Hexadecimal Number System forms the backbone of the digital system such as microprocessors, microcontrollers etc. It is a number system which consists of 16 elements, in which 10 numbers from 0 to 9 and 6 alphabets from A to F are used. Any other number can be represented in the hexadecimal number system with the help of the combination of these 16 elements.
The word hexadecimal is formed from two words, “HEX” and “DECIMAL”. Hex means 6 and decimal mean 10, the sum of these two is 16 which signify its base. Thus, the hexadecimal number system is also known as “Base-16” number system.
The reason behind this is that the radix or base of the hexadecimal number system is 16. We have already discussed in our previous article that the base of the number system is the number of elements building that number system.
Significance of Hexadecimal Numbers
The Hexadecimal number is a favourite alternative for researchers working on digital systems. They prefer hexadecimal numbers over binary and octal numbers.

Are you confronting the same question????
This is because the binary number representation of small numbers is simple and short in length. But what about large numbers, i.e. numbers with 32 digits, 64 digits or even more. In this case, binary number representation will be a long string of 0’s and 1’s. There may arise the possibility of error either in reading the number or writing the number.
This problem can be solved with the help of hexadecimal number system. Each group of four digits of binary numbers can be written into a single digit of the hexadecimal number. Thus, hexadecimal number reduces the length of the number representation by 1/4th.
In our previous article in category digital electronics, we have discussed that octal numbers also reduces the length of the number string, but it reduces the length by 1/3th. While hexadecimal is more efficient as we need only one digit in hexadecimal number to represent 4 digits of the binary number.
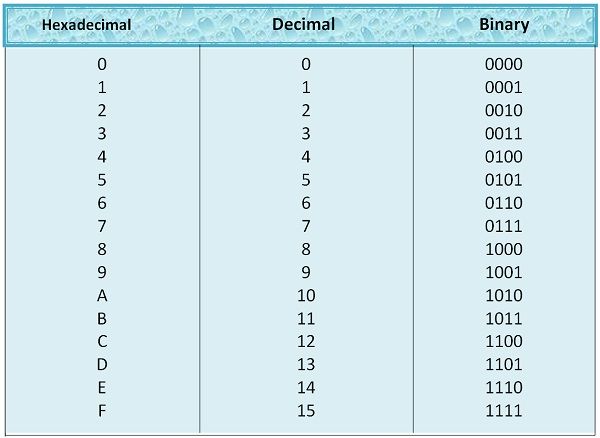
Counting in Hexadecimal Number System
The counting in hexadecimal number system starts with 0. The other numbers can be understood with the help of the table below. The number 10 in hexadecimal number system is represented by A, then 11 by B and so on. This type of alphabetic representation is used in hexadecimal number system to distinguish it from decimal number system.
If we write the number 10 directly, it will make the numbering system complicated and confusing. We will not be able to identify that whether this 10 is of decimal or hexadecimal.
Thus, in order to recognize that whether we are dealing with the decimal number system and hexadecimal numbers system, we use alphabets A, B, C, D, E and F to denote 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 respectively.
Conversion from Hexadecimal to other Number System and Vice Versa
Hexadecimal to Decimal
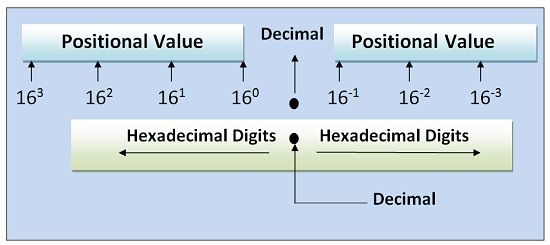
To convert a hexadecimal number into the decimal number, we need to multiply each digit of hexadecimal number with 16 raised to the power of the positional value of the digit. In case of decimal point is present then the positional power will increase consequently from 0 to higher values when moving leftward from the decimal. Similarly, it will increase in negative powers on moving rightwards from the decimal.
Let’s consider an example.
(131.F2)16 = 1*162 + 3*161 + 1*160 + 15*16-1 + 2*16-2
= 256 + 48 + 1 + (15/16) + (2/256)
= (305.9453125)10
Decimal to Hexadecimal
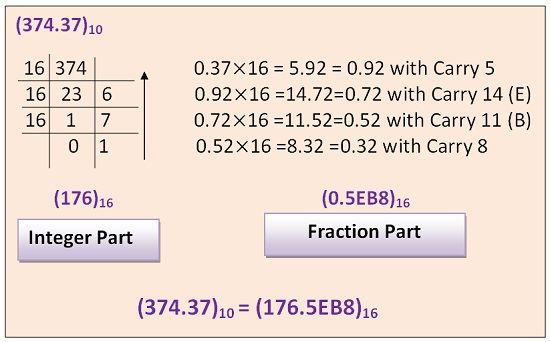
The decimal number can be converted into hexadecimal by dividing the number continuously by 16 and writing all the remainders in reverse order. If the decimal number consists of a decimal point, then the integer part will be converted separately and fraction part will be converted separately.
The integer part will be converted by successively dividing the number by 16 as it is the base of the number system. The fraction part will be converted by consecutively multiplying the fraction part with 16 and separately writing the carry part.
The entire process of conversion of the decimal number into hexadecimal number can be understood by the below-mentioned example.
Hexadecimal to Binary
The conversion from hexadecimal to binary is simple and can be completed in a single step. Each digit of the hexadecimal number system can be written into its 4-digit binary equivalent. You can add zeroes if the binary equivalent consists of 3 digits. Thus, the entire binary digits are written in a sequence to get the binary equivalent of the hexadecimal numbers.
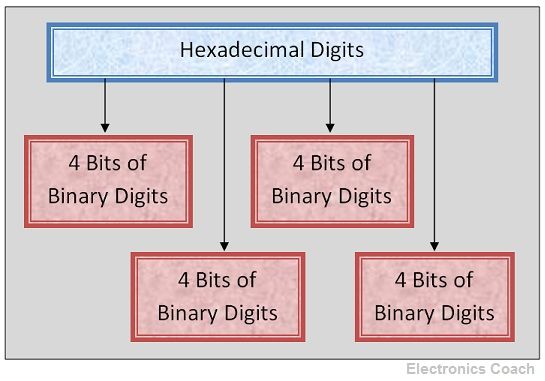
The conversion process can be understood more clearly with the help of the example. Let’ consider a hexadecimal number (A6B.F5)16. Now to convert this number into binary, we need to write each digit’s binary equivalent.

