Definition: On-line UPS abbreviated as OUPS is a type of UPS that uses a combination of rectifier and inverter circuits in order to provide continuous power to the load from the supply source without any interruption. From continuous power here we mean that power is supplied to the load in case of availability from the source and power outage as well with zero transfer time.
On-line UPS is sometimes also known as double-conversion system. The reason for calling it so because, within an online UPS system, power conversion occurs twice as the circuit includes a rectifier and an inverter.
We will go through a detailed idea of how an online ups system works. But before that let us have an introductory idea about-
What is UPS?
UPS is an acronym used for Uninterruptible Power Supply and serves as a central element of an accurately designed power protection system. Here the name itself is indicating that it is somewhat denoting a supply source that offers continuous power i.e., without interruption.
Thus, in simplest form, one can define UPS, as a supply system that offers uninterrupted power to the ac load by converting dc into ac. Basically, there are enormous fields that require a continuous source of power without any interruption. Some of these fields are:
- Medical care systems,
- Safety monitoring systems,
- IT and networking fields,
- Data centers,
- AMT units.
As loss of power supply in the functioning of these systems may lead to severe consequences such as removal of important data.
The figure below represents the block diagram representation of typical UPS:
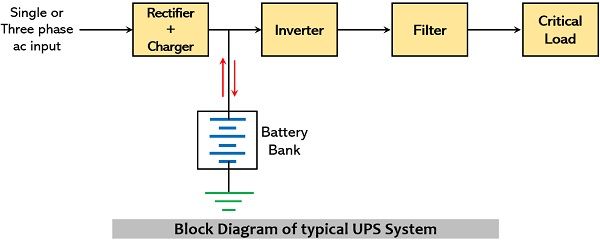
Its major components include a rectifier, inverter, battery bank, filter circuit, and critical load. Either a single-phase or a three-phase input signal is provided as input to the rectifier.
In normal operating conditions, the current is drawn from the ac mains while in case of power outage backup source provides current. Here battery is used as the backup source to deliver power to the load in case of power failure.
Introduction to Online UPS
We have discussed in the beginning that an online UPS is the one that provides power supply to the load. The supply provided to the load is of uninterruptible nature because initially, load draws current from the main supply source however, in case of power failure the load draws current from battery backup, and that too with zero transfer time.
Now, the question arises – what is transfer time here?
So, transfer time is defined as the time duration which the UPS circuit takes to switch path from supply mains to the battery backup in order to provide power to the load. On-line UPS offers zero transfer time as its static switch is present in normally on-state.
Hence, online ups is designed to provide utility power to either till the time required to properly shut the critical equipment without loss of data or till the time to extend the operation when the generator comes for the rescue. There is off-line ups also which differs from on-line ups according to the way of its operation.
Block Diagram and Working
The figure below represents the block diagram of On-line UPS system:
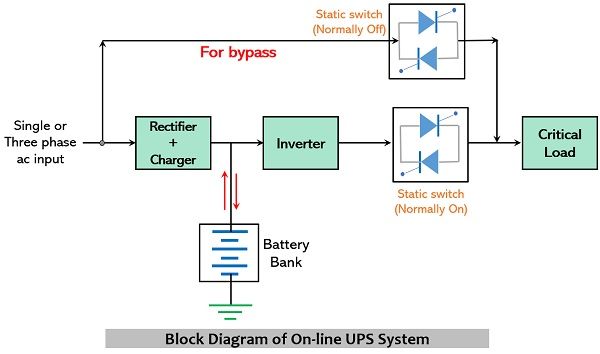
Here in the above arrangement, it is clearly shown that power to the critical load can be provided in three ways. These are as follows:
- First, directly from ac mains to the critical load (including rectifier, inverter circuit, and primary static switch).
- Second, from battery backup to critical load (including inverter circuit only).
- Last, from ac mains to critical load (without including rectifier and inverter circuit) via following the path (i.e., bypass) through the secondary static switch.
It is to be noted here that the primary static switch is in normally on state always but gets turned off only when the UPS system fails. And for bypassing action secondary static switch which is kept off normally now gets on.
Depending on the above-discussed three configurations, the working principle of online ups is explained.
Condition I: When supply mains is on
The supply will provide a single-phase or three-phase ac signal as input to the rectifier circuit. The rectifier circuit will change the applied ac input into a dc signal. The dc output of the rectifier is simultaneously fed to the inverter as well as the battery in order to charge the latter. Thus, the rectifier here acts as a charger as well as a rectification unit thus is of high rating.
The dc signal fed to the inverter will convert the dc signal into ac. This ac signal is provided to the normally on-static switch through which the ac power is delivered to the load. Hence, in this mode of operation, power to the critical load is supplied along with simultaneous charging of the battery.
Condition II: When supply mains is off
In the absence of an ac input signal, the rectifier will be in a temporarily disconnected state, in such a condition, the stored power within the battery is provided to the inverter. And from this point, the inverter starts operating like the previously discussed condition i.e., taking the dc input and converting it into ac output and providing it to the load via normally on static switch.
However, the supply from the battery backup must not add any delay or interruption to the operation. The battery backup is utilized either till the time of restoration of the ac supply or until the battery power gets drained off, whichever condition occurs first.
As inverter has to supply constant power to the load in both the above-discussed cases hence must be properly and carefully designed.
Condition III: When UPS fails
When the inverter circuit breaks out or fails then it will not allow the load to draw the current from supply input. But still, for proper operation, the supply input must be delivered to the critical load. So, in this situation, through a bypass route, the load draws power from the source.
Basically, when the inverter circuit fails then the secondary static switch comes to on-state from normally-off state. And through this, the ac signal will reach the load with zero phase discontinuity in merely one-fourth of the complete cycle time period.
The moment the secondary static switch gets turned on, an alarm intimates the attendant reading the failure of the UPS system thus can be diagnosed and corrected.
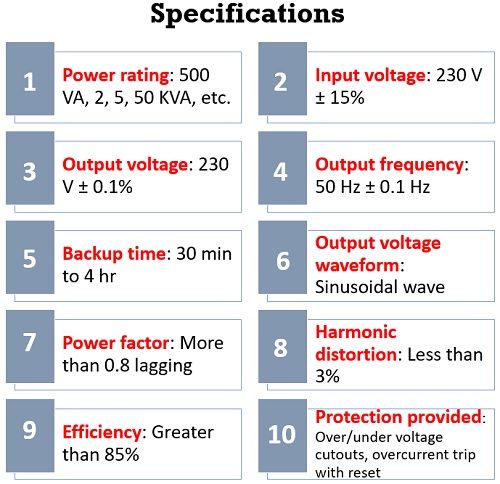
Specifications
The specifications of online UPS are shown below:
Advantages of On-line UPS
- It offers power conditioning along with complete isolation of the load from the ac input.
- Uninterrupted power is delivered to the load all the time.
- Power failure does not hinder the mode of operation.
- The transfer (changeover) time is negligible due to always-on condition.
Disadvantages of On-line UPS
- A continuous on mode generates more heat thus large heat sink is required.
- Complex design.
- Expensive
- High power dissipation.
Thus, on-line UPS finds applications in those fields of operation where continuous power is required without any switching operation.
Leave a Reply