Definition: Resistor is an electronic device which is used to provide an obstruction in the path of current. Resistors are used in electronics circuits for various applications. It is used as the load in amplifier circuits. A resistor is used with the capacitor to provide discharge of capacitor when the power supply is removed. It is also used in filter circuit with inductor and capacitor.
Characteristics of Resistors
The resistor has two characteristics which are resistance and power dissipation capacity. The resistance can be expressed in ohms while the power dissipation capacity can be expressed as watt. Resistors are available for various purposes in the range of 0.01 Ω to 1012 Ω. The standard power ratings in which resistors are available widely is from 1/8 watt to 250 watts.
There cannot be a single resistor which can meet all our requirements. Thus, a different application needs a different type of resistor which possesses desired specification and tolerance suitable for that particular purpose.
Types of Resistor
Fixed Resistor
The resistors which possess fixed resistance is called fixed resistor.
The various types of fixed resistors are as follows:
Carbon Composition Resistors
This is the most general and commonly used resistor. In this, the resistive material is composed of carbon clay, and the leads of the resistor are made up of tinned copper. The entire arrangement is enclosed within the plastic casing in order to prevent the entire casing from moisture and other harmful atmospheric condition which may lead to deterioration of the resistor.
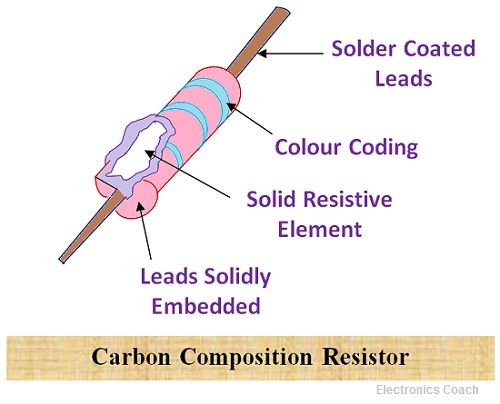
The advantage of using the carbon composition resistor is that it is cheap and reliable. Its stability is excellent through out the lifetime of the resistor. The Disadvantage of using carbon composition resistor is its high sensitivity. When temperature variations occur, it affects the working of the resistor.
The range of the carbon composition resistor varies from few ohms to 22 Mega Ohms. The tolerance range of carbon composition resistor lies between ±5 to ±20 %.
Wire Wound Resistors
The wire wound resistor is created by wounding a wire around the insulator cylindrical core. These wires are made up of material such as constantan and manganin. Constantan is an alloy which is made up of 60% copper and 40% nickel. These materials possess high resistivity thus they are used as a resistor.
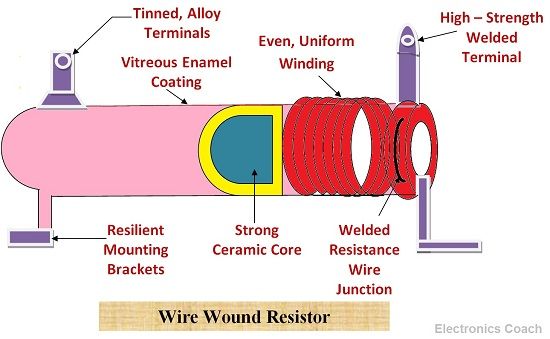
The advantage of using the wire wound resistor is that it is made by wounding a wire of high resistivity material around an insulating core. The length, width and size of the wire can be controlled. Thus, the resistivity of the wire can also be controlled. Therefore, the wire wound resistor is less sensitive to temperature variation as compared to carbon composition resistor.
The tolerance range of wire wound resistor lies between 0.01% to 1.0%. The resistance range of the wire wound resistor lies between 1 Ω to 1 M Ω.
Metal Film and Carbon film Resistors
The metal film or carbon film resistor can be formed by depositing a layer of high resistivity material such as carbon or some other metal on an insulating material such as glass. The resistance values obtained by this method is approximate. Therefore, if we want to find the exact methods then we need to trim the layer of carbon deposition.
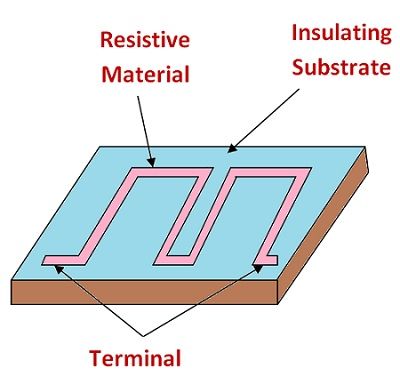
The range in which metal film resistors are available is from few ohms to 10,000 MΩ. The advantage of using metal film resistor is that its size is small as compared to wire wound resistors.
