Definition: A thermocouple is a device that is used to measure temperature. These are active transducers as they work on the principle of energy conversion. It does not require any source of power for their operation.
These are basically temperature sensors that measure temperature in the form of EMF. To make up thermocouple pair certain combinations of metals must be used. These combinations of metals are so chosen that a linear rise in emf is produced with the rise in the temperature of the circuit.
It is used in temperature measurement of up to 1400⁰C.
Working Principle of Thermocouple
Thermocouple works on the principle of Seebeck effect. Now the question arises what is Seebeck effect?
When metals of dissimilar materials are joined at both the ends. Each having different junction temperature than the other, a potential difference induces in the circuit. Thus current is created in the circuit.
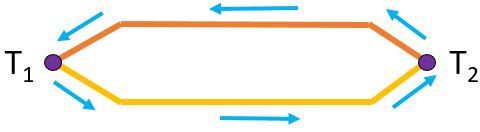
The same is the case with Thermocouples also, which we will discuss in the upcoming section.
Constructional Details of Thermocouple
As we have already discussed that it consists of metal wires of two different materials. The choice of the material is based on the range of temperature to be measured, the exposure environment of the material, its stability, mechanical strength etc.
The junction point of the thermocouple is merely divided into 3 categories based on its applications
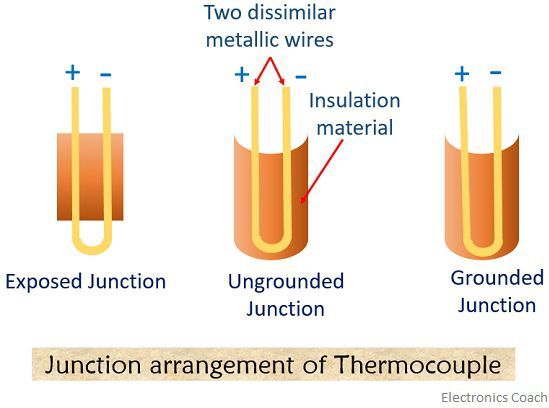
- Grounded junction – In grounded junction, the two metallic wires are welded together along with the protective sheath. This type of junction is used by thermocouple to measure temperature in the corrosive environment.
- Ungrounded junction – Here, there is a complete isolation of conduction from that of the protective sheath. in case of high-pressure application purpose, ungrounded junctions are used.
- Exposed junction – Whenever there is a need to measure the temperature of the gas, then exposed junction are used. These are also used where fast response is required.
Bare conductors are not used by thermocouples until and unless the atmospheric condition permits their use. The condition can be the one when the temperature to be measured is low and the atmosphere is non-corrosive. By reducing the mass of measuring junction the sensitivity of thermocouples can be reduced.
Working of Thermocouple
The two junctions are created using 2 dissimilar metal wires as we have discussed earlier.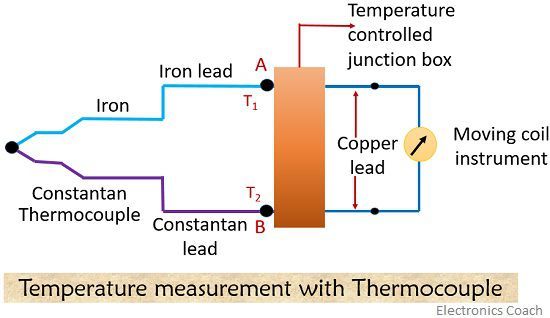
As we can see in the diagram points A and B denote the two junctions and the temperature of the junction is denoted by T1 and T2. This difference in temperature between the two junctions generates emf in the circuit. The voltage generated in the circuit is extremely small and is measured in terms of millivolts.
When the temperature of the two junctions becomes equal, it will generate equal and opposite emf that cancels out each other thus causing no current to flow through the circuit.
The total current flowing through the circuit depends on the emf induced in the circuit. That, in turn, depends on the temperature difference of the two junctions.
