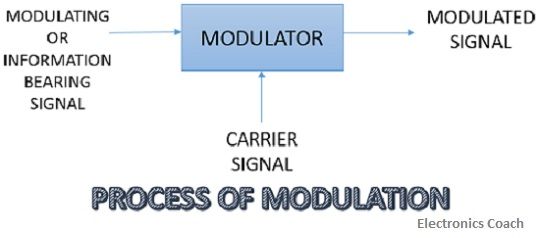
Definition: Modulation, the process in which the carrier signal is varied according to the information bearing signal also called the modulating signal.
During modulation, some characteristics it can be amplitude, frequency, or phase is varied in accordance with the original information-bearing signal that has to be transmitted.
The receiver at the destination end won’t be able to understand that particular modulated signal so it uses demodulator section and demodulates that signal so as to get original baseband signal.
Now the thing that comes to our mind is what a baseband signal is?
The baseband signal is nothing but the original message signal that the user actually wants to transmit which is unconverted or we can say unmodulated. These unmodulated signal generally occupies frequency spectrum from 0Hz as we can see in the picture given below-
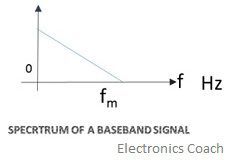
Let’s take an example and make it more clear, an audio signal can have a baseband range from 20Hz to 20KHz but during transmission when the signal gets modulated it goes to a higher inaudible range.
When any baseband signal is transmitted such as in telephone network where the electrical form of sound signal is directly placed on telephone lines for transmission it leads to several difficulties in communication that can be the effect of noise or crosstalk.
This is the only reason why we convert a baseband signal into a bandpass signal.
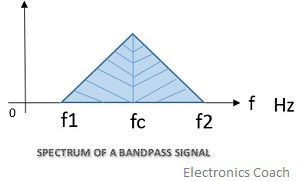
Another question that arises in our mind is what a bandpass signal is?
When the baseband signal is modulated or converted so as to transmit it to a longer distance it is known as bandpass signal. These signal have non zero lowest frequency in its spectrum. The frequency band of these signal is not adjacent to zero frequency.
Radio waves and ultrasound waves best suit the example for bandpass signal. During modulation, the carrier signal which we use is basically a carrier which carries modulating signal from end to the other.
For example, when a person rides his/her bicycle, the person can be assumed as the signal to be modulated and bicycle can be viewed as the carrier signal.
Need of Modulation
During modulation as we have discussed earlier that a low-frequency signal is modulated to have a high-frequency signal which ultimately gives us several advantages during transmission which are briefly discussed below
- Height of the antenna is reduced: When we transmit a radio signal antenna height must be a multiple of λ/4 where λ is the wavelength whose value is λ = c/f.λ is directly proportional to the speed of light and inversely proportional to the signal frequency. This means that higher the frequency lesser will be the value of λ that result in the shorter height of antenna which can be practically installed. Thus we can say modulation reduces the antenna height.
- Avoid mixing of signals: It avoids the mixing of various signals. Suppose we have transmitted some baseband signals by multiple transmitters then all the signal will be in between the same frequency band i.e., in between 0 to 20KHZ which result in mixing of signals and receiver will not be able to separate them. But if we modulate all the signals with different carriers then the signals will have different frequency range so that they can be easily separated at the destination.
- Increase in the range: The low-frequency message signal has another drawback that it cannot travel much longer distance during transmission as the signal gets attenuated. However, if we increase frequency then attenuation gets reduced thereby increasing the range of data transmission.
- Multiplexing can be done: Modulation makes multiplexing possible. Through multiplexing, we can use the same channel to transmit various signal at the same time. But it gets successful only when the signal is modulated because modulation provides different frequency range to the signals. Due to which they can be transmitted through the same channel at the same time.
Types of Modulation
- Analog
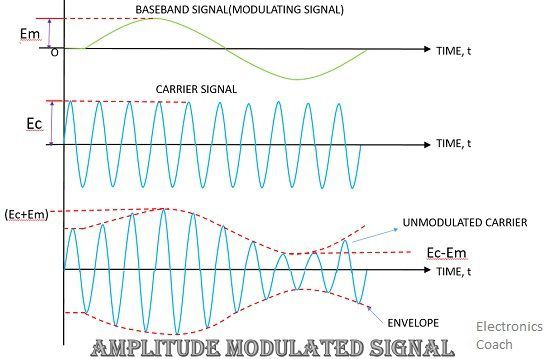
- Amplitude Modulation: It is the process in which the amplitude of carrier signal is varied according to the amplitude of the message signal. This mode of modulation is very simple and straightway to modulate any baseband signal. It is the most effective and easiest way of modulation.
