Definition: Electric Drives are electromechanical systems designed to control the motion of electrical machines. It is considered an important component of various industrial processes equipment as it helps in easy optimization of motion controlling. It is regarded as a complicated control system that controls the rotation shaft of the motor.
A typical drive system has single or multiple electric motors along with a controlling system by which the rotation of the motor shaft is controlled. The major components that constitute the electric drives are electric motor, energy transmitting device, working (or driven) machine.
Concept of Electric Drives
The concept of electric drive was introduced in the year 1838 in Russia by B.S. Iakobi. Industrially, electric drives were adopted in the year 1870, however, it is now everywhere adopted in a wide range of applications.
We know that motion controlling is quite prominent in various domestic and industrial applications. In order to generate the desired motion and maintain smooth controlling a specific system is incorporated which is given the name drives.
We have already discussed that the components of electric drives are an electric motor, energy transmitting device, and working machine. The power required for the desired motion to take place is supplied by the electric motor. While in order to deliver the supplied power to the driven machine for the operation to take place an energy transmitting device is used. The driven or working machine is responsible for the desired production process that is required to occur within the system.
Examples of working machines are pumps, food mixers, pumps, etc.
Thus, we can say that an arrangement that contains an electric motor along with controlling and energy transmitting elements is regarded as an electric drive. Mainly electric drives provide a motion control mechanism as it converts electrical energy into mechanical energy so that motion can be imparted to different machines.
Block Diagram of Electric Drives
The figure given below shows the typical block diagram representation of an electric drive system:
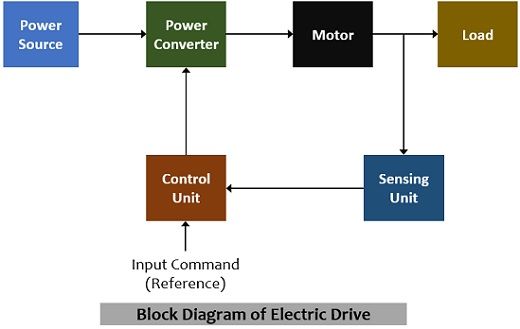
The crucial components that are incorporated here are the power source, power electronic converter, motor, load, control unit, and a sensing unit.
Let us now discuss each block individually.
1. Power Source: This unit is responsible for providing the power which is needed by the system to do the desired operation.
2. Power Controller or Converter: Following are the functions that are performed by this unit:
- This unit is responsible for the conversion of supplied input electrical energy into a form that can drive the motor (generally mechanical energy).
- The power controller controls the power input provided to the motor that can be handled by the same. Basically, this control is necessary because power flowing through the system decides the torque-speed characteristics which the load requires.
- When transient operations like starting, braking, etc. within the system take place, this unit helps in limiting the current to specific levels so that voltage overloads or dips can be avoided.
There are several types of power converters and we have made a separate content on the same.
3. Control Unit and Sensor Unit: This unit performs the action of controlling the power converter according to the provided input as well as the feedback signal obtained from the load under the closed-loop operation. Basically, the control unit works in conjunction with the sensor unit which actually senses the voltage or current signal as feedback to have the proper operating conditions. The sensing unit is responsible for sensing the current or speed of the motor. It protects as well as provides closed-loop operation.
4. Electric Motor: This mainly converters the applied energy into mechanical motion. Mostly DC motors used in the electric drive systems are in series, shunt, or compound form while AC motors used are slip ring induction motors. Sometimes stepper motors or brushless DC motors are also used in special cases.
5. Load: The load which is the part of the system is specified according to the torque/speed characteristics of the system such as pumps, machines, etc. The electric motor and load operate in compatibility with each other in terms of torque-speed characteristics.
Classification of Electric Drives
There are various parameters on which the classification of electric drives exists however, majorly electric drives are classified into two categories namely,
- DC Drives: The DC drives are the ones that where the motive power that excites the system is DC in nature. Their main applications are involved in adjustable speed drives and position control. Here dc motors are used along with the power electronic converters.
- AC Drives: The operation of AC drives is based on the AC type of supply input. These are lightweight than dc drives. AC drives can be of two namely induction motor drives and synchronous motor drives.
Advantages of Electric Drives
- The operation offers flexibility in managing the characteristics of the system.
- This offers easy (instant) starting or loading.
- Electrical energy is used to power the system and it can easily be transferred, stored, and handled.
- The electric motors which constitute the drive system exhibit high efficiency with low losses and considerable overloading capability. Thus, provides more life span as the noise factor is less and the need for maintenance is also low.
- It is easy to get the dynamic load characteristics up to a large range of speed and torque from the steady-state and dynamic performance of the system.
- The control unit functionality can be easily performed using a software approach, making use of microcontrollers thereby making the approach easy.
- It can perform the four-quadrant operation in the Torque/Speed plane. Here regenerative braking takes place thereby offering considerable energy saving.
- With the advent of power electronics devices like SCRs, efficient power converters can be formed and so the power feeding to the drives can become easy.
Disadvantages of Electric Drives
- It does not operate without a power supply.
- The value of the obtained drive output power is low.
- It offers a poor dynamic response.
- In the case of power breakout, the whole system operation gets failed.
- It is expensive.
Applications of Electric Drives
Electric Drives has an enormous number of industrial as well as domestic applications including pumps, fans, motors, transportation systems, turbines, engines, etc. Not only this, it is useful in various electric tractions such as trains, buses, trolleys, and vehicles powered with solar energy. Some other applications are in Lathe machines, shears, frequency converters, air compressors, refrigeration, and air conditioning, belt conveyors, etc.
Leave a Reply