The major difference single-mode and multimode optical fiber is that in single-mode optical fiber light ray propagates only through a single path. On the contrary, in multimode optical fiber several light rays propagate through the waveguide at the same time.
Another crucial difference between single-mode and multimode optical fiber is that single-mode fiber has a smaller core diameter as compared to multimode fiber.
We will discuss some other important differences between single-mode and multimode optical fiber but before that have a look at the contents to be discussed under this article.
Content: Single-mode Vs Multimode Optical Fiber
Comparison Chart
| Parameter | Single-mode Optical Fiber | Multimode Optical Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Number of propagating mode | Only one | More than one |
| Core diameter | Small | Large |
| Optical source | LASER | LED |
| Bandwidth | More | Less |
| Handling and coupling | Difficult | Easy |
| Initial cost of fiber | Low | High |
| Attenuation | Less | More |
| Transmission rate | High | Low |
| Signal transmission distance | Long | Short |
| General colour coding | Yellow | Orange or Aqua |
| Modal dispersion | Absent | Present |
| Numerical Aperture | Low | High |
| Preferred fields | In telecom and CATV networks | In security systems and LANs |
Definition of Single-mode optical fiber
A single-mode optical fiber is a type of optical fiber that allows the propagation of only a single ray of light along the fiber. Here, the core to cladding diameter is 9 to 125 micrometres.
It is also known as uni-mode optical fiber or mono-mode optical fiber.
The diameter of the core is very small due to which only a single light ray gets transmitted through it.
As we are already known to the fact that an optical fiber has three basic parts namely- core, cladding and coating(buffer).
A typical single-mode optical fiber is shown below: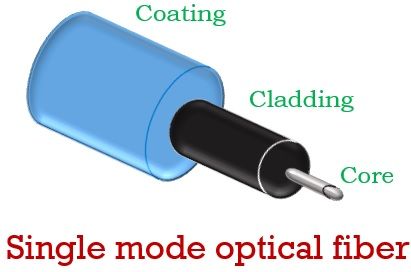
The core which is the central part consist of only a single fiber strand. The emitted light from the source travels through this particular section. The small diameter of the core requires a sharp focused light beam as its source. Thus uses a LASER as its optical source.
Due to the transmission of only a single light ray, single-mode optical fiber possesses minimum signal distortion. Thus, modal dispersion is not noticed that supports the long-distance transmission of signal with an appreciably enhanced transmission speed. This resultantly provides greater bandwidth which serves as an advantage of single-mode optical fiber.
Another aspect of single-mode optical fiber is that its small core size makes its handling somewhat difficult. Along with this, projecting light into the core also becomes a hard task.
All the advantages associated with single-mode optical fiber makes their use suitable with the emerging optical technologies.
Definition of Multimode optical fiber
Another type of optical fiber is multimode optical fiber. In multimode optical fiber, several light rays propagate through the fiber at the same time, but, each reflects at a certain different angle than other during transmission.
The core to cladding diameter in case of multimode optical fiber is 50-62.5 to 125 micrometres. The figure below shows a basic multimode optical fiber.

Here, the diameter of the core is large that permits multiple light rays to transmit through it thus uses LED as its optical source. As several modes propagate through the core thus there exist more possibilities of interference of various modes. Due to this intermodal dispersion occurs in multimode fibers.
As long-distance transmission can increase the chances of dispersion within the fiber thus these are mostly used in applications associated with short distances. The multimode fiber is expensive optical fiber but the transmission equipments associated with multimode fibers costs less.
Whenever there is a need to have a connection within the building, then multimode fibers are the first choice nowadays because of their reliable nature.
Key Differences Between Single-mode and Multimode Optical Fiber
- A single-mode optical fiber has a core diameter of about 8 to 10 micrometres while in a multimode optical fiber the core diameter is nearly about 50 to 62.5 micrometres.
- A single-mode fiber generally uses LASER as its optical source as it needs a light source with narrow spectral width.As against, when we consider a multimode optical fiber then it operates efficiently with LED because due to the large core diameter it does not requires a focused beam.
- As the dimensions of single-mode optical fibers are small thus its handling and coupling is quite difficult as compared to multimode optical fibers.
- The propagation of only a single light ray results in less attenuation in single-mode optical fiber. However, due to multiple reflections of light rays attenuation is more in multimode optical fiber.
- As fewer losses are associated with a single-mode optical fiber thus they have the ability to transmit a particular signal to longer distance in comparison to multimode optical fiber. Transmission distance of single-mode fibers is nearly 50 times greater as compared to multimode fiber.
- Single-mode optical fibers are less expensive as compared to multimode optical fibers but instruments associated with single-mode optical fibers makes it expensive as compared to multimode optical fiber.
- When we talk about bandwidth utilization then single-mode optical fiber has higher bandwidth nearly about 400 MHz/km whereas multimode fiber has lower bandwidth in the range of 50 – 60 MHz/km.
Conclusion
So, from the above discussion, we can conclude that both single and multimode fibers have their own unique property. Thus, their utilization depends on the need of the system. It is noteworthy that transmission wavelength of single-mode fiber is between 1260 to 1640 nm and that of multimode fiber between 850 to 1300 nm.
Leave a Reply