Definition: Fast Recovery Diode is a semiconductor device which possesses short reverse recovery time for rectification purpose at high frequency. A quick recovery time is crucial for rectification of high-frequency AC signal. Diodes are mostly used in rectifiers because they possess ultra-high switching speed.
The major problem with the conventional diode is that they possess quite high recovery time. Due to which the rectification of high frequency is not possible with a conventional diode.
Construction of Fast Recovery Diode
The fast recovery diode is constructed in the similar manner by which ordinary diode is constructed. The major difference in construction between these diodes and conventional diodes is the presence of recombination centres. In fast recovery diodes, Gold (Au) is added to the semiconductor material. This leads to augmentation in the numerical value of recombination centres due to which the lifetime (?) of charge carriers decreases.
The semiconductor material used in these diodes is Gallium Arsenide (GaAs). And with the addition of Gold (Au) in the semiconductor material, the recovery time becomes less (about 0.1ns). On the other hand, the value of recovery time in case of silicon is 1-5 ns. Thus, it is evident that addition of materials like gold decreases the recovery time.
Working of Fast Recovery Diode
Consider an AC signal of low frequency, now if it is used in an application where low voltage DC is required. Then, in this case, we need a rectifier for converting AC to DC. If we will use a conventional diode for rectifying the AC signal, then it may rectify efficiently.
But if we want to rectify high-frequency AC signal then the diode may not work properly. The reason behind this is that at low frequencies the width of signal pulses is more i.e. there is sufficient time for a diode to change its state between positive half of cycle and negative half of cycle.
It can be understood like the signal is striking slowly. Thus, diode easily switches between positive half signal and negative half signal. But this is not the case when high-frequency signal strikes diode for rectification.
When the frequency of the signal increases the time period decreases because the frequency of the signal is inversely proportional to the time period of the signal. Thus, at high frequencies, the pulse width becomes small.
Due to which the AC signal changes extremely fast from positive half to negative half. Now, in this case, if we want to rectify such signal we need a diode which possesses low recovery time so that it switches fast from positive half of signal to negative half of signal. The rectification speed of diode should match the frequency of AC signal.
Role of Fast Recovery Diode
Fast recovery diodes are employed for such application. The addition of Gold (Au) in Gallium Arsenide (GaAs)increases the density of recombination centres in the semiconductor material. Due to which the lifetime of charge carriers (?) reduces and they recombine quickly and the recovery time reduces.
It is to be noted that the recovery time of the diode is directly proportional to the lifetime of charge carriers (?). Thus, more the lifetime of charge carriers more will be the time they take to recover from forward biased and vice versa.
Thus, by the addition of such material in the semiconductor, we increase the switching speed of the diode up to a large extent so that they can be used for the high-frequency application. They have quick recovery time that’s why they are called fast recovery diode or fast rectifier diode.
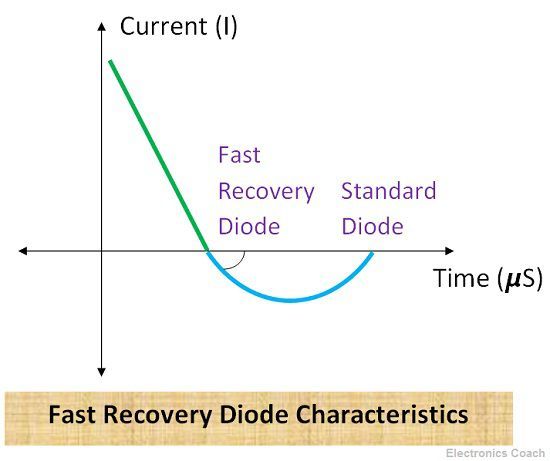
The limitation is that we cannot increase recombination centres beyond a limit. Although we can add gold atoms to create more recombination centre and it will definitely increase switching time by lowering recovery time but along with this the reverse current will also increase. The reverse current in a diode is directly proportional to the recombination centres.
Classification of Fast recovery Diode
The fast recovery diode can be classified into two types on the basis of its construction. One is formed by diffused P-N junction and the other is metal semiconductor diode. The metal semiconductor diodes possess ultra high switching speed because they involve only majority charge carriers. And the effect of minority charge carrier storage is negligible.
They are also classified on the basis of maximum average rectified current, packaging type and operating voltage.
Advantages of Fast Recovery Diode
- Ultrahigh Switching Speed
- Low reverse recovery time
- Improved efficiency as compared to conventional diodes.
- Reduced loss
Disadvantage of Fast recovery diode
It possesses high reverse current when recombination centres are increases by adding Gold(Au).
Applications of Fast Recovery Diode
- Rectifier: These diodes are used in rectifier especially for high-frequency rectification.
- Industrial and commercial areas: They are used in electronics circuits in various industries and automobile sector.
- Radio signal detector: They are used in radio signal detectors to detect high-frequency RF waves.
- Analog and Digital communication Circuits: In analogue and digital communication circuit these diodes are extensively used for rectification and modulation purpose.
These are some of the applications of fast recovery diode. The diode is called fast recovery diode because its reverse recovery time is extremely low. Thus, it switches quickly from reversed mode to forward mode.
Ashwani says
Once I was searching fast recovery diode and I came to see electronic coach.com, it is fantastic I saw there the advantages, disadvantages, applications and many more things I saw is fantastic.
Krati P says
Thanks for the appreciation !! You can also look at other articles on our website to explore the concepts of electronics.
Punkaj Gupta says
Great information… awsm
Rajneesh says
are fast recovery diodes also used in consumer appliances?