Characteristics of JFET: The characteristics of JFET is defined by a plotting a curve between the drain current and drain-source voltage. The variation of drain current with respect to the voltage applied at drain-source terminals keeping the gate-source voltage constant is termed as its characteristics. Basically, the characteristics are of two types that are output characteristics or drain characteristics, and the another is transfer characteristics.
Let us discuss each of the mentioned above type with characteristics curve. One point should be kept in mind while elaborating output characteristics that the output characteristics can be observed in two scenarios.
In the first case the output characteristics are observed when there is no bias, i.e. there is no voltage applied between gate and source terminals. Another condition is that the biasing is applied between gate and source terminals. In both the condition the variation of drain current is different.
Output Characteristics or Drain Characteristics
- In the absence of external bias: In this case, as there is no voltage between gate and source terminal, thus, the drain current will flow from drain terminal to source terminal. We have already discussed in the working of JFET that majority charge carriers flow from source to drain and as a consequence of which the current flows from drain to source.

Now, what does this means? It clearly implies that the channel width is more as the width of depletion layer will not vary initially because there is no external reverse biasing. This allows a large magnitude of current to flow through the channel.
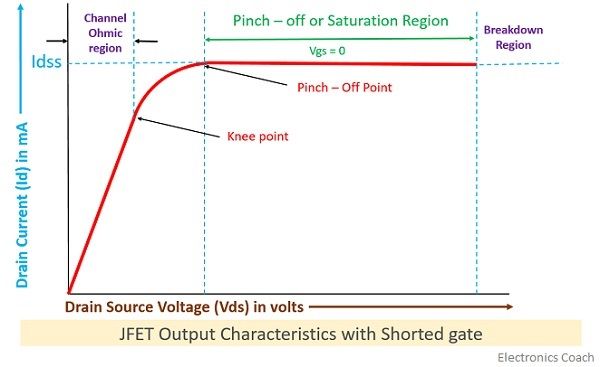
In this case, the N-type channel will simply behave as resistance region. The flow of current from drain to source will create the voltage drop between gate and source. This will eventually result in reverse biasing of the gate-source terminal. The reverse biasing will be more towards drain region that source region.
Terminologies involved in JFET characteristics
- Knee Point: There exists a point in the characteristics curve where the variation of drain current with drain-source voltage appears to be linear. But after this point, the linearity changes into a curve.
- Channel Ohmic Region: The region to the left of the knee point in the characteristics curve is the channel ohmic region.
- Pinch-off point: The point in the curve above which the drain current does not increases further no matter how much we are increasing the drain to source voltage, this point is termed as the pinch-off point.
- Pinch-off Voltage: The voltage at the pinch-off point is termed as pinch-off voltage because at this voltage the current is completely turned to be constant.
- Drain-Source Saturation Current: The drain to source saturation current is the current which becomes constant or completely enters a saturation state.
The region after the pinch-off point in the curve is termed as saturation region. When the JFET is allowed to work as an amplification device, the JFET utilizes this region for operation.
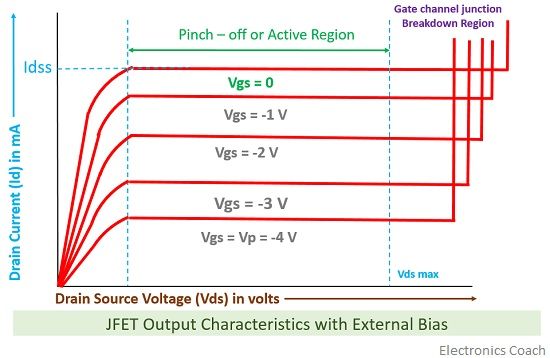
- With external bias: When the external bias is applied to the gate-source terminal, the gate-source terminal becomes reversed bias externally. Obviously, if we are supplying an external voltage, then we can achieve the pinch-off point quite early as compared to the circuit which is not biased.
It is clearly evident from the characteristics curve of external bias. The different values of voltage give different values of current.
It is to be remembered here that when we are observing the drain characteristics with respect to the variation in drain-source voltage, then the value of gate-source voltage should be kept constant.
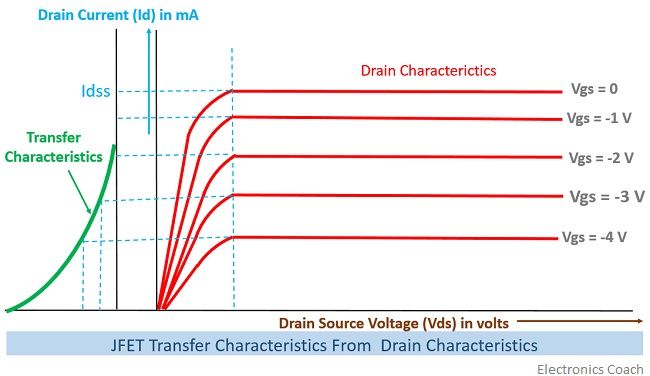
Transfer Characteristics
The transfer characteristics can be determined by observing different values of drain current with variation in gate-source voltage provided that the drain-source voltage should be constant. The transfer characteristics are just opposite to drain characteristics.
One just needs to remember the concept that in drain characteristics we are keeping the gate-source voltage constant and determining the values of drain current at different values of drain-source voltage while in transfer characteristics we are keeping the value of drain-source voltage constant.
The characteristic curve of transfer characteristics of JFET is described below; it can be easily observed that the value of drain current varies inversely with respect to gate-source voltage when the drain-source voltage is constant.
In this article, we have discussed the output characteristics or drain characteristics and transfer characteristics of an N-channel JFET. What if we want the characteristics of P-channel JFET? Is there will be variation in P-channel JFET characteristics?
The answer to this question is NO. The characteristics curve will remain same. The only difference which will occur is that in case of P-channel the current contributing carriers will be hole rather than electrons in N-channel. Besides, the polarities of gate-source voltage and drain-source voltage will also be reversed in case of P-channel JFET.
Thobescu says
Thank you
Very usefull
nice day
Shyamakant Pandey says
Very useful. Good