Definition: Optical amplifier is a device used in an optical communication system to directly amplify (boost) optical data signal without changing it into its electrical form.
By making use of Optical amplifiers in optical fiber communication, the optical integrity of the whole system is retained.
Need of Optical amplifier
During signal transmission, it is necessary to employ amplifiers within the network in order to have a distortionless data signal.
When we talk about an optical communication system where data is transmitted in the form of light through fiber cable then the system also requires an amplification unit. This is so because when the signal is sent from an end to the other then various factors degrade the quality of the signal. Due to which it sometimes becomes impossible to regain the original information from that particular signal.
If we use an electronic amplifier unit then it necessarily requires some additional units in order to convert the optical signal into electrical form and vice-versa. This process is somewhat time-consuming and makes the data transmission rate slower. However, the arrival of optical amplifiers has eliminated this problem. Thus, employing the optical amplifiers in an optical communication system allows us to have signal transmission to longer distance and at a faster rate without attenuation.
Working of a basic optical amplifier
An optical communication system basically contains a transmitter, a receiver and a fiber cable that carries the information from an end to the other. However, an additional unit, optical amplifier in between the transmitter and receiver section is placed in order to boost the signal level.
As it is true that a signal when transmitted through a fiber cable experiences least attenuation as compared to any other medium like a coaxial cable. However, signal amplification is also required during transmission through fiber cable in order to have long distance transmission.
The figure here, shows the amplification operation of an optical amplifier:
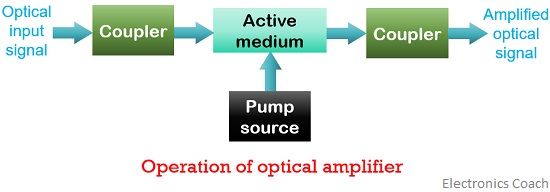
The electrons present in the active medium gets energy from the pump source and gets excited to higher energy level. These electrons then triggered by the optical signal that causes them to return to a lower energy level.
Thus stimulated emission occurs and several photons having same energy is emitted by the excited electrons while returning to ground state.
Hence, an amplified optical signal is achieved.
As we know that optical amplifier utilizes stimulated emission and for its occurrence, population inversion must be created whose mechanism is the same as that used in laser diodes.
As both the optical amplifier and laser diodes holds a similar structure but due to the absence of an optical feedback mechanism, only the applied input signal can be boosted. Thus, optical amplifiers do not have the ability to produce coherent output at its own.
Application of optical amplifier
Optical amplifiers can be employed in 3 ways between transmitter and receiver in order to achieve desired signal amplification.
A booster or power amplifier is placed immediately after the transmission unit. It enhances the level of the signal before the signal is provided to the optical link for transmission. This is done in order to accomplish long-distance transmission.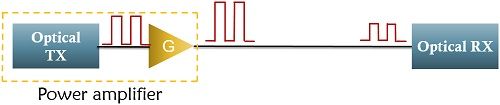
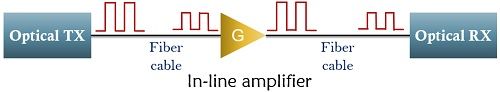
When we talk about inline amplifier unit then it is placed at some distances in the fiber link itself in order to restore the original message signal from the distorted one. As it offers medium gain then it becomes necessary to place multiple in-line amplifiers in case of long-distance transmission.
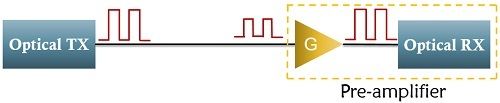
A pre-amplifier is usually placed at the receiving end of the system. The transmitted signal must be of such level that it can be easily detected by the receiver. A signal that has transmitted a very long distance gets highly attenuated despite several amplifications during its journey. This causes difficulty for the receiver to detect the respective signal.
Thus, a preamplifier, having high gain is amplified by a preamplifier just before entering the receiver unit.
It is to be noted here that the gain of an amplifier depends on the intensity and wavelength of the transmitted light signal.
Classification of optical amplifier
Optical amplifiers are basically classified into 3 categories namely:
- Semiconductor optical amplifier
- Doped fiber amplifier
- Raman amplifier
- Semiconductor optical amplifier: It is abbreviated SOA and its active medium is composed of alloys of the semiconductor from group III and V. They have the excellent capability to operate in both O-band along with C-band. They offer a rapid gain response of about 1 to 100 ps. Its gain varies with the variation in signal bit rate.
- Doped fiber amplifier: It is abbreviated as DFA and the active medium is formed by lightly doping silica core with rare earth elements. Thus, also known as earth (erbium) doped fiber amplifier (EDFA). The working of DFA does not rely on the bitrate and format of the signal.
- Raman optical amplifier: It is based on stimulated Raman scattering, thus named so. For signal amplification, it requires a standard transmission fiber cable. It is noteworthy in case of Raman amplifier that they do not require population inversion mechanism for amplification purpose.
Thus, we can conclude that an optical amplifier widely finds its application for the transmission of optical signal up to several kilometres.
Leave a Reply