The emf induced in a thermocouple is given by-![]()
: ∆θ = difference of temperature in between hot junction and the reference junction.
a, b = constants
Usually, the value of ‘a’ is very large in comparison to ‘b’
Therefore emf is given by-![]()
Or![]()
Thermocouple output measurement
The emf generated in the device results from the temperature difference between measuring junction and the reference junction. The output can be measured by the following methods-
Millivoltmeter– Connecting a Millivoltmeter at the reference junction to measure its temperature is the simplest method. The deflection is proportional to the current flowing through the circuit.
Potentiometer– The commonly known method for temperature measurement is with the help of potentiometers. At balanced condition, no current is drawn from the circuit whose emf is being measured.
Amplifiers with output devices– Cheap and compact dc amplifier are made by the use of a transistor and integrated circuit. The output of the thermocouple is amplified by the amplifier and is feed to the indicating device. But in this case, an auxiliary source of power is required.
Types of Thermocouple
These are classified as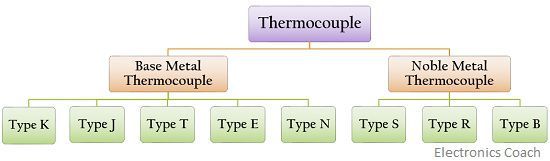
Base metal Thermocouples– In this category of Thermocouple, the base metal is made from common and inexpensive materials such as Nickel, Iron, Copper.
Following types fall under this category-
- Type K Thermocouple– It consists of Nickel-Chromium or Nickel-Alumel. It is most commonly used. It is inexpensive and has a wide temperature range at the same time it provides accuracy and reliability. It has the temperature range from -330 to 2300⁰F. Its wire colour code is yellow and red.
- Type J Thermocouple– It consists of Iron/Constantan. It permits smaller temperature range and has a shorter lifespan at a higher temperature. As oxidation problem is associated with Iron, some precautions must be taken when using this type of thermocouple in an oxidising environment. Its temperature range lies in between 32 to 1400⁰F and wire colour code is white and red.
- Type T Thermocouple– These consist of Copper/Constantan. This category of the thermocouple is very stable and is used in very low-temperature applications such as in cryogenics. The temperature range of type T Thermocouple lies in between -330 to 700⁰F and its wire colour code is blue and red.
- Type E Thermocouple– It is composed of Nickel-Chromium/Constantan. At moderate temperature, it provides higher stability as compared to Type K and Type J. This type of Thermocouple has the highest emf vs temperature values among all commonly used Thermocouples. The temperature range is between -330 to 1600⁰F and wire colour code is purple and red.
- Type N Thermocouple– It is composed of Nicrosil/Nisil. It is slightly expensive and shares almost similar accuracy and temperature limits as that of K Type. The temperature range lies in between 32 to 2300⁰F and wire colour code is orange and red.
Noble Metal Thermocouple– It has the ability to withstand high temperature and is made up of expensive materials.
Following types fall under this category-
- Type S Thermocouple– It is composed of Platinum Rhodium- 10%/ platinum. It is mostly used in high-temperature applications. But can be used for lower temperature applications due to high stability. It is mostly used in Biotech industries.
- Type R Thermocouple– These are composed of Platinum Rhodium-13%/ Platinum. It is more expensive as it contains more percentage of Rhodium as compared to Type S. Its performance is almost similar to that of Type S.
- Type B Thermocouple– These are composed of Platinum Rhodium- 30%/ Platinum Rhodium-6%. It is known to be the highest temperature limit thermocouple among all others. It provides the highest stability and accuracy at high temperature.
Advantages of Thermocouple
- It is always a better circuit for conveniently measuring the temperature at a particular point.
- These are cheaper as compared to the resistance thermometers.
- They are more suitable to record rapid changes in temperature as compared to other devices.
Disadvantages of Thermocouple
- In case of precision work, they are not widely used as they have lower accuracy when compared with other devices.
- In the case when precious metals are used they require extra protective tube which has to be chemically inert and vacuum tight.
Non-thermocouple materials can also be used as terminal blocks or splices until there is no temperature gradient across these devices.
Valmik Patel says
Valuable and engaging content. Thanks