Definition: The Electronic Multimeter is a device which is used for the measurement of various electrical and electronic quantities such as current, voltage, resistance etc. The multimeter name is given to it to define its ability to measure multiple quantities.
It is provided with inbuilt power supply necessary for the functioning of the device. Any component such as a resistor, battery can be connected to its outer probes for the measurement of the electronic quantity. In order to understand how a single meter can measure multiple electrical quantities, we need to look into its constructional feature and the components which make it a multimeter.
Construction and Components of Multimeter
The multimeter basically consists of a bridge DC amplifier, rectifier, PMMC meter, function switch, internal battery and an attenuator. The function of the attenuator is that it helps to select a particular range of voltage values. The rectifier is essential in a multimeter for the conversion of AC voltage into DC voltage. The internal battery is needed for the operational mechanism of the multimeter.
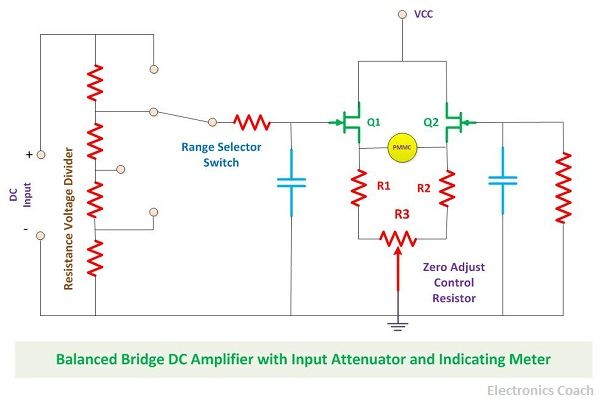
The Bridge DC amplifier is nothing but two Field effect transistor connected opposite to each other with three resistors and forming a bridge-like structure. The two resistors are for balancing the bridge, and the third resistor is a zero adjust control resistor.
Working of the Multimeter
The Multimeter performs its operation by providing the input voltage to the gate terminal of the FET, and this gate voltage is responsible for the increase in the source voltage of the FET. The PMMC meter is connected between the two FET.
In the ideal condition, no current should flow from PMMC meter so thus it must show zero deflection, but in the practical implementation, the PMMC meter shows some deflection. This is undesirable in steady state. Thus a zero adjusts control resistor is used for adjusting the value of current to zero. After this again, the PMMC shows no deflection.
But make sure the above condition is defined when no input is applied to it. When the input is applied to it either by connecting a resistor or any other component, the circuit switched to the active state and the changes in the circuit due to the connection of the component is deflected with the help of PMMC meter.
There are series of steps which is to be followed while measurement. First, the multimeter should be tested whether is it working or not. If it is not working the battery requirements of the device should be checked.
After this, we need to set the knob of the multimeter to set it on the values or quantity which is to be measured. For example, if we want to measure resistance then the multimeter should be set to option “ohm”. Apart from this, we need to set the range of multimeter.
It is significant to set the range of multimeter because if you are measuring the resistance of the resistor which possesses value in kilo-ohms and the range of multimeter is not set and by default it is in ohm or mega-ohms, then you will get wrong results. Therefore it is crucial to set the range of the multimeter properly.
Measurement of Resistance by Multimeter
The resistance can be measured by multimeter easily by connecting the two probes of the multimeter with two ends of a resistor. The unknown resistor the resistance of which is to be measured is connected to the function switch and the battery.
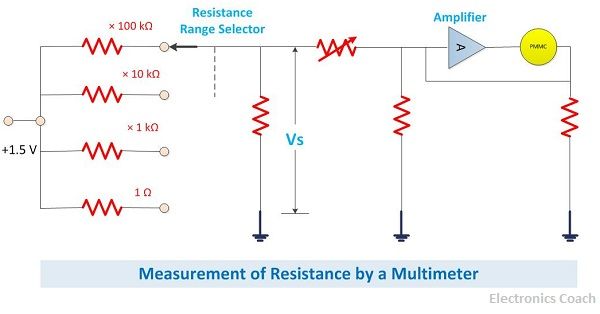
The battery of 1.5 V is connected to the circuit when the resistor is connected the circuit becomes complete, and the voltage across the resistor is measured by the circuit, and the particular range is indicated by the PMMC meter.
There are various resistors that are connected in parallel; all these resistors possess different values of resistance. The range which is to be measured can be set and also a particular range of value of resistance can be connected to the unknown resistor.
The Amplifier connected in series amplifies the signal. The signal gets distorted as it passes through the circuit. Moreover, the current also flows from that path in which the resistor is connected. And we all are aware of the fact that the value of voltage drop across the resistor is directly proportional to the value of the resistor.
Thus, as the value of resistance increases the value of the voltage drop across it increases, and thus the PMMC meter shows the deflection accordingly. In this way, the value of resistance is measured.
Anon says
The content is really simple and easy to understand. Thanks and great work. 🙂
Utkarsh Dubey says
very easily understandable…thanks for this
Jahan says
Very usefull content. Good Job!