Diode and Transistor are considered as the backbone of electronic devices and Circuit. But the similarities between these crucial devices of electronics realm end here. The main difference between diode and transistor is that a diode is a two terminal device which allows current in one direction only from the anode to the cathode.
On the contrary, a transistor is a three terminal device which passes current from high resistance region to low resistance region. The word transistor itself express its function, the word transistor is derived from two words, Transfer and Resistor. Thus, it is considered a device which transfers resistance from one region to another.
There are certain factors which differentiate these two devices such as depletion region, applications etc. We will discuss all these factors with the help of comparison chart.
Content: Diode Vs Transistor
Comparison Chart
| Parameters | Diode | Transistor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A diode is a two terminal device which allows current to pass in one direction only. | Transistor is a three terminal device which allows current to flow from high resistance region to low resistance region |
| Formation | It is formed by joining a P-type semiconductor with N-type semiconductor. | It is formed by sandwiching a layer of P-type or N-type material between two N-type or P-type material on either end. |
| Circuit Symbol |  | 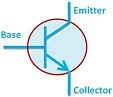 |
| Depletion Layer | Only one depletion region is formed. | Two depletion region are formed. |
| Number of Junctions | Only one junction between P-type and N-type semiconductor. | Two Junctions are formed one in between emiter and base and other between base and collector. |
| Terminals | 2 terminals are there in a diode i.e. anode and cathode. | 3 terminals are there in transistor i.e. emitter, base and collector. |
| Considered as | It can be considered as a switch. | It can be considered as a switch or an amplifier. |
| Applications | Rectifier, voltage double, clipper etc. | Amplifier, Oscillator etc. |
Definition
Diode
A diode is formed by combining two semiconductor specimens of which one is P-type semiconductor and other is an N-type semiconductor. The junction formed by joining these two semiconductors is termed as PN junction. The depletion layer is formed due to different concentration of charge carriers in both the region.
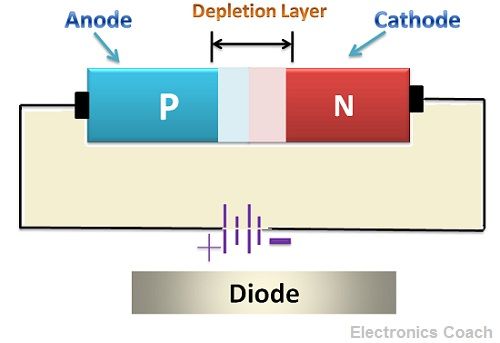
The P-type semiconductor has holes as majority carriers while N-type semiconductor has electrons as majority carriers. Now, the behaviour of PN junction will be different in unbiased mode and biased mode.
Let’s discuss unbiased mode first. In an unbiased mode, the electrons from N-region and holes from P-region will move towards the junction due to the concentration gradient. A stage will reach when no more charge carriers will diffuse across the junction. This stage is called saturation stage.
After this, the electrons and holes which have reached the junction will recombine. Due to this the movement of further majority carriers will get restricted. The region so formed is called depletion layer. It will create an internal electric field.
Now moving towards biased mode, when biasing is applied, i.e. connection of P-type with the positive terminal and N-type with negative terminal. The forward current will starts flowing from anode to cathode. The width of the depletion region decreases with increased forward biased.
Similarly, the width of the depletion layer increases with the reversed biased condition in reverse biased mode. The current which flows in the diode is because of the minority charge carriers. This is called reverse saturation current because it gets saturated after a particular reverse voltage. Then it does not increase further with the increase in reverse voltage.
The reverse current increases only with the increase in temperature.
Transistor
A transistor is a three terminal device, which consists of three regions and two junctions. The regions are the emitter, base and collector. The two junctions are the base-emitter junction and base-collector junction.
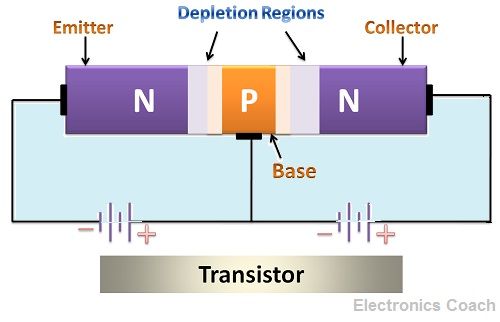
These regions have different characteristics, and they all are of different size. The emitter is highly doped so that more charge carriers can be created; the base is lightly doped so that only a few charge carriers will recombine there and the collector is moderately doped.
The size of the collector is more than emitter as well as collector while the size of the base is smallest among all three regions. The width of the depletion layer between collector and base is more than the width of the base-emitter junction.
The emitter and base are connected to the battery in such a manner that they work in forward biased mode while the collector and base are connected to battery in such a way that it becomes reversed biased. Therefore, the majority charge carriers will flow from emitter to base and then base to collector. The larger the size of the collector, the more will be the charge carriers it collects and the heat dissipation will also take place easily.
Key Differences Between Diode and Transistor
- The crucial difference between diode and transistor is that the diode is two terminal device while the transistor is the three terminal device.
- PN junction diode consists of one depletion region, i.e. between P-type and N-type, but the transistor consists of two depletion layers.
- The diode is considered as a switch as it can perform switching, but the transistor can perform switching as well as amplification.
- The diode needs only one battery source to perform its operation while the transistor needs two battery sources to perform its function.
Conclusion
The diode is a two-terminal unidirectional device while the transistor is a three terminal device which passes current from high resistance region to low resistance region via the base. A diode is used in various applications of electronics such as in rectifier, clipper, clamper, voltage multiplier, switches etc. A diode act as a switch. It is ON when it is forward biased, and it is OFF when it is reversed biased.
Transistor can act as a switch and also as an amplifier. The application creates the major difference between diode and transistor. Diodes are of various types such as zener diode, PIN diode, photodiode, light emitting diode etc. while transistors are mainly of two types bipolar transistor and field effect transistor.
Naila says
this has been a great article for my research. I like how the topic is well summarized and it is easy to understand for beginners like me.
Fathi Zenati says
Thank you!
AYANTUNMBI RAPHAEL says
I love this
Great work