Power electronic converters are classified into four major categories. Out of the four major categories, two are further classified. A power electronic system may have one or more power electronic converters. Here in this content, we will discuss each type of power converter in brief.
The power semiconductor devices that constitute the power converter exhibit switching characteristics to shape the input power of one form to an output power of some other form.
Introduction
Power Converters have turned out to be a crucial component of the household as well as commercial equipment. In our previous content, we have discussed that power electronic technology handles the controlling process of conversion of one form of electric energy into another form. This conversion of energy provides voltage and current in such a form that suits various user requirements.
We have already discussed that power electronic devices are a combination of converter and controller where the converter functions according to the control signal generated by the controller. A power electronic converter is composed of power semiconductor devices controlled by integrated circuits.
An important aspect of converters is signal conditioning. Signal conditioning offers signals of the pure form i.e., free from harmonics. In a general way, it is said that getting an absolutely clear signal is impossible. But we can reduce harmonics to some extent using a simple low pass LC filter.
Types of Power Converters
Static Power converters execute power conversion quite efficiently. Power electronic switches have solid-state devices with components like inductors and capacitors. Generally, inductors and capacitors exhibit negligible power loss characteristics in comparison to resistors.
The classification of power converters are as follows: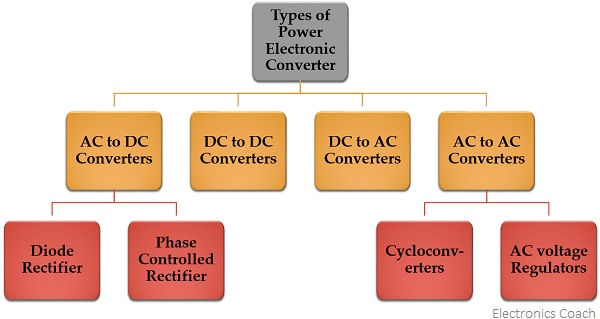
Let us now understand each type separately.
AC to DC Converters
A type of converter that changes input AC signal into a DC is known as AC to DC converter. We have already learned in basic electronics that the devices that convert the AC signal into DC signal are known as rectifiers.
AC to DC Converter is further classified as:
Diode Rectifiers: This rectifier circuit changes applied ac input voltage into a fixed dc voltage. Either a single-phase or three-phase ac signal is applied at the input. These are mainly used in electric traction and in electrochemical processes like electroplating along with in battery charging and power supply. These are also used in welding and UPS related services.
Phase Controlled Rectifiers: Unlike diode rectifiers, phase-controlled rectifiers are designed to convert a fixed value of ac signal voltage into a variable dc voltage. Here line voltage operates the rectifier hence these are sometimes known as line commutated ac to dc converters. Similar to diode rectifiers, here also the applied ac signal can be a single-phase or three-phase ac signal. Its major applications are in dc drives, HVDC systems, compensators, metallurgical and chemical industries as well as in excitation systems for synchronous machines.
DC to DC Converters
The converters that convert the dc signal of fixed frequency present at the input into a variable dc signal at the output are also known as choppers. Here the achieved output dc voltage may have a different amplitude than the source voltage. Generally, power transistors, MOSFETs, and thyristors are the semiconductor devices used for their fabrication. The output is controlled by a low power signal that controls these semiconductor devices from a control unit.
Here forced commutation is required to turn off the semiconductor device. Generally, in low power circuits power transistors are used while in high power circuits thyristors are used.
Choppers are classified on the basis of the type of commutation applied to them and on the basis of the direction of power flow. Some major uses of choppers are in dc drives, SMPS, subway cars, electric traction, trolley trucks, vehicles powered by battery, etc.
DC to AC Converters
The devices that are designed to convert the dc signal into ac signal are known as inverters. The applied input is a fixed dc voltage that can be obtained from batteries but the output obtained is variable ac voltage. The voltage and frequency of the signal obtained are of variable nature. Here the semiconductor device i.e., the thyristor is turned off by using either line, load, or forced commutation.
Thus, it can be said that by the use of inverters, a fixed dc voltage is changed into an ac voltage of variable frequency. Generally, the semiconductor devices used for its fabrication are power transistors, MOSFETs, IGBT, GTO, thyristors, etc.
Inverters mainly find applications in induction motor and synchronous motor drives along with UPS, aircraft, and space power supplies. In high voltage dc transmission system, induction heating supplies as well as low power systems of mobile nature like flashlight discharge system in photography camera to very high power industrial system.
Like choppers, in inverters also conventional thyristors are used in high power applications and power transistors are used in low power applications.
AC to AC Converters
An ac to ac converter is designed to change the ac signal of fixed frequency into a variable ac output voltage.
There are two classifications of ac to ac converters which are as follows:
Cycloconverters: A cycloconverter is a device used for changing ac supply of fixed voltage and single frequency into an ac output voltage of variable voltage as well as different frequency. However, here the obtained variable ac signal frequency is lower than the frequency of the applied ac input signal. It adopts single-stage conversion. Generally, line commutation is mostly used in cycloconverters however forced or load commutated cycloconverters are also used in various applications.
These mainly find applications in slow-speed large AC traction drives such as a rotary kiln, multi MW ac motor drives, etc.
AC Voltage Controllers (AC voltage regulators): The converters designed to change the applied ac signal of fixed voltage into a variable ac voltage signal of the same frequency as that of input. For the operation of these controllers, two thyristors in an antiparallel arrangement are used. Line commutation is used for turning off both the devices. It offers the controlling of the output voltage by changing the firing angle delay.
The major applications of ac voltage controllers are in lighting control, electronic tap changers, speed control of large fans and pumps as well.
Leave a Reply