The main difference LED and LCD is that the LED works on the principle of electroluminescence i.e. it generates light due to recombination of electron and holes while LCD do not generate light of its own but control the light energy and modify it in such a way that some area of the display screen appears bright while some areas appear dark.
Although, LED and LCD both are the types of the display device but the brightness level of LED is more than that of LCD. The power requirement is also one of the main factors which differentiate LED and LCD. As LCD do not generate light on its own, thus the power is required only for modifying the existing light so the power required will be very low in magnitude. But the LED needs power for generation of light thus power requirement in case of LED is more.
The LCD can be fabricated or designed in any particular size according to the specific application. While this is not the case with LED. We will discuss some more significant differences between LED and LCD with the help of comparison chart. But before starting with comparison chart, let’s have a look at the roadmap of this article.
Content: LED and LCD
Comparison Chart
| Parameters | LED | LCD |
|---|---|---|
| Operation manner | The LEDs generates light due to recombination of charge carriers. | The LCD modifies the external light by passing it through the liquid crystals fed between polarizers. |
| Viewing Angle | The viewing angle of LED is about 150 degree. | The viewing angle of LCD is less than that of 100 degree. |
| Temperature Range for operation | The temperature range of operation in case of LED lies between -400 degree Celsius to 850 degree celsius. | The temperature range of operation in case of LCD lies in the range of -200 degree Celsius to 600 degree Celsius . |
| Brightness Level | The brightness level of LED is high and thus LEDs provide good quality display. | The brightness level of LCD is lower than that of LEDs and thus the quality of LCD display is lower than that of LED. |
| Power Requirement | The power requirement of LED is in the range of 10-250 mW. | The power requirement of LCDs is less than that of LEDs, it is about 10-20 µW. |
| Operating Voltage | The operating voltage of LED lies between 1.5 V to 5 V DC. | The operating Voltage of LCD is in the range of 3 to 20 V ac. |
| Lifetime | The lifetime of LEDs is about 100,000 hours. | The lifetime of LCDs are less in comparison to LEDs i.e. about 50,000 hours. |
| Response Time | 50- 500 ns | 50-200 ms |
| Cost | Costly | LCDs are cheaper as compares to LEDs |
| Weight | Light as compared to LED | Heavy |
Definition
LED
The LED is an acronym of Light Emitting Diode; it generates light when electrons in conduction band recombine with holes in the valence band. The LEDs are made up of semiconductors such as GaAsP and GaP, the semiconductor material such as silicon and germanium are not used in the construction of LED.
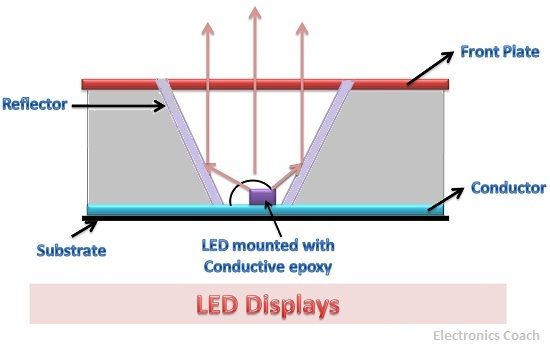
The semiconductor such as silicon and germanium release energy in the form of heat when holes and electron recombine but we want energy in the form of light to operate LED. The semiconductor such as Gallium Arsenide, Gallium Phosphide release energy in the form of light during recombination of electrons and holes. This process is called electroluminescence.
Thus, LED converts the electrical energy into light energy. The conversion efficiency of LEDs is much higher than that of the tungsten lamp. The LEDs are used for display devices but the power requirement is quite large. For displaying a single digit the LED require 10-250 mW of power. The brightness level of LED display is very high thus, it provides a good quality display.
LCD
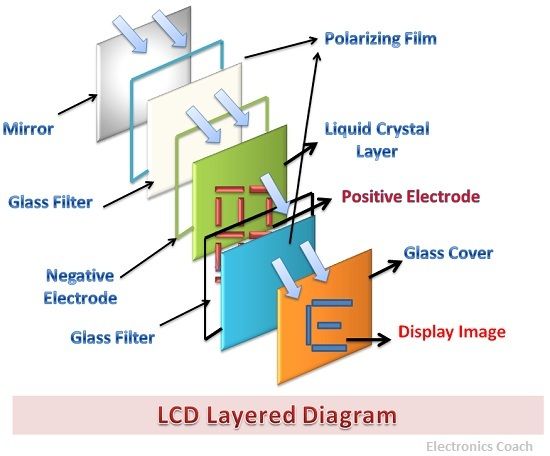
LCD is an acronym for Liquid crystal display; the nematic crystal is used for the construction of LCD. The nematic crystal is the liquid crystal, the liquid crystal can be considered as the fourth state of the matter. This is because the liquid crystal has the property of solid as well as liquid. The crystal structure is responsible for the solid characteristics of liquid while the ability of the liquid crystal to flow imparts it the property of the liquid.
The LCD consists of a light source which supplies light from external source to the liquid crystal. The liquid crystals are filled between the polarizing films. These polarizers are applied voltage from the external electric field. The voltage applied through external electric field modifies the liquid crystal in such a way that the light is absorbed by the rear polarizer and this light creates dark and bright spots on the screen.
The liquid crystal is fed between the front polarizer and rear polarizer, when the voltage is not applied from the external electric field then the light ray rotate at the right angle and is reflected back to the external source. To prevent this polarizer are coated with conducting material and the electric field is applied to it.
The electric field of 1000 V/m2 is applied to the liquid crystals, for each 10 µm thick layer of the nematic crystal the applied electric field is 10 V.
Key Differences between LED and LCD
- Power Requirement: The power requirement is one of the key difference between LED and LCD, LEDs generate light of its own and thus needs less power i.e. about 10-250 mW, while LCD does not require much power as they just modify the existing light by passing it through liquid crystals. Therefore, the power required by an LED is about 10-20 µ
- External Interface: External interface circuitry is required in case of LED when it is operated by an integrated circuit as LED requires high power for its operation. The LCD does not require external circuitry even when it is operated by an integrated circuit. The IC chip can be connected directly to LCD as it requires low power.
- Life of Display: The lifetime of LEDs is much more than the lifetime of LCD. Due to the presence of liquid crystals, the possibility of chemical degradation in LCDs is more. Thus, LCDs possess the lifetime of 50,000 hours while LEDs possess a lifetime of about 100,000 hours which is much higher than that of LEDs.
- Response Time: The response time of LEDs are in the range of 50-500 ns while the response time of LCDs lies in the range of 50-200 ms.
- Colour of Light Emitted: The light emitted by LEDs is generally of red, blue, green, white and yellow while the light emitted by LCD is invisible.
Conclusion
The LED and LCD, both are display device but the properties of both are quite different. The LEDs are more advanced and provide better quality as compared to that of LCDs. The larger viewing angle, higher brightness level, wide range of temperature and lower response time makes LED a good choice for display.
garry shepherd says
But from a technical point of view is an LED essentially a subset of an LCD?? (So they could both be considered to be LCDs ??)