The LED operates on the principle of electro-luminance while photodiode works on the principle of the photoconduction. In a Light emitting diode, when electrons and holes recombine, the energy is released in the form of light. Thus, it is termed as Light-emitting diode. On the contrary, photodiode generates current when it is exposed to the source of light.
LED and Photodiode are reverse of each other. LED generates light with the help of charge carriers while photodiode generates current due to incident photons. In a nutshell, LED converts electric energy into light energy but Photodiode converts light energy into electrical energy.
Contents: LED and Photodiode
Comparison Chart
| Parameters | LED (Light Emitting Diode) | Photodiode |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Two terminal device which converts electrical energy into light energy. | Two Terminal Device which converts light energy into electrical energy. |
| Working Principle | Works on the principle of Electro-luminance. | Works on the principle of Photoconduction. |
| Semiconductor used | Gallium Arsenide Phosphide (GaAsP) or Gallium Phosphide (GaP) | Germanium and Silicon |
| Biasing Mode | Forward Biased Only | Reversed Biased Only |
| Problem of Leakage Current | No leakage current | Reverese saturation current is significant. Dark current flows when no light rays are incident on it. |
| Applications | Indicator in AC circuit, Alphanumeric and Numeric display etc. | Switching, high speed counting, ac coupled signalling etc. |
Definition
LED
LED is an acronym for Light Emitting Diode. It is formed by a forward biased PN junction. When electrons in N-type semiconductor combine with holes in the P-type semiconductor, they release energy in the form of light or heat.
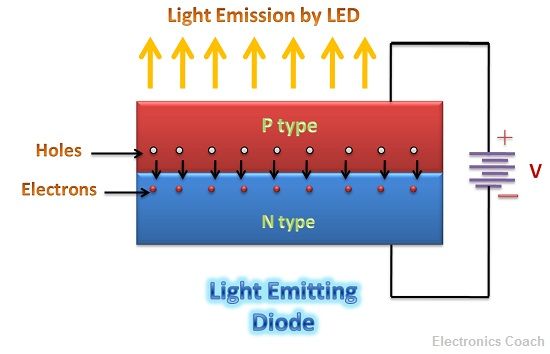
In germanium and silicon semiconductor the energy is released in the form of heat or light. While in semiconductor materials such as GaAsP and GaP, the energy is released in the form of light. Therefore, these materials are utilized in the construction of LED.
The electrons in conduction band possess higher energy than holes in the valence band. Thus, recombination is possible only when electron gives some part of the energy. This concept is called electro-luminance and LEDs are based on this.
One more crucial point in the construction of LEDs is the usage of the thin film of Gold. This is because the light if enter into the internal structure of LED will reflect to the top surface by this gold film. Thus, the intensity of light emitted will be high.
But if the semiconductor material is reverse biased, i.e. the P-type semiconductor is connected to negative terminal of the battery and N-type is connected with positive terminal of the battery, then LED will not emit light.
LEDs do not operate in reversed biased mode. If we operate it in reversed biased mode, it may lead to deterioration of LED.
Photodiode
A photodiode is also made up of PN junction diode, but when the PN junction surface is placed in the light source, the charge carriers in the photodiode get energy, and they start moving. The movement of charge carriers in the diode results in the generation of electric current in the photodiode.
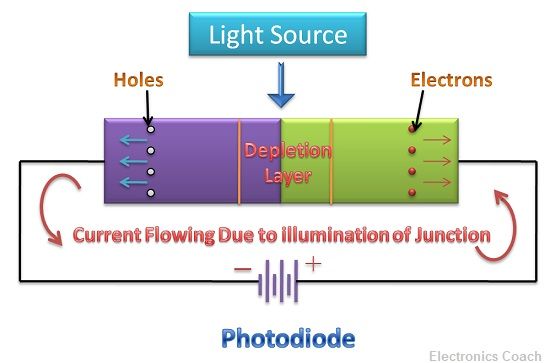
This process is termed as photoconduction as the process of conduction is possible only using Photons. Photodiode operates in reversed biased mode.
The entire structure of photodiode is placed inside a plastic case so that the light radiation do not get scattered. One of the surfaces of the plastic case is chosen for illumination by light rays, and another surface is painted black. The intensity of light radiation will decide the intensity of electric current generated.
Based on this principle of photoconduction, phototransistors can also be made. Instead of using diode we can use a transistor, and electric current can be generated using photons.
Key Differences Between LED and Photodiode
- Function: The function of the LED and Photodiode is contrasting. LED emits photons due to electron-hole recombination, while Photodiode provides energy to electron and holes by exposing itself towards light radiation.
- Operating Principle: As we have discussed above the operating principle of LED and Photodiode is also different. The principle on which LED works is called Electro-luminance, i.e. Lumination using Electric charges. While the photodiode works on the principle of Photoconduction which means conduction using photons.
- Biasing: LED always operate in forward biased mode, it cannot be operated in a reversed mode as it will destroy it. A photodiode is a device which operated in reversed mode only.
- Conversion form of Energy: LED converts electrical energy into light energy and photodiode converts Light energy into electrical energy.
- Material Used: LED is made up of GaAsP or GaP. Germanium and silicon semiconductor are not used in the manufacturing of LED. Photodiodes are made up of Germanium and silicon semiconductor.
Conclusion
LED and Photodiode, both are two terminal devices, but they differ in their working mechanism. They are completely different devices. One generates electricity and other generates current. The intensity of light produced by LED is directly proportional to the applied voltage. The higher the voltage, the higher will be the light intensity.
Similarly, the intensity of electric current generated by the photodiode is directly dependant on the intensity of light rays falls on it. But a term is associated with photodiodes, i.e. dark current, this is the current that flows in the reversed biased photodiode when no light is incident on it.
Leave a Reply