Definition: AC voltmeters are designed in a manner so that they can measure the AC voltage under measurement. The main difference between AC voltmeter circuit and DC voltmeter circuit is the usage of a rectifier. The rectifier is used in order to transform the AC voltage into DC voltage.
Block Diagram of AC Voltmeter
To develop a basic understanding of AC voltmeter, it is crucial to have a brief idea of the block diagram of AC voltmeter circuit. The block diagram of AC voltmeter resembles the block diagram of DC voltmeter except the fact that rectifier is used in case of AC voltmeter.
The input to be measured is given to the attenuator circuit which performs the operation of selection of a particular range of voltage. The output of attenuator is given to rectifier which converts the AC voltage into pulsating DC voltage. Then the final output of DC amplifier is given to the PMMC meter.
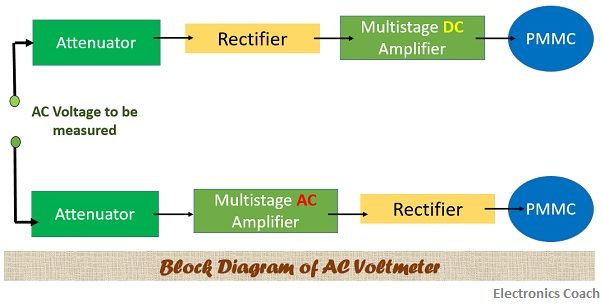
The rectifier can be used before the multistage amplifier or after the amplifier. This depends on the type of amplifier used in AC voltmeter. If we are using multistage AC amplifier, then the rectifier circuit will be used after the amplifier. On the contrary, if the multistage amplifier used is DC, then the rectifier should be used before it.
The amplifier is a vital component because it amplifies the signal which got attenuated during the measurement procedure. The usage of the amplifier increases the cost of the circuit. If the designing needs to be economical, then we should use multistage DC amplifier.
Classification of AC voltmeters
There can be three types of AC voltmeters based on the type of measurement it provides. These are average reading, peak reading and true RMS reading AC voltmeter.
Average Reading AC Voltmeter
The average reading voltmeter measures the average value of the AC voltage. The scale calibrated in average reading voltmeter is in terms of RMS value. This is because most of the AC voltages to be measured are in sinusoidal form. Besides, it is economical to measure the average value of AC voltage rather than its true RMS value.
Average reading voltmeters can be designed in various manners such as by using vacuum diode, semiconductor diode or a full wave rectifier.In this, the voltage-current characteristics must be linear, because the change in voltage is measured by the change in current.
Let’s understand first the basic construction of AC voltmeters using vacuum diode.
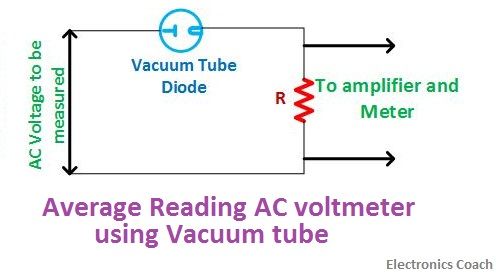
The requisite factor in such voltmeters is that the resistance of plates of vacuum tube should be low so that it does not create variation in linear characteristics of plate voltage and current.
For this, the resistance used in series with vacuum tube should possess sufficiently high value so that the linear characteristics can be maintained. The current across the resistor is fed to an amplifier which is connected with a PMMC meter used for measurement.
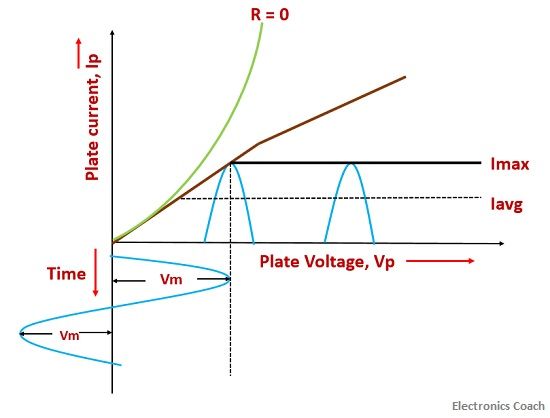
The above graph shows the variation of plate voltage and plate current.
Now, let’s consider an average reading AC voltmeter using semiconductor diode. In this, the semiconductor diode operated for an alternate half cycle. This is because it operated on the principle of half wave rectifier.
![]()
The average current through the diode can be given by the below equation. The value of 1.11 represents the form factor. The multiplying factor of 2 represents the half wave rectification phenomenon.
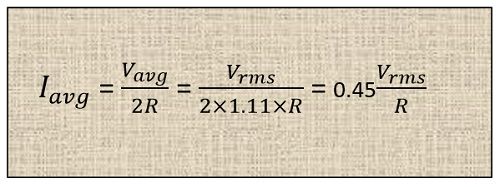
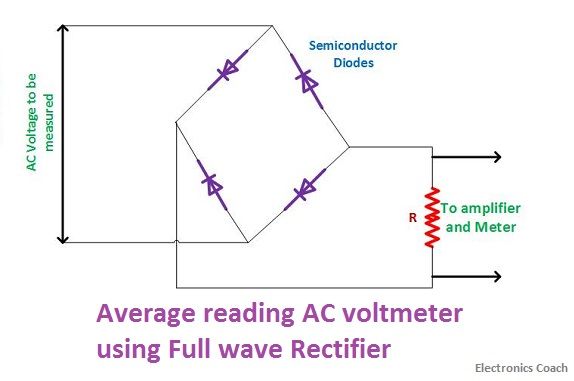
The average voltmeter can also be designed with the help of full wave rectifier. The average current in case of full wave rectifier will be double to that of half wave rectifier.
