Definition: Resistance thermometer is a device that is used to determine temperature by the variation in the resistance of a conductor. It is commonly known as Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD) and is an accurate temperature sensor.
RTD is not used for dynamic temperature measurement.
Working Principle of Resistance Thermometer
As we know, in Resistance thermometer, the resistance of the conductor is dependent on the variation in temperature. When the temperature of the metal is increased, there is an increase in the vibrational amplitude of the atomic nuclei of the material.
This resultantly increases the probability of collision of free electrons with that of the bounded ions. Thus, the interruption in the motion of the electron causes resistance to increase. Hence, causing temperature associated with it to increase.
This is how RTD works.
Resistance temperature detector is typically made up of nickel, platinum, copper or tungsten. However, platinum is used as a primary element in such accurate temperature sensors due to its chemically inert nature. So, that it can be used in the hostile environment to reduce the chances of oxidation.
In a metal, the change in resistance with respect to temperature is given by the following relationship:
Rt = Ro (1 + αt + βt2 + ϒt3 ———)
: Ro = resistance at 0⁰ C
Rt = resistance at t⁰ C
α, β, ϒ etc are constants here.
Construction of Resistance Thermometer
The figure below shows the structural arrangement of a platinum RTD
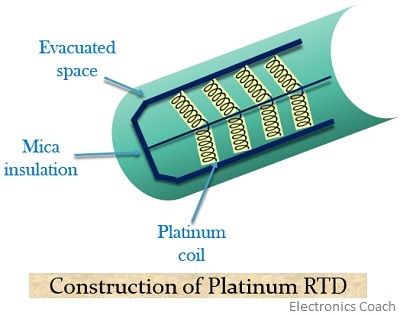
It consists of a mica crossed frame, inside which a platinum in coil form is present. The whole arrangement is placed in an evacuated tube of a stainless steel. The coil form arrangement generates the least strain when the temperature rises. As tension increases with an increase in the strain. So, this will cause an undesirable change in the resistance of the wire.
We can have better electrical insulation when mica is placed between the evacuated tube and platinum coil.
It is noteworthy here that, the material used must be pure enough to provide proper results.
The purity of platinum can be checked by the measurement of R100 /Ro. As for pure platinum material, the value of the ratio should be higher than 1.390
Basic equation for Resistance Thermometer
As we know,
Rt = Ro (1 + αt + βt2 + ϒt3 ———)
Rt from the above equation can be approximated as:
Rt = Ro (1 + αt + βt2 )
When the element is pure platinum,
α = 3.94 Χ 10-3 /⁰C
β = – 5.8 Χ 10-7 /(⁰C)2
The above equation can be rewritten as:
Rt = Ro (1 + C tpt)
: C = mean resistance temperature coefficient between 0 ⁰C and 100 ⁰C.
tpt = platinum temperature coefficient
and is given by
![]()
: Rt, Ro, R100 are the resistance at t ⁰C, 0 ⁰C, 100 ⁰C
The fundamental interval of the thermometer is denoted by R100 – Ro
The equation given below shows the difference true temperature ‘t’ and platinum temperature ‘tpt’
![]()
: δ = constant
The value of δ lies between 1.488 to 1.498. Since a smaller value of δ indicates a high degree of purity.
The type of wire used in RTD determines its effective range. The temperature range of platinum RTD is between 100 ⁰C to 650 ⁰C.
Characteristics of materials used in Resistance Thermometer
The figure below shows the typical resistance temperature characteristic of various types of materials used in RTD.
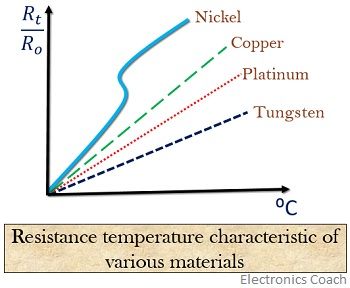
As gold and silver are less resistive materials thus these are hardly used in RTD construction. When we are talking about resistivity then tungsten has high resistivity but it is restrained for high-temperature applications.
Another element used in the construction of RTD is copper due to its low resistivity but has low linearity. Thus, platinum is preferred among all other elements.
Resistance Thermometer Circuit
Basically, RTD circuits are Wheatstone Bridge circuits but it is noteworthy that it is not a simple Wheatstone bridge but a modified form.
RTD can be connected in one of the arms of the Wheatstone bridge, as shown in the figure below:
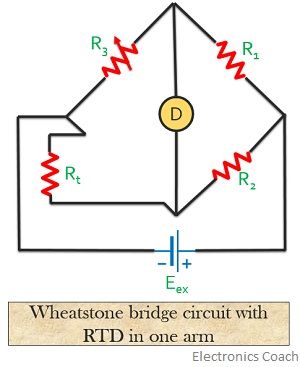
Here, R1 and R2 are 2 fixed resistances, R3 is a variable resistance and Rt is the detector resistance.
At balance condition,
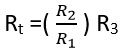
When R1 = R2
Rt = R3
The variable resistance R3 here is an adjustable potentiometer. To avoid all the effect that rises due to temperature changes, the resistors employed in the circuit are made up of manganin. This is so because manganin has the lowest temperature coefficient of resistance.
Circuit designing considerations in Resistance Thermometer
In RTD certain things are to be kept in mind while designing the circuit. These are as follows:
1. Lead wires of some appropriate length are required to connect the RTD into the circuit. So, if the temperature varies it will consequently vary the resistance in the bridge circuit. So, one must keep a proper distance between the point where RTD must be installed and the measuring point.
2. The current that flows through RTD, account for the heating effect in the circuit. Thus, the generated heat increases the temperature of the RTD sensor.
This is a self-heating effect and we cannot avoid it. The only thing which we can do is a compromise with the sensitivity of the instrument. A reduction in current through RTD will definitely reduce the heat generation rate but, the sensitivity of the device also reduces. However, it can be improved with proper amplification.
The increase in temperature of the device due to self-heating effect can be given as:
![]()
: ∆T = rise in temperature in ⁰C
P = power dissipated in RTD in watts
Pd = Dissipation constant of RTD in W/ ⁰C
3 Wire Resistance Thermometer
The figure below shows the circuit for a 3 wire RTD
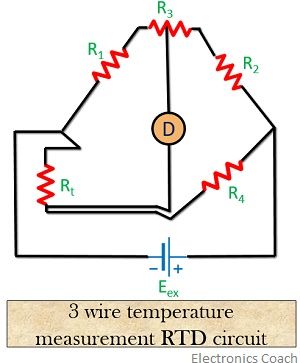
To compensate for the effect of variable lead wire resistance, 3 wire method is used. Basically, copper lead wire is used having similar length and diameter in order to have equal resistance.
In industries, 3 wire RTDs are most commonly used.
Advantages of Resistance Thermometer
- It provides highly accurate results.
- RTD provides a vast operating range.
- Due to its high accuracy, RTD is used in all such applications where precise results are needed.
Disadvantages of Resistance Thermometer
- The sensitivity of platinum RTD is very less for the minor variation in temperature.
- RTD possess slower response time.
One of the most common RTD indicator used earlier was a quotient or cross coil measuring instrument. Although it is cheap and robust in nature, bridge type RTD having digital indication has replaced it.
Leave a Reply