A voltmeter is an instrument which measures the voltage between two points of a circuit while Ammeter measures the current flowing in the circuit. Voltage is measured in Volts while Current is measured in Amperes. Thus, the unit in which voltmeter measures the voltage is volt while the unit in which ammeter measures the instrument is Ampere.
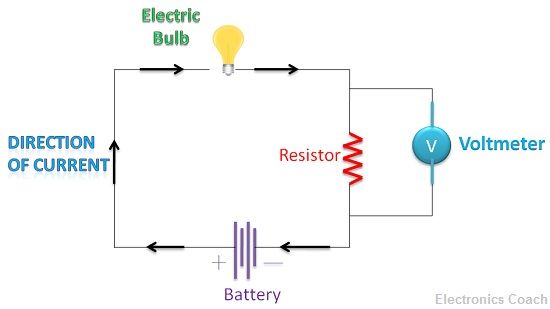
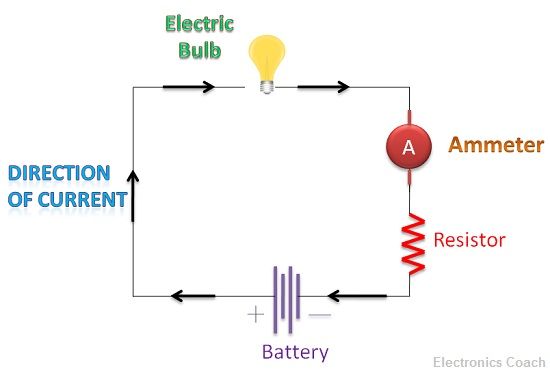
The other significant difference between Voltmeter and Ammeter is connection architecture. The voltmeter is connected parallel across the load when we want to measure the voltage across it. The ammeter is connected in series in the circuit. This is because the magnitude of the current is same across every component connected in series in a circuit while the voltage is same across the components which are connected in parallel between two points in the circuit.
The other crucial differences between Voltmeter and Ammeter are described below in Comparison Chart.
Content: Voltmeter and Ammeter
Comparison Chart
| Parameters | Voltmeter | Ammeter |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A measuring instrument which measures voltage difference between two points. | A measuring instrument which measures current flowing in the circuit. |
| Connection | Connected in parallel | Connected in series |
| Unit of Scale Calibrated | Scale is calibrated in volts | Scale is callibrated in Ampere |
| Ideal Resistance | Infinite | Zero |
| Practical Resistance | High resistance as compared to Ammeter | Very low resistance as compared to Voltmeter |
| Accuracy | Less accurate than Ammeter | More accurate as compared to Voltmeter |
Definition
Voltmeter
A voltmeter is a measuring instrument which measures the voltage difference between the two points when connected in parallel across those points. The voltmeter is made up of a coil which is placed in magnetic field.
When current flows in a closed loop, the effect of the magnetic field can be experienced across it. Thus, if current carrying coil is placed in the external magnetic field, it will experience the magnetic force due to which the coil will deflect and the pointer of the voltmeter points to a particular value on the scale of the voltmeter.
This entire arrangement is known as indicator system as it indicated through the pointer. The utilization of magnetic force for the deflection of the coil for indicating voltage is the principle of Analog Voltmeter. ,On the other hand, digital voltmeter uses Analog to digital conversion devices so that the analog voltage can be converted to digital.
Digital Voltmeters are much popular these days. The unit of voltage is volts. Thus the measuring device displays the results in volts. The term volt is used for voltage because Alessandro Volta has discovered electrical battery. Thus, the unit of the voltage provided by the battery is kept in his name.
Voltmeters are available in various range; it can measure from Millivolt to Gigavolt. The voltmeter is also provided with spring arrangement so that when the current flowing through the coil stops, then the spring will enable the coil to deflect the pointer towards zero.
Resistance of Voltmeter
Ideally, the resistance of the voltmeter should be infinite. This is because when it is connected in parallel, it should not withdraw any current from the circuit, but to create the magnetic effect and repulsion, it is necessary to withdraw some amount of current. Thus, practically the resistance of the voltmeter cannot be infinite, but it will be of some low magnitude.
Ammeter
An ammeter is a measuring instrument which measures the current flowing in the circuit. It is connected in series in the circuit. It is also comprised of current carrying coil which is placed in the magnetic field. When current starts flowing through the coil, the magnetic field is created around the coil.
If this coil is placed in the external magnetic field, then the magnetic field created across the current carrying coil will experience the force of repulsion. This force of repulsion will enable the coil to deflect the pointer on the scale of the ammeter.
The higher the intensity of the current flowing through the coil the more will be the deflection of the pointer. In this way, the ammeter shows the value of current flowing in the circuit. The unit of current is Ampere. Thus the scale of the ammeter is in ampere.
It can measure various ranges such microamperes, milliamperes. The ammeter measuring microamperes is termed as microammeter. Similarly, the one measuring the current in milliampere is termed as milliammeter.
Resistance of Ammeter
In an ideal case, the resistance of ammeter should be zero, because it should allow the entire current flowing in the circuit through it, only then it will give the exact value of the current flowing in the circuit, but it is not possible in the real scenario.
Practically, the ammeter possesses a certain value of resistance. Thus, no matter how efficient the ammeter is, it will give minor errors in measurement because they possess small value of resistance
Key differences Between Voltmeter and Ammeter
- Measurement of: The key difference between voltmeter and ammeter is that both these devices measure different quantities. One measure voltage and the other measure current. A voltmeter measure voltage difference between two points in the circuit while ammeter measure current in the circuit.
- Way of Connection: The voltmeter is connected in parallel in the circuit while ammeter is connected in series.
- Resistance: The resistance of the voltmeter is much higher than the resistance of the ammeter. Ideally, the voltmeter should have infinite resistance while ideal ammeters have zero resistance.
- Accuracy: The accuracy of the ammeter is higher than the accuracy of the voltmeter.
Conclusion
The voltmeter measures the voltage difference between two points in the circuit while ammeter measures the current flowing through the circuit. If we want to measure the current flowing through the load, we need to connect the ammeter in series with the load. While if we want to measure the voltage across the load, we need to connect a voltmeter in parallel with the load.
Both are the measuring devices used to measure electrical energy. Electrical energy can be measured either in terms of voltage or in terms of current, and thus, we can calculate electrical power with the help of either of these parameters.
Nowadays, digital Multimeters are very popular for measuring electrical quantities. Instead of using two different meters for measuring current and voltage we can use one single instrument for measuring current as well as voltage.
Leave a Reply