it is clear that on-line ups do not have the transfer switch. Thus, the transfer time in case of on-line ups is zero. This means that in case of power outage the power supplied will appear like continuous power.
The on-line ups is called double conversion system, because the rectifier, battery and inverter is directly connected to the device which needs the power to run.
When the AC mains power is available, the rectifier converts AC power into DC, and then the battery will store the DC and pass it to the inverter, the inverter will then convert the DC power into AC and supply it to the device.
In this way, the device which is connected to the on-line ups will always get supply from inverter whether the AC mains power is available or unavailable.UPS is the crucial device which supplies constant power in case of primary power failure. But it can provide power for short duration of time.
Leave a Reply