Definition: Point contact diode is formed by touching a metallic wire with an N-type semiconductor to form a small area of contact. This form a small point junction. It is widely used because such a small point junction possesses a small value of junction capacitance. Thus, the charge storage at the junction is low. Due to this, the switching ability of diode is much better than a conventional diode.
Construction of Point Contact Diode
It is formed by a contact of an N-type semiconductor substrate and tungsten or phosphor bronze wire (Cat whisker). The semiconductor used in the construction of point contact diode can be either silicon or germanium but Germanium is used extensively because it possesses higher carrier mobility.
The dimension of the semiconductor substrate is about 1.25 mm square and its thickness is 0.5 mm thick. One phase of the semiconductor substrate is soldered to the metal base by the technique of radio frequency heating.
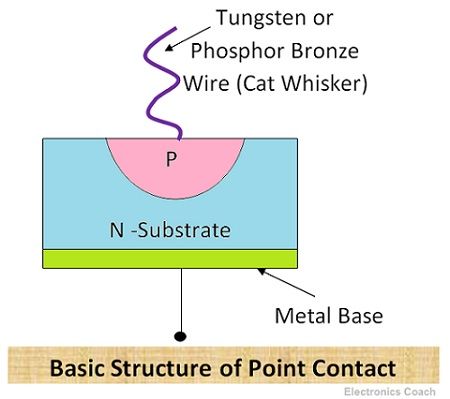
The cross sectional area of tungsten wire or cat whisker is in few ?m. It is joined to N-type semiconductor but the phase of the substrate joined to cat whisker should be opposite to that of metal contact phase. The anode and cathode terminal are connected through metallic contacts.
Working of Point Contact Diode
When forward bias is applied to point contact diode the current produced in the device is passed through the cat whisker. Due to this, the tungsten wire gets heated. Due to this heating, the wire undergoes deformation. Thus, a small gap is deliberately left for the expansion of wire under the large current.
When the wire gets heated, the semiconductor in the contact with the wire also gets heated. Due to this, it gets melted and atoms from whisker are passed to semiconductor crystal. Thus, the whisker acts as a P-type semiconductor. Therefore, a P-N Junction is formed but the area of the junction is very small. It can be assumed as a pointed junction.
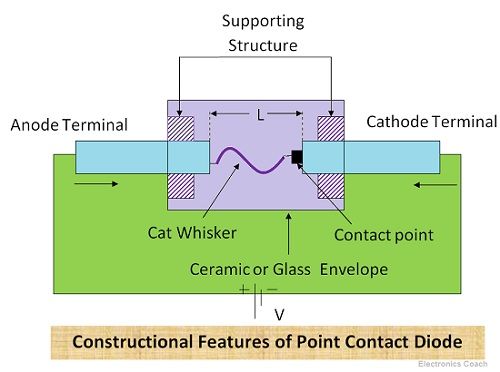
Although the junction cannot be seen clearly because the size of the junction is very small, it can be considered as point junction. The entire device is enclosed in glass or ceramic envelope. Besides, the supporting structure is provided to N-type semiconductor and cat whisker to provide mechanical strength to the device.
The junction capacitance and diffused capacitance in this diode is very small i.e. about 0.1 to 1pF. This is because the area of contact between the wire and the N-type substrate is very small. Due to the small area of junction the density of charge carriers near junction is very low. Thus, the low charge storage imparts it the ability to switch fastly.
Approximate Small Signal Equivalent Circuit
The approximate small signal equivalent circuit is described in the below diagram. The total capacitance is the sum of CT and CD.
C = CT + CD and Cg = ɛ0A/L
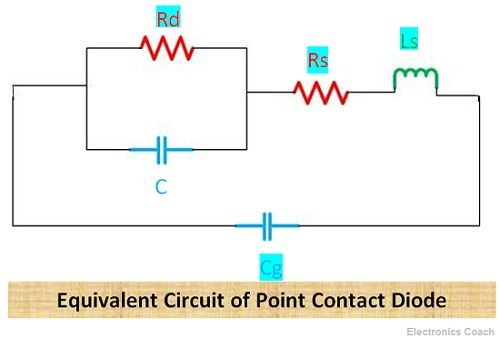
Where Cg is the geometric capacitance
Rd = dV/dI
Where Rd is the nonlinear resistance of the diode, and series resistance Rs and Inductance Ls represents the effects of ohmic contacts, bulk semiconductor and whisker.
Advantage of Point Contact Diode
Suitable for High Frequency: Due to fast switching, it is suitable for high-frequency applications.
Disadvantages of Point Contact Diode
- Lower Current Rating: The diode has lower current rating due to which the diode resistance is large under forward bias.
- Less Reliable: The small area of contact is not very rugged and thus, it is less reliable than a conventional diode.
Applications of Point Contact Diode
- High-Frequency Circuits: Due to small junction area and low junction capacitance and diffused capacitance as discussed above, the diode is suitable for high-frequency applications (about 10 GHz).
- Radio Frequency Mixers: In communication, Mixers play a crucial role in circuitry and the point contact diode is used extensively in radio frequency mixers.
- Detector Circuits: For detecting high-frequency signal these diodes play a crucial role in circuitry.
- Video Detector: It also finds application in video detector.
- Envelope detector and detector circuits of radio and television: Point contact diodes are also used in envelope and television detector circuit because it switches rapidly from one state to another state.
These are the applications of Point contact diode. Point contact diode does not involve two semiconductor pieces to form two electrodes but it uses metallic wire and a semiconductor specimen.
Happygift says
Thanks for these good notes.