Definition: Off-line UPS, sometimes called standby ups is equipment that offers uninterruptible power supply immediately to the connected device through the battery when detects electric supply failure within the circuit. An offline ups offers the most basic type of power protection to the appliances.
Basically, in offline ups, ac power to the load is directly supplied from an ac source in normal condition. However, in case of a power outage, the inverter is used to supply ac power to the load through the battery which acts as a backup.
Before dealing with a detailed idea of offline ups let us have an overview on-
What is UPS?
UPS stands for Uninterruptible Power Supply and is used as a means to provide power to the electrical or electronics equipment whenever the condition of power outage occurs. It is given the name uninterruptible supply because it makes sure that the power should be continuously provided to the load even after the supply failure.
It is to be noted here that the use of UPS is not always associated with complete power failure. This is so because a ups comes to rescue a circuit operation even when the electricity supply falls to an inadequate voltage level. The backup power which a ups provide to the load equipment depends on its size and the technology with which it is built.
UPS serves as major equipment of IT industries as they require a continuous power supply for their operation and to protect the loss of data. These industries may include chemical power plants, medical systems, safety monitoring systems, data center units, etc. where constant power supply is necessary. Thus, ups acts as a boon to such systems.
Introduction to Off-line UPS
We have mentioned at the beginning itself that offline ups are the ones that offer one of the basic levels of power protection to the equipment. From one of the basic levels, we mean that this type of ups shows suitability towards small and non-critical loads. In such loads, protection is needed against momentary power loss or surges, like to prevent data loss of personal computers when electric supply disrupts.
An offline ups permits a direct supply of input power to the load without inverter or rectifier circuitry, meanwhile charging the battery. But as soon as the power fails the inverter comes into action.
In the previous content, we have talked about on-line ups, which is considered as one of the best ways to deal with conditions related to low power level or complete power failure. In on-line ups we have seen that the load is subjected to drive the power from ac supply and when a power failure occurs then instantly the battery backup comes into action without any delay.
The reason behind this is that here the load is simultaneously connected to the power supply and battery backup with the help of two static switches (on and off adversely). In normal operating conditions, the critical load drives power from the source however, if a power failure occurs then immediately the battery will start serving the load, leading to offer uninterrupted services. This is so because this type of UPS offers zero switching time (transfer time).
An offline ups does not offer zero transfer time as the transfer time of such devices varies between 3 to 8 milliseconds. However, the popularly known value is 5 milliseconds. Due to this reason, these are used with small or non-critical loads that may handle this small amount of disruption.
Working of Off-line UPS
UPS is a device that includes a rectifier, filter, inverter, static switches, and battery backup as its major components. By the use of these components, power is supplied normally and from the backup to the load in case of power disruption.
An off-line UPS operates differently from that of on-line UPS and this difference in operation is generated mainly due to the circuit arrangement. The complete circuit operation takes place in two modes. Let us now discuss each mode of operation separately.
Mode I: When ac mains is on
When the ac supply provided to the circuit is active then the load drives the current from the mains. The ac signal first passes through the surge suppressor and then through the filter in order to reach the load. The surge suppressor here is used to protect the load (electrical and electronic equipment) from voltage spikes (known as transients) of the applied ac signal. Thus, is present right within the line that connects the supply to the load.
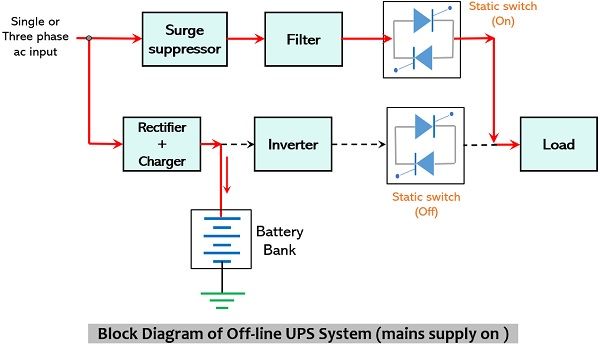
The output of the surge suppressor is given to the filter circuit that only passes the desired frequency component through it and blocks the unwanted. The filtered ac signal is then provided to the load via a normally on static switch present between the filter and the load.
However, at the same time, the ac input signal from the supply mains is fed to the rectifier circuit which converts the applied ac signal into rectified dc output. Here the rectifier acts as a battery charger because the dc output of the rectifier is used to charge the battery. Thus, charging of the battery and driving the load occurs simultaneously by the applied ac signal. This happens till the time the supply mains is present.
Mode II: When ac mains is off
During the ongoing process of driving the load and battery charging if a power failure occurs then the normally on static switch between the load and the filter will immediately gets turned off.
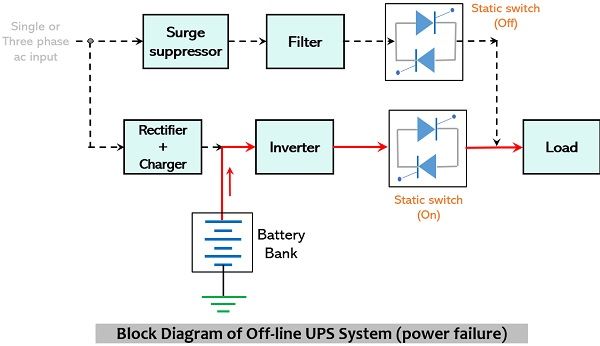
Once it gets off, the inverter comes into action. Now, the inverter which was off previously, will take the dc signal from the battery backup and convert it into ac signal. By the time, the static switch that was previously off will now gets on and passes the ac output of the inverter towards the load. Thus, even after supply failure, the load will get the power to continue the operation.
It is to be noted here that around 5 milliseconds of time is required for switching of the static switch in case of off-line ups which was zero for on-line ups.
Now, the question arises – what happens for that 5 milliseconds within the circuit when the ac source fails and the inverter remains inactive?
A switched-mode power supply consists of the capacitor. The capacitor holds this much charge within it that can supply power and drive the load for such a small time duration. Thus, no disruption in supply is experienced by the load and this prevents data loss or any unwanted shutting down of the device.
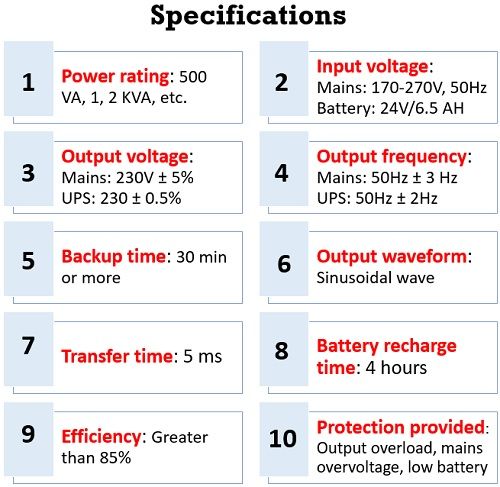
Specifications
The specifications of off-line ups are as follows:
Advantages
- It is more efficient and reliable than online ups. This is because the inverter is not on all the time unnecessarily.
- It is inexpensive.
- The operation is quite simple due to separate paths for the two modes of operation.
- Due to non-continuous operation, large heat sinks are not required.
Disadvantages
- It is not suitable for critical loads as here mains and load are not electrically isolated from each other.
- This sometimes fails in case of power fluctuating conditions.
It is given the name standby because the inverter activates only when the supply source fails.
Leave a Reply