Advantages of Average Reading AC voltmeter
- Low Power Consumption
- High input impedance
- Simple Construction
- Uniform scaling
Disadvantages of Average Reading AC Voltmeter
- The circuit under measurement should possess low resistance otherwise it will load the circuit.
- The linear characteristics should be strictly maintained because non-linear characteristics will create issue during measurement of low voltages.
- It is appropriate only in audio-frequency range because, in radio frequency range, errors occur due to distributed capacitance.
Peak Reading AC Voltmeter
The peak reading voltmeter can also be designed in two ways. One is by using vacuum tube and another with the help of semiconductor diode. The difference between the peak reading and average reading circuit arrangement is only that the capacitor is not used in case of average reading while it is used in case of peak reading voltmeter.
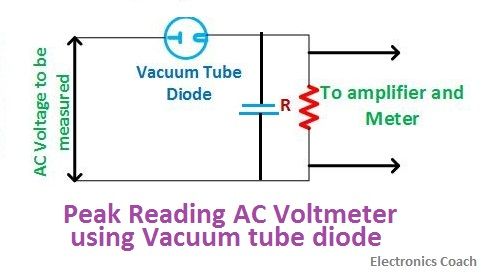
The above circuit shows the AC voltmeter using vacuum tube. The capacitor is connected in parallel to the resistance of high magnitude. The resistance is connected in parallel to the amplifier and the PMMC meter.
In the same way, it can be designed with the help of semiconductor diode. In place of the vacuum tube, we need to connect semiconductor diode in this case.
![]()
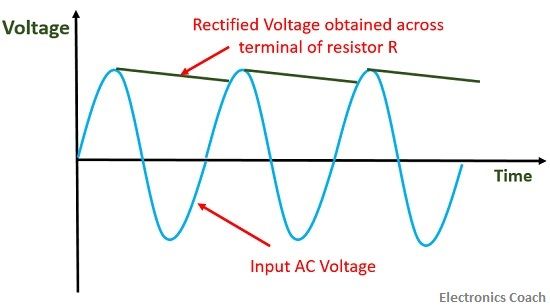
The working of the peak reading voltmeter can be easily understood with the help of above two circuits. When the input voltage is applied the capacitor starts charging until it attains its peak value. When the capacitor attains peak voltage, it starts getting discharged through the resistor.
The main disadvantage of using peak reading AC voltmeter is that it is not suitable for the measurement of a low voltage signal. This is because, in case of the low input voltage, the electrons at high velocity still contribute to current flow in the circuit which produces errors in the measurement.
True RMS reading AC Voltmeter
The average reading voltmeter is economical and provides RMS value of sinusoidal waveforms then what is the need for true RMS reading AC voltmeters?
And that too when the cost of true RMS reading voltmeter is higher than that of average reading AC voltmeters. This is because in case of non-sinusoidal waveforms we need to calculate true RMS voltage which is not possible with the help of average reading AC voltmeter. In such case, we need true RMS reading voltmeter.
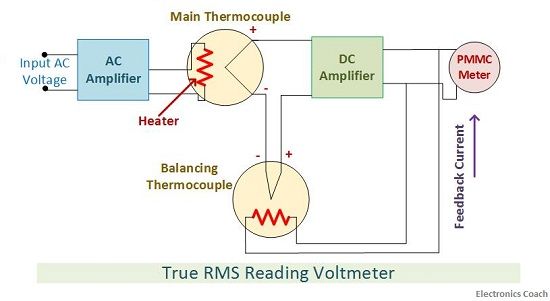
Principle of True RMS reading AC voltmeter
The heating power associated with the waveform varies directly with the square of the RMS value of the voltage. Thus, if by some means we succeed in measuring the heating power of the waveform we can easily measure the RMS value associated with the input waveforms.
For this purpose, a thermocouple is utilized. The thermocouple is an instrument which is used for measuring heating power of waveforms.
Working
The thermocouple used here will fetch input voltage from AC amplifier. This is because the magnitude of the signal should be sufficiently high in order to provide correct measurements. The thermocouple will receive the input waveforms through its input terminal. This thermocouple is called main thermocouple.
The non-linearity associated with the main thermocouple needs to cancel out. Otherwise, it will create errors in the final measurements. For this purpose, the balancing thermocouple is used. The non-linearity produced by balancing thermocouple and the non-linearity produced by the main thermocouple cancel out each other.
In this way, it acts as a balancing bridge circuit. The feedback current supplied by the AC amplifier is used for balancing in case of any error signal produced. When the input is not applied to the main thermocouple, then the output of both thermocouples will be equal and will produce zero voltage signal.
Thus, true RMS reading AC voltmeter provides an aid to measure the RMS value of the non-sinusoidal waveform. It must be kept in mind that dynamic range of AC amplifier should be sufficiently high so that peak excursion created by input waveform does not exceed the range of AC amplifier.
Ankita says
Please I want accuracy precision sensitivity and resolution range of ac voltmeter