A type of servomotor that uses AC electrical input in order to produce mechanical output in the form of precise angular velocity is known as AC servo motor. AC servomotors are basically two-phase induction motors with certain exceptions in designing features.
The output power achieved from ac servomotor ranges between some watt to a few hundred watts. While the operating frequency range is between 50 to 400 Hz. It provides closed-loop control to the feedback system as here the use of a type of encoder provides feedback regarding speed and position.
Introduction
In the previous articles, we have discussed servomotors. Further, we have seen that servomotors are majorly classified into two way, that are ac servomotors and dc servomotors.
It is known to us that servomotors act as rotary actuators that are designed to convert electrical input into mechanical acceleration. It operates on servomechanism where the position feedback is used to control the speed as well as the final position of the motor.
Basically, due to the applied electrical input, the motor rotates and obtains a certain angle, the position of the rotor is provided again to the input where it is compared in order to check whether the achieved position is desired or not. In this way, precisely the accurate position is obtained.
Construction of AC Servomotor
We have already said in the beginning that an ac servomotor is regarded as a two-phase induction motor. However, ac servomotors have some special design features which are not present in normal induction motor, thus it is said that two somewhat differs in construction.
It is mainly composed of two major units, stator and rotor.
- Stator: First have a look at the figure shown below, representing stator of ac servomotor:
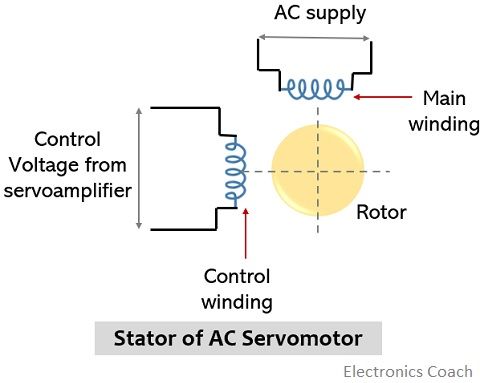
The stator of ac servo motor consists of two separate windings uniformly distributed and separated at 90°, in space. Out of the two windings, one is referred as main or fixed winding while the other one is called control winding.
A constant ac signal as input is provided to the main winding of the stator. However, as the name suggests, the control winding is provided with the variable control voltage. This variable control voltage is obtained from the servo amplifier.
It is to be noted here that to have a rotating magnetic field, the voltage applied to the control winding must be 90° out of phase w.r.t the input ac voltage.
- Rotor: The rotor is generally of two types; one is squirrel cage type while the other is drag cup type.
The squirrel cage type of rotor is shown below: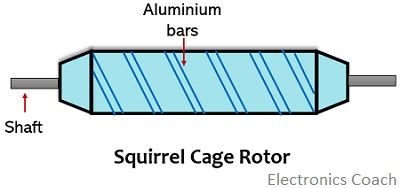
In this type of rotor, the length is large while the diameter is small and is constructed with aluminium conductors thus weighs less.
It is to be noted here that the torque-speed characteristics of a normal induction motor have both positive as well as negative slope regions that represent unstable and stable regions, respectively.
However, ac servo motors are designed to possess high stability thus, its torque-slip characteristics must not have a positive slip region. Along with this the torque developed in the motor must reduce in a linear manner with speed.
To achieve this the rotor circuit resistance should have a high value, with low inertia. Due to this reason, while constructing the rotor, the diameter to length ratio is kept smaller.
The reduced air gaps between the aluminium bars in the squirrel cage motor facilitate a reduction in magnetizing current.
Let us now see the representation of the drag cup type rotor: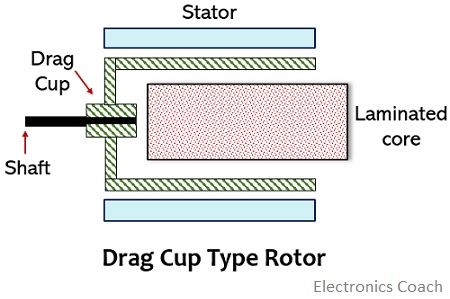
This type of rotor is different in construction from that of squirrel cage one. It consists of a laminated core of aluminium around which drag cup is present with certain air gaps on both the side.
These drag cups are attached with a driving shaft that facilitates its operation.
The two air gaps in both sides of the core lead to reducing the inertia thus is used in applications where there is a low power requirement.
Working Principle of AC Servomotor
The figure below represents the AC two-phase induction motor that uses the principle of servomechanism: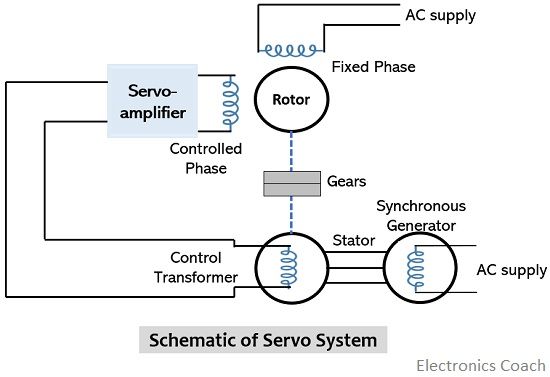
Initially, a constant ac voltage is provided at the main winding of the stator of the ac servomotor. The other stator terminal of the servomotor is connected to the control transformer through the control winding.
Due to the provided reference voltage, the shaft of the synchro generator rotates with a particular speed and attains a certain angular position.
Also, the shaft of the control transformer has a certain specific angular position which is compared with the angular position of the shaft of the synchro generator.
Further, the comparison of two angular positions provides the error signal. More specifically, the voltage levels of the corresponding shaft positions are compared which generates the error signal.
This error signal corresponds to the voltage level present at the control transformer. This signal is then provided to the servo amplifier which generates variable control voltage.
With this applied voltage, the rotor again attains a specific speed and starts rotation and sustains until the value of the error signal reaches 0, thereby attaining the desired position of the motor in the AC servomotors.
Torque-Speed Characteristics
The figure below represents the torque-speed characteristics of the two-phase induction motor: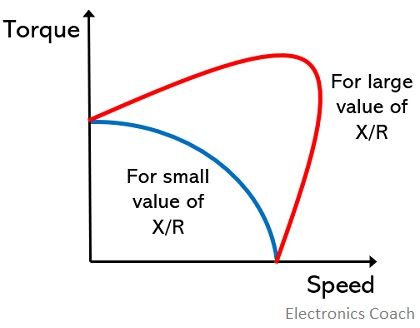
We have already discussed that the motor must be designed in a way to provide linear torque-speed characteristics, in which the torque changes in a linear manner with the speed. However, as we have seen in the above figure that the torque-speed characteristics here are not actually linear.
This is so because it depends on the ratio of reactance to resistance. The low value of the ratio of reactance to resistance implies that motor possesses high resistance and low reactance, in such case, the characteristics is more linear that high value of the ratio for reactance to resistance.
Features
- These are low weight devices.
- It offers reliability as well as stability in operation.
- There is not much noise generated at the time of operation.
- It offers almost linear torque-speed characteristics.
- As brushes and slip rings are not present here thus it reduces maintenance cost.
Applications of AC Servomotors
Due to the various advantages offered by the AC servomotors, these majorly finds applications in the instruments that operate on servomechanism, in position controlling devices, computers. Along with this these also find applications in tracking systems, machine tools and robotics machinery.
Leave a Reply