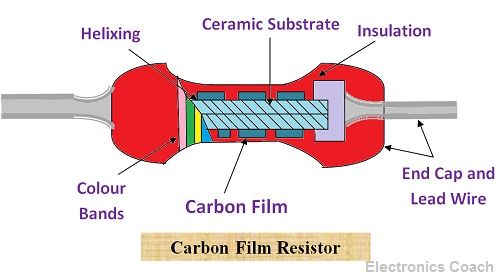
Carbon Film resistors offer lower resistance offers lower tolerance, and the value of resistance is also smaller. On the contrary, the metal film resistors offer higher tolerance than carbon film resistor and the values of resistance is also higher than that of metal film resistor.
The metal film resistors are also called precision type resistor because with the help of these an accuracy of ±1% can be achieved. The disadvantage of metal film resistor is that it is costly in comparison of carbon film resistor.
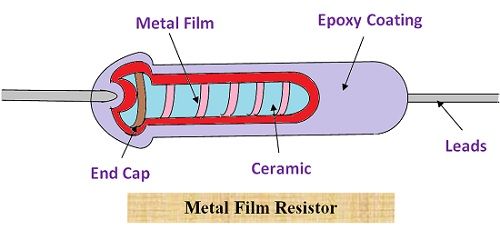
They are usually used in low-level amplifier because it possesses low noise characteristics which is suitable for such applications.
Variable Resistor
The variable resistors are the one which offers variable value of resistance. Thus, it is also known as an adjustable resistor.
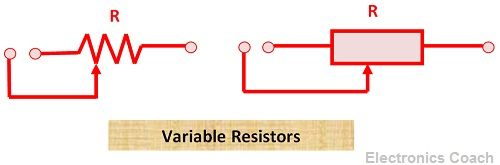
Variable resistor has three leads, in which two leads are fixed, and one is movable. Thus, through with this movable lead the value of the resistance varies.
Colour Coding of Resistors
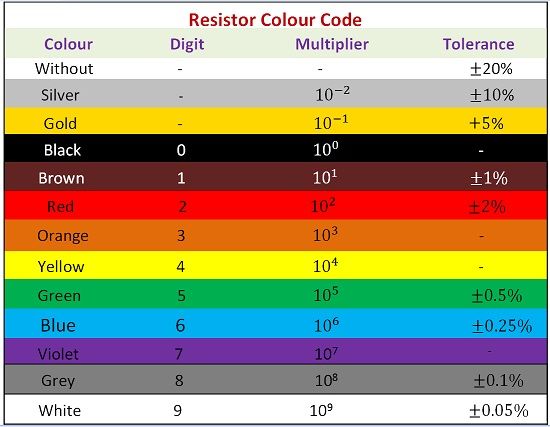
Colour Coding is the means of identifying the resistance and tolerance of resistor with the help of colour bands on the resistor. The colour band on different position have different positional value.
One may think that what is the need to identify from the colour band, why not to print the values on resistor itself? The values are printed on the resistor if the size of the resistor is large, but is the resistor is so small then it is not possible to print the values on it.
The fixed resistor can be further classified into two types, which are general purpose resistors and precision type resistors. General Purpose resistors are those which have a tolerance of ±5% and have four colour bands, while precision resistors are those which have a tolerance of ±2% and have five colour bands.
The general purpose and precision colour codes and their values are given in the table below.
General Purpose Resistor Coding
The first and second band signifies the first and second digit of the resistance value. The third band indicates the number of zeros following first two digits. If the third band is gold or silver, it signifies the multiplication factor of 0.1 and 0.01 respectively.
The fourth band indicates the tolerance of the resistor. It can also be understood as the deviation from the specific value of resistance. Let’s consider an example of resistor having colour bands of red, green and yellow, this implies that the resistance value is 25×104
The tolerance value for the above-considered resistor does not have the fourth band thus, the tolerance value will be ±20%.
Precision Resistor Coding
The precision code resistor consists of 5 colour bands. The first band of the precision resistor is never black. The first three bands of precision code resistor determine the first three digit of the resistance value. The fourth band signifies the multiplication factor. The fifth band signifies the tolerance value of the resistor. Thus, with the help of five bands the resistance value is calculated more precisely.
Leave a Reply