Definition: According to Bohr’s theory, each and every shell and subshell of atoms contain a discrete amount of energy. An atom has different energy levels. When atoms are brought closer to each other, electrons at outermost shell interact with each other. This bonding force between electrons is called as an inter-atomic interaction.
This interaction causes the change in energy levels of electrons at the outermost shell. This change will give rise to energy band theory, and hence electrons will not be at the same level, the levels of the electrons are changed to a value which is higher or lower than that of the original level.
Each substance consists different amount of electron energy present in the energy bands, based on these different energy levels. Energy band are then further classified as:
- Valence band
- Forbidden Energy Gap
- Conduction Band
These Band can be explained as
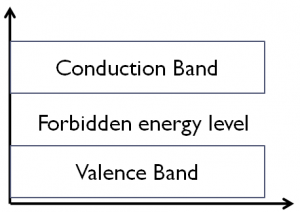
Valence Band:
At absolute zero temperature, there are the different range of energies present in the solid and the band which is formed by the highest range of energy is called valence band this band is filled with valence electrons.
Valence band can also be explained as, When atoms are brought closer together to form a solid, the discrete energy levels are disturbed because of quantum mechanical effects, and many electrons in the group of the individual atom occupy a band of levels in the solid, this band of levels called as valence band. This band is formed by the electrons at an outermost shell.
It is located below the Fermi level. Electrons in the valence band have lower energy than the electrons in the conduction band. In atoms, the electrons present in the valence band is loosely bound to the nucleus. The electrical conductivity of a solid depends on the capability to move the electrons from the valence band to the conduction band
Forbidden Energy Level:
Forbidden energy gap is also known as Fermi energy level. It is the electronic energy band where there is no electron state exists due to quantization energy. The band obtained by separating conduction band and valence band is called as forbidden energy band or forbidden gap.
In solids, the electrons do not stay in forbidden gap as there is no energy state in this region. With the help of forbidden gap, we can determine the major factor, i.e., the electrical conductivity of the solid.
Conduction Band
The energy band formed by the energy levels of the free electrons is called conduction band. The conduction band is an empty band or partially filled band, but when the external field is applied to the electrons in the valence band, the electrons jump from the valence band to the conduction band and becomes free electron.
Electrons in the conduction band have higher energy than the electrons in the valence band. In the conduction band electrons are not bound to the nucleus of the atom.
Conduction band can also be defined as empty states which are broadened into a band of levels. This band is placed above the Fermi level. It is the lowest range of vacant electronic state.
Yi sun shin says
Nice one
Harmas Q. says
Helped me understanding the concept well and in my assignment too.
Michelle says
This is awsm ….please carry on!
MohanLal seervi says
Very clear presentation about topic