The crucial difference between JFET and MOSFET is that in JFETs, the conductivity of the channel is controlled by the electric field across the reverse-biased PN junction. Conversely, in MOSFET, the conductivity of the channel is controlled by transverse electric field across the insulating layer deposited on the semiconductor material.
When we talk about the operating principle and characteristics then the two are almost similar. Although some aspects differentiate the two. MOSFET is basically an advanced version of FET. It was simply invented to overcome the disadvantages of FETs.
Both finds its applications in amplification of electric signals as they have the ability to change conductivity with respect to the voltage applied.
Till now we have discussed crucial factors that discriminate FET from MOSFET. Now, let’s move further and discuss other important difference between FET and MOSFET using the comparison chart.
Content: JFET Vs MOSFET
Comparison Chart
| Parameters | JFET | MOSFET |
|---|---|---|
| Mode of operation | It operates only in depletion mode. | It can be operated in either depletion or enhancement mode. |
| Symbol | 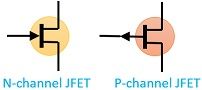 | 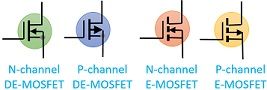 |
| Input impedance | JFET have much smaller input impedance mainly of the order of 108 Ω. | MOSFETs have much higher input impedance of about 1010 to 1015 Ω due to small leakage current. |
| Characteristic curve | As JFET has higher drain resistance, the characteristic curve is more flatter. | The characteristic curve is less flat than those of JFET. |
| Drain resistance | JFET has drain resistance of the order of 105 to 106 Ω | Drain resistance in case of MOSFETs is of the order of 1 to 50 K Ω. |
| Fabrication | Fabrication process of JFET is more difficult than MOSFET. | MOSFET can be easily fabricated thus it is more widely used. |
| Cost | Manufacturing of JFET is cheaper as compared to MOSFET. | MOSFETs are slightly expensive as compared to JFET. |
| Susceptibility to damage | It does not require special handling. | These are more susceptible to overload voltage and requires special handling. |
Definition of JFET
JFET is an acronym for Junction field effect transistor. The device consists of 3 terminals gate, source and drain.
In a JFET, an electric field is applied across the gate terminal that controls the flow of electric current. The current that flows from drain to source terminal is proportional to the applied gate voltage.
JFETs are basically of two types basically N-channel and P-channel.
The voltage applied across the gate to source terminal allows the electron to move from source to drain. Thus a current from drain to source flows that is termed as drain current ID.
When gate terminal is made negative with respect to the source, the width of the depletion region increases. Thus allowing less number of electrons to move from source to drain as compared to no bias condition.
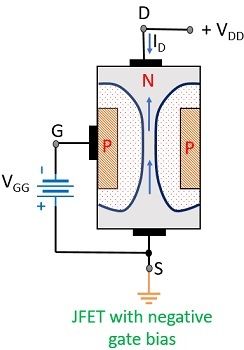
As more negative gate voltage is applied the width of the depletion region will further increase. Due to this, a condition is reached which cuts off the drain current completely.
JFET has a longer life and it possesses higher efficiency.
Definition of MOSFET
MOSFET is an acronym for metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor. Here also the conductivity of the device is varied according to the applied voltage. MOSFET is an advancement of FET.
MOSFETs are of two types
- Depletion type MOSFET and
- Enhancement type MOSFET
In a depletion MOSFET there exist a pre-constructed channel. So, the applied gate to source voltage switches the device to off condition.
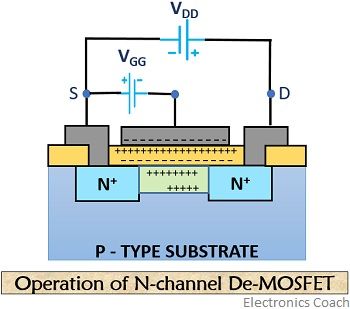
On the contrary, in an enhancement type MOSFET, no any pre-constructed channel exists. Here, conduction starts on the creation of channel by the applied voltage.
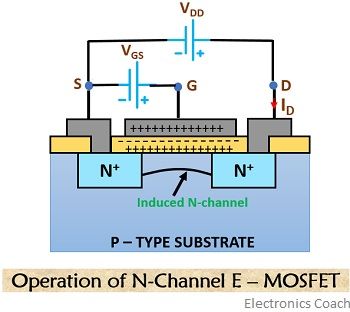
In a D-MOS the negatively applied gate potential increases the channel resistance thus reducing the drain current. On the contrary, in E-MOS large positive gate voltage is required for its operation.
Key Differences Between JFET and MOSFET
The following points describe the difference between JFET and MOSFET:
- The factor that generates the key difference between JFET and MOSFET is that a JFET operates in only depletion mode. While MOSFET operates in both depletion and enhancement mode.
- JFET is normally termed as ON devices. As the negative gate to source voltage turns the device to OFF state. As against MOSFET is termed as normally OFF devices because in E-MOSFET applied gate voltage turns ON the device.
- Due to small leakage current, the input impedance of MOSFET is much higher as compared to JFET.
- Talking about operational speed, FET possesses slower operations and provides high drain resistance as compared to MOSFET.
- JFET possess flatter characteristic curve than those of the MOSFETs.
Conclusion
From the above discussion, we can conclude that MOSFET is somewhat better than JFET. When we talk about electrometer applications then MOSFETs are more useful than JFETs.
Shreyansh Sharma says
The website is very good, the best part is colourful simple diagrams and layout is relatively good. The sequence of content is also good and useful.
Thank you
Roshni Y says
Thanks a lot…keep reading