Definition: The particles like an ion, atom or molecule which has an electric charge on it, is known as the charged particles. The atom consists nucleus which has protons and neutrons on it and the outer shell of the atom consists electrons which move around its orbit. The total charge of the atom is neutral because it has an equal number of positive and negative charges on it.
The charge on the atom may be positive, negative or neutral. The particles which consist more positive charge is known as a proton, whereas the particles which have more numbers of negative charges is known as electrons. The particle which does not consist any charge is called neutron.
The charge on the particles is measured in coulombs. The single unit proton has 1.602 X 10-19 C of charge, and the electron has -1.602 X 10-19 C.
Types of Charged Particles
There are two types of electrically charged particles. They are
- Negatively Charged Particles
- Positively Charged Particles
Types of the electric charge particles are explained below in details.
Negatively Charged Particles – Electrons within an atom is known as the negative charge particles. The negatively charged particles have more electrons as compared to positive charge particles. The atom becomes negatively charged when it gains the electrons from another atom. The mass of negative charge particle is 9.11 X 10-31kg.
Positively Charged Particles – When an atom loses electrons from it, then it becomes positively charged. The positive charge of an atom is known as the proton. The mass of the positive charge particles is 1.672×10-27kg.
The mass of neutron is 1.674×10-27kg
Coulomb’s Law of Electrostatic Force
The charged particles exert force when placed in an electromagnetic field. When the two same charged particles are placed near to each other then they repel each other. Similarly, when the two opposite charged particles are nearly placed, then they attract each other. The force on the charged particles depends on the coulomb’s law.
Coulomb’s law states that “The force between two point charges is the direct multiplication of two charges and inversely as the square of the distance between them. This law is also known as the Inverse square law. The force is a vector quantity, i.e. It has magnitude and direction. The force between the two charges is expressed as
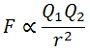
Where, Q1 and Q2 – Charges in Coulombs.
r – distance between two charges.
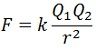
k – proportionality constant.
![]()
Hence the equation of force becomes
![]()
Energy Stored in Charged Particles
The energy stored in the charged particle is given by the law of conservation of charges. According to the law of conservation of charges the energy stored in the charged particle is given by the sum of potential & kinetic energy. The kinetic energy is possessed by the motion of charges, and the potential energy depends on the position of the charge.
The potential energy is given by the multiplication of potential to the charge under consideration
![]()
And the Kinetic energy is expressed as ![]() The total energy stored in the charged particle is given by the equation
The total energy stored in the charged particle is given by the equation
![]()
![]()
The energy stored in the charge particles are measured regarding electrons volt, i.e., Ev.
Krati P says
It’s a matter of huge pleasure for us that our contents are helping you. Stay in touch with us to read more articles.