AC is an acronym of Alternating Current while DC is an acronym of Direct Current. The major difference between AC and DC is that DC is unidirectional current while AC is bidirectional Current. DC is constant with time while AC changes at every instant of time.
The major drawback of using DC is, it starts deteriorating with distance. The power supplied by DC source is not convenient for long distance as it will diminish with the increment in the distance. This is not the case with AC. Thus it is reliable for transmission.
AC and DC, both are the types of electric current but both contrast each other regarding generation, flow in circuit and applications. Another important difference between AC and DC is the magnitude of the voltage. DC voltage is low-level voltage while AC is high-level voltage.
Content: AC and DC
Comparison Chart
| Parameters | AC (Alternating Current) | DC (Direct Current) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | AC is the type of electric current which varies instantaneously with time. | DC is the type of electric current which remains constant with time. |
| Long Distance Transmission | Suitable for long distance transmission as power losses are minimum. | Not suitable as power loss is directly proportional to distance. |
| Flow of Electrons | Bi-directional flow of electrons | Uni-directional flow of electrons |
| Freqency | Between 50 Hz to 60 Hz, different in different countries | Frequency of DC is zero. |
| Power Factor | It lies between 0 and 1. | In DC, it will be always 1. |
| Graphical Representation | Sinusoidal Wave | Constant line |
| Generation Mechanism | By placing current carrying coil in rotating magnetic field. | By placing current carrying coil in steady magnetic field. |
| Generating Devices | Alternators | Cells or batteries |
| Type of Load | It can be resistive, inductive or capacitive. | Only resistive |
| Capacitive Impedance | Capacitor allows DC to pass thorugh it, thus capacitive impedance will be low. | Capacitor blocks DC, thus capacitive impedance will be infinite. |
| Applications | High Voltage application such as home appliances, office equipments. | Low Voltage applications in electronic circuits |
Definition
AC (Alternating Current)
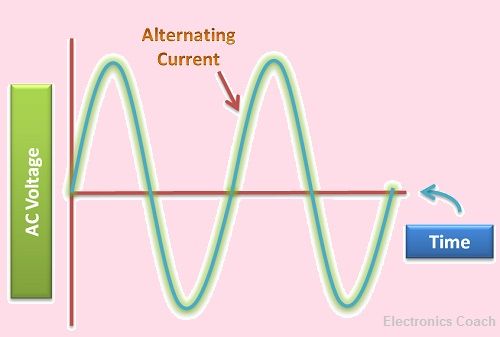
AC is the type of electric current in which polarity of the current does not remain constant. The current is the consequence of flow of electrons. If electron flow in one direction, it is unidirectional current but if it flows in 2 directions, i.e. forward and backward it is called bidirectional current.
AC is bidirectional Current. You must be thinking what makes AC conduct bidirectionally. Your answer lies in the generation of AC. The current carrying wire is placed in rotating magnetic field. Now, the direction of flow of electrons also varies with the movement of the magnetic field.
AC can also be generated by placing a wire in the static magnetic field, but now the current carrying wire needs to be rotated. The conclusion of the story is either we need to rotate current carrying wire, or we need to rotate magnetic field provided that the remaining parameter is constant.
Let me discuss what happens exactly when the wire carrying current is placed in rotating magnetic field? The electrons are flowing in the wire experiences the magnetic force, and they will get attracted to one of the poles of the magnetic field. If the field is rotated again the direction in which electrons are getting attracted will change.
This changes the direction of flow of electrons and thus, AC generation takes place. The generation of AC sis much simpler and convenient than DC. Moreover, AC power does not diminish with increase in distance. Thus, it is appropriate for long distance transmission.
The representation of AC signal or AC can be more clearly understood with the help of graphical diagram represented below.
DC (Direct Current)
Direct current is also caused by the flow of electrons, but the generation process of direct current is opposite to that of AC. Unidirectional current can be generated if the wire carrying current is placed in the static magnetic field.
The electrons flowing in the wire will experience the force in one direction only because the magnetic field is steady. Thus, the flow of electrons in one direction will generate DC. DC power gets diminished with the increase in the distance of transmission. This makes it unsuitable to use for long distance transmission.
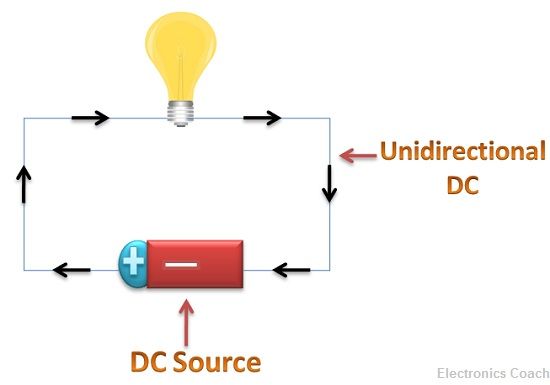
The examples of DC power generation devices are the cell, battery etc. These devices possess a particular value of DC voltage. Usually, these values are low. Thus, a cell or battery have the energy to push electron to make them flow in the circuit. But these devices do not have enough energy to pull these electrons. Thus, only unidirectional current is generated.
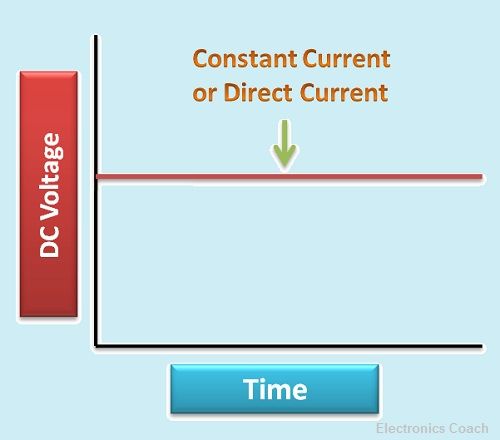
If we observe the graphical representation of DC, it is evident that DC is constant with time.
Key Differences Between AC and DC
- Directional Feature: It is one of the key features which differs AC and DC. DC is a unidirectional type of electric current while AC is bidirectional electric current.
- Generation: AC and DC possess different generation procedures and devices. DC is generated by static magnetic field while AC is generated with the aid of dynamic magnetic field. Besides, AC is generated by generators while DC is generated by cell, batteries by converting the chemical energy of cell or battery into electrical energy.
- Frequency of Signal: The frequency of AC signal varies from 50 Hz to 60 Hz. It is different in different countries. DC signal has zero frequency. Frequency is the number of cycles per second. As DC signal do not cycle varying with time, thus it has zero frequency.
- Type of Load: Load connected in AC can be capacitive, resistive, or inductive. On the contrary, the load connected in DC circuit is always resistive.
- Power Factor: The power factor of alternating current lies between 0 to 1 while power factor of DC is 1.
- Ease of transmission: The AC power can be transferred easily and efficiently as compared to DC power.
- Voltage level: The DC voltage is low-level voltage while the AC voltage is high in magnitude.
- Storage: AC cannot be stored while DC can be stored in cell or batteries. We can convert AC into DC using rectifier in our chargers while we can convert DC into AC using inverters. But the storage of AC is not possible.
Conclusion
The AC is bidirectional, high magnitude current which can be transmitted to long distance without power loss. On the contrary, DC is a low magnitude, unidirectional current which is not suitable for transmission up to a long distance. The passive parameter in AC is impedance, but in DC the passive parameter is resistance.
Erhan Berber says
Really helpful explanations. Thank you.