The significant difference between LED and LASER lies in the working principle. LED emits light as the consequence of charge carriers recombination across P-N Junction, while LASER emits light as a result of photons striking the atom and compels them to release the similar photon. A laser works on the principle of stimulated emission and LED works on the principle of Electro-luminance.
Thus, in LASER every released photon strike another atom to release similar photon and therefore, the beam of light thus produced is coherent in nature. On the contrary, the light produced by LED is incoherent. Thus, light emitted by LED consists of many colours while light beam generated by the LASER is monochromatic i.e. single colour light.
LED is the acronym of Light Emitting Diode while the LASER is the abbreviated term used for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation.
Content: LED and LASER
| Parameters | LED | LASER |
|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | Electro-luminance | Stimulated Emission |
| Full Form | Light Emitting Diode | Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation |
| Response | Slow Response | Fast response in comparison to LED |
| Driving Current | It ranges from 50 to 100 mA. | It ranges from 5 to 40 mA. |
| Nature of Emitted Light | Incoherent and consists of various colours. | Coherent and Monochromatic. |
| Junction Area during Manufacturing | Wide Junction Area | Narrow and small Junction |
| Bandwidth Range | It lies in the range of 10 to 50 THz. | It lies in the narrow range i.e. from 1 MHz to 2 MHZ. |
| Power to light Conversion Efficiency | Approx 20 % | Approx 70 % |
| Numerical Aperture of the obtained Light Beam | Higher in LEDs | Extremely low as compared to LEDs. |
| Cost | Low cost and thus economical. | High cost and thus used in the specific application. |
Definition of LED
The LED is considered as the optical source for various crucial applications. The main principle behind its working is electro-luminance. In this phenomenon, the forward biased P-N junction emits light when electrons and holes recombine at the junction.

The electrons in the conduction band are at a higher energy level and the holes are in valence band which is at the lower energy level. When these electrons from conduction band jump into valence band they release some amount of energy. This energy can be in the form of heat or light.
The recombination of charge carries will be either an exothermic reaction or endothermic reaction. If electrons are on higher energy level and it tends to combine with the hole, it needs to emit energy. As recombination occurs only when the energy of both the recombining charge carriers should be comparable.
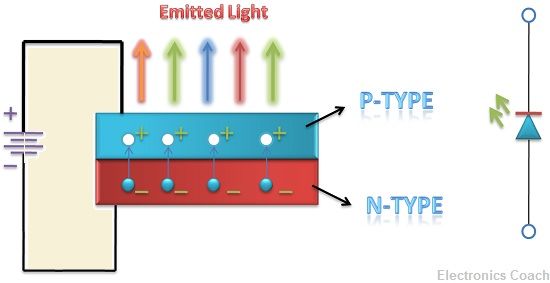
The semiconductor such as Germanium and Silicon emit energy in the form of heat while semiconductor such as GaAsP (Gallium Arsenide Phosphide) and GaP (Gallium Phosphide) emit energy in the form of light. Thus, this type of semiconductor is used in the manufacturing of LED.
LED are significant over various optoelectronic devices because it possesses fast response time in order of 0.1 microseconds. The light emitted by LED consists of various radiations of narrow wavelength. It comprises of visible radiations.
If the power to light conversion efficiency of LED is compared with that of a tungsten lamp, it will be 10 to 50 times higher than that of it which clearly makes it an appropriate optoelectronic device.
Definition of LASER
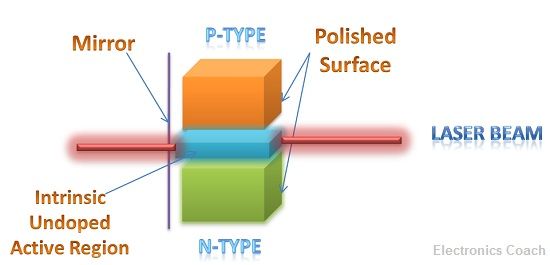
The LASER works on the principle of stimulated emission of radiation. Thus, it is called Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. The stimulated emission is the emission of the photon by striking the atom with the similar photon.
If electrical energy is supplied to the electron at the lower energy level, it will jump from valence band to conduction band absorbing the additional energy supplied to it. This process is called Absorption.
When the electron is at higher energy level it is unstable, in order to become stable it releases some part of its energy. This energy can be in the form of heat or light. If the energy released is in the form of light then it will emit a photon. This is process is called spontaneous emission.
When the photon strikes the atom it will strike the electrons at higher energy state then as result of collision these electrons will become unstable due to high energy and energy imparted by the striking photon. Thus, this electron will move to lower energy state and release a photon in addition with the incident photon. This is called stimulated emission.
Stimulated emission occurs in the LASER diode. The light beam is formed by emission of a photon which is similar to the incident photon. And these emitted photons will emit more photons similar to the incident one. In this way, the beam produced is coherent and monochromatic.
Key Differences Between LED and LASER
- The light beam produced by LED and LASER also creates a key difference between LED and LASER. The light emitted by LED consists of various colours while the light beam produced by LASER consists of a single colour.
- The working principle of LED and LASER also created major differences. LED works entirely on the principle of electro-luminance which means lumination by means of electrons. On the other hand, LASER works on the principle of stimulated emission.
- The another key difference between LED and LASER is the junction area. The area of the junction in case of the LASER is extremely narrow as light is allowed to pass from the extremely small area in case of the LASER. On the other hand the in LED, the junction area is wider. Thus, light is allowed to pass through over a wide area.
- The concentration of charge carriers such as electron and holes are also different in LED and Laser. In case of the laser, the concentration is very high while in Led it is very low. Thus, Laser is used in the surgical instrument in the medical field as it possesses sufficient energy that it can even cut the object in contact with it.
Conclusion
LED and LASER, both are the optoelectronic device, both the device generated light. But the working principle of light generation and construction architecture creates the difference. The output power generation capacity of laser diode lies in the range of 20 to 100 mW.
The protection of Eyes should be taken care when dealing with these optoelectronic devices especially in case of the LASER. It generates high energy beam.
GT Adamz says
Wow, I have learned alot, thanks.