Binary to Hexadecimal
The conversion from binary to hexadecimal can be achieved by forming a group of 4 digits of the binary number and then writing the hexadecimal equivalent of the binary group. We can add a number of zeroes according to our convenience in order to complete the group of 4 digits. We have to form groups starting from LSB and moving towards MSB.
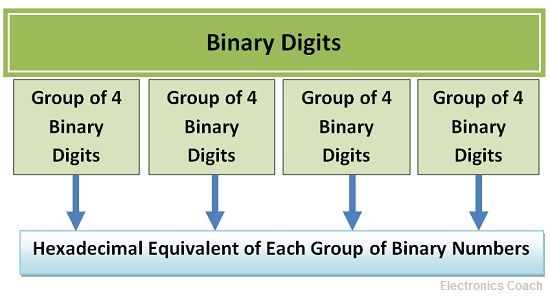
Let’s understand this with the help of an example

Hexadecimal to Octal
The hexadecimal number can be converted into Octal in two steps. First by converting the hexadecimal number into the binary number. Secondly, by converting the binary number into Octal. We are well familiar with the conversion of binary to Octal. Firstly by forming a group of three binary digits starting from LSB to MSB and then writing its Octal equivalent.
Thus, the Octal equivalent of hexadecimal number can be obtained.
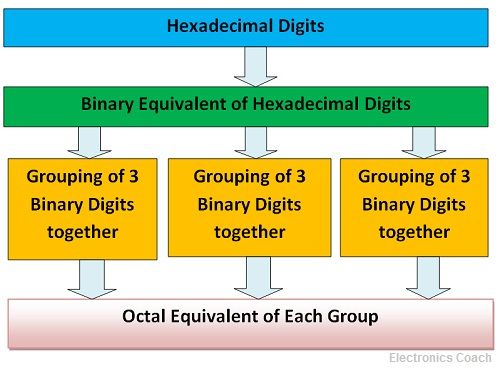
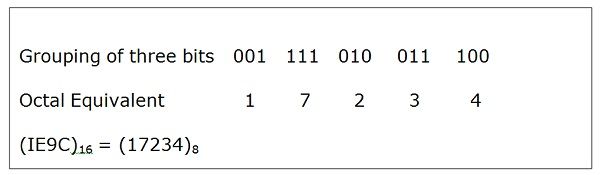
For example: Consider a hexadecimal number (IE9C)16
Octal to Hexadecimal
The octal number can be converted into hexadecimal by converting it first into binary then into hexadecimal. The binary numbers are grouped into 4 bits each. Thus, the hexadecimal equivalent of 4 bits binary number can be written in a single step.
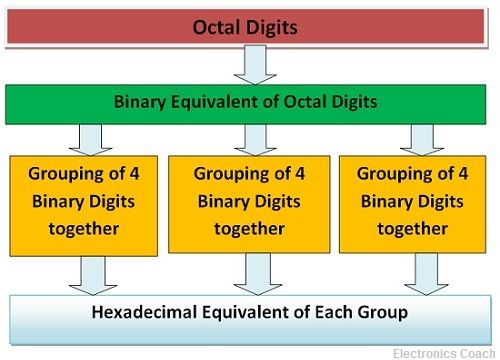
Let’s consider an octal number (2715)8
 With the help of these conversion methods, you can easily convert hexadecimal number system into binary, octal and binary decimal number system. Hexadecimal is extensively used in microprocessor and microcontroller programming.
With the help of these conversion methods, you can easily convert hexadecimal number system into binary, octal and binary decimal number system. Hexadecimal is extensively used in microprocessor and microcontroller programming.
Leave a Reply