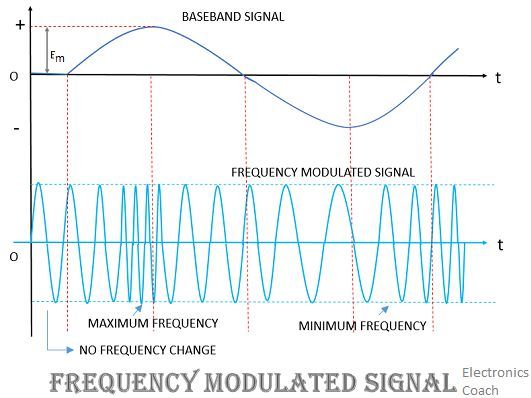
- Frequency Modulation: This type of modulation has mainly its application during radio communication. When the frequency of the carrier is varied according to the amplitude of information bearing signal then this modulation is known as frequency modulation. Here, carrier’s amplitude remains constant. In this, the information is carried by frequency variation. The most important factor is the amount of variation of signal frequency. Better SNR can be achieved through FM as compared to AM in case of wider bandwidth.
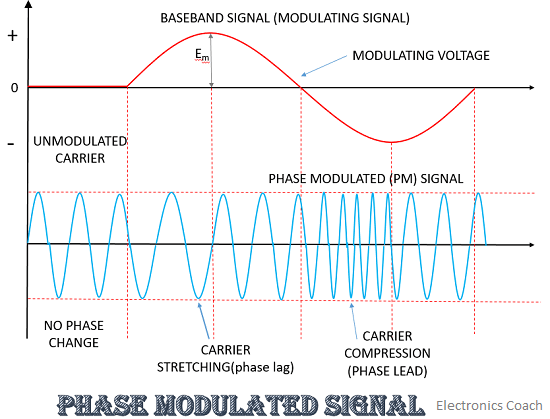
- Phase Modulation: Here, the phase shift of the carrier is varied according to the amplitude of carrier wave. When we apply phase modulation it leads to change in frequency too.
- Pulse Analog Modulation: In pulse modulation, the carrier is in the form of pulse rather than being a sine wave as in other types of modulation.
- Pulse amplitude modulation or PAM: In this, the amplitude of carrier which is in the form of pulses is varied according to the amplitude of modulating the signal.
- Pulse width modulation or PWM: The width of the pulsed carrier is varied according to the amplitude of modulating the signal.
- Pulse position modulation or PPW: The position of the pulses is varied according to information-bearing signal in pulse position modulation.
- Amplitude Modulation: It is the process in which the amplitude of carrier signal is varied according to the amplitude of the message signal. This mode of modulation is very simple and straightway to modulate any baseband signal. It is the most effective and easiest way of modulation.
- Digital
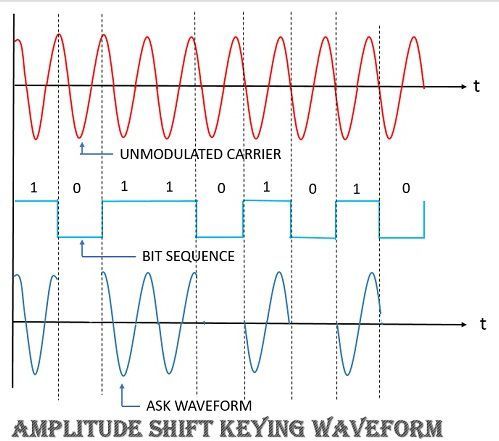
- Amplitude shift keying or ASK: The signal carrying digital bit stream is modulated with the amplitude of carrier signal.
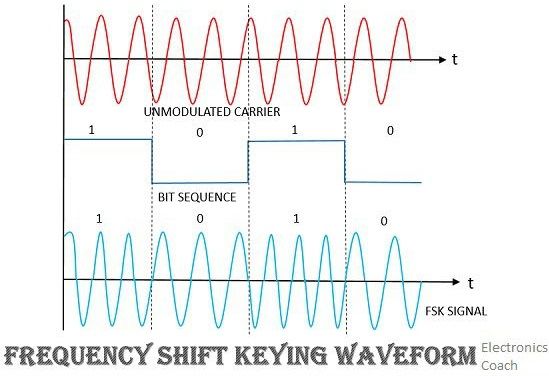
- Frequency shift keying or FSK: In this, the frequency of carrier signal is varied according to the digital bit stream of information bearing signal.
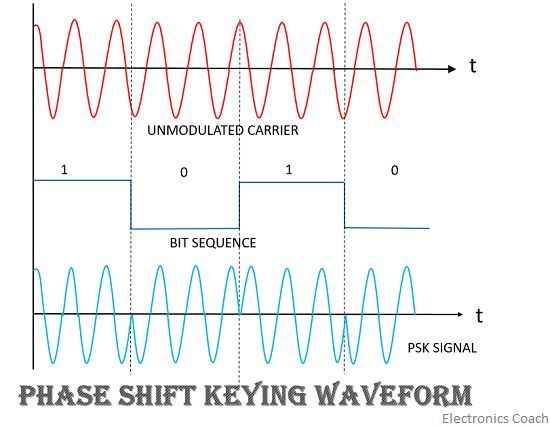
- Phase shift keying or PSK: This technique ensures the data to be transmitted in a more efficient manner as compared to FSK. In this, the phase of the carrier is varied with respect to the digital bit stream of the information signal.
- Amplitude shift keying or ASK: The signal carrying digital bit stream is modulated with the amplitude of carrier signal.
Digital communication supports higher noise immunity than analog communication. But at the same time, digital data requires more bandwidth as compared to an analog signal.
In Digital communication, error detection and correction can be implemented easily. Digital modulation provides much more efficient results when compared to analog communication.
Leave a Reply