Definition: The word Transistor is formed from two words, one is “Transfer” and other is “Varistor”. This implies a device which transfers resistance from one channel of the circuit to other is called transistor. It is a three terminal current controlled device which can either be operated as switch or amplifier by providing small signal voltage. It is one of the significant types of active devices.
Significance and History of Transistor
You must be thinking what is the need of transistor???
Let me explain this with the subvention of history. In the beginning of 20th century when the vacuum triode was invented, it was considered as the significant development in the field of electronics. This is because devices such as computers were entirely based on them.
But the problem started with their size which can capture the entire room. Now you can imagine what will happen if the entire room consists of a single processing system. Obviously, to work with it is a cumbersome process.
Fortunately, we have compact size processing system in the contemporary world. But this all has become possible with the invention of the transistor. In the year 1947, John Bardeen along with William Shockley & Brattain invented the transistor. The consequences are quite evident. Now, all the computing devices are available in small size which we can easily carry with us anywhere.
Construction
Let’s discuss constructional features of the transistor, how this 3 terminal device is formed. A diode is two terminal device, thus, if we merge the two diodes provided that one terminal is common, the resulting device will comprise of three terminals.
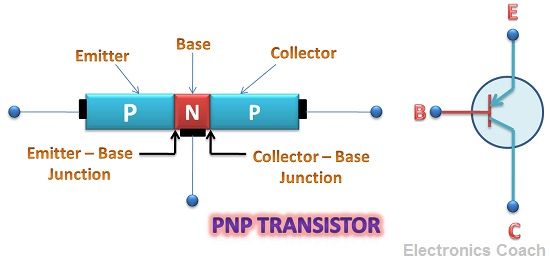
This is how a transistor is constructed. We can use either sandwiched P-type layer of the semiconductor between two N-type semiconductors or by sandwiching N-type layer between two P-type semiconductor specimen. The transistor formed in the former case will be NPN transistor and that formed in the latter case is PNP transistor.
The three terminals have specific names that are as follows:-
- Emitter
- Base
- Collector
We will discuss functions of these three terminals in the working of the transistor.
A transistor is a semiconductor device, so the semiconductor material used in its construction can be either germanium or silicon, but silicon is preferred over germanium because it possesses smaller cutoff current.
Working of Transistor
The transistor as its names suggests transfer resistance from one channel to other channels. Thus, as there are three terminals of the transistor, i.e. base, emitter and collector. Thus, there are two junctions of the transistors. One is the Emitter-base junction, and the other is Collector- base junction. I intend to explain the working of the transistor with the help of these paramount parameters.
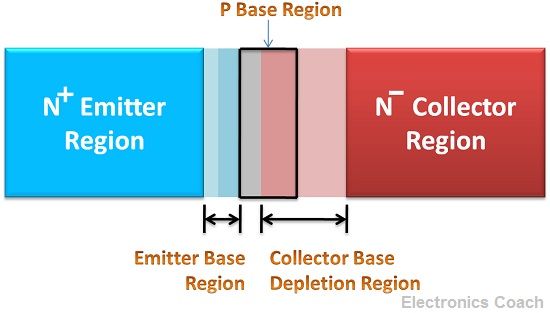
Before I delve into the working details of the transistor, let’s understand these three significant terminals of the transistor and their characteristics.
- Emitter: Emitter terminal is the heavily doped region as compared two base and collector. This is because the work of the emitter is to supply charge carrier to the collector via the base. The size of the emitter is more than base but less than the collector.
- Base: The size of the base region is extremely small, it is less than emitter as well as the collector. The size of the base is always kept small so that charge carriers coming from the emitter and entering base will not recombine in the base region and will be directed towards the collector region. The doping intensity of base is also less than emitter and collector for the same reason mentioned above.
- Collector: The collector terminal is moderately doped, and the size of the collector region is slightly more than emitter region because all the charge carriers coming from the emitter recombine at base and heat is released in this process. Thus, it is necessary for the collector terminal to be large enough so that it can dissipate the heat and the device may not burn out.
Unbiased Transistor
Let’s consider an NPN transistor which is unbiased. Unbiased means it is not provided with any external voltage source. In this condition, the majority charge carriers in emitter region will move towards the base region.
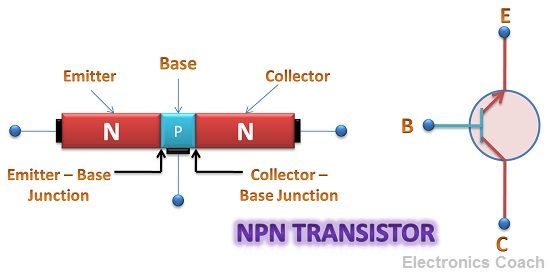
Due to moderate doping and small size of the base terminal, only 5-10% of the charge carriers entering base will recombine. Please note that we have considered NPN transistor so majority charge carriers in emitter will be electrons.
Thus, only a few electrons will recombine at the base and the remaining will start moving towards collector. Thus, 90-95% of the electrons emitted by an emitter will get recombined with holes in collector region. This movement of electron and holes in the circuit result in the generation of current.
Mainly, the transistors work in three regions that are as follows:
- Active region: This region is utilized for the operation of the amplifier.
- Saturation Region: In this region, the transistor is operated when we need switching operation. In this region, the transistor acts as ON switch.
- Cut Off Region: In this transistor works as a closed switch.
Advantages of using Transistors
- Compact Size: These small size transistors have ushered to design compact processors. We need not to work anymore with that large size vacuum tubes based computers. All thanks to the inventors of transistors.
- Light Weight: The entire arrangement of the transistor is packed in a single case with heat sink and three terminals. This entire casing is extremely lightweight which adds to the advantage of the transistor and make it a portable device.
- High Operating Efficiency: Transistors possesses high operating efficiency no matter whether we are using it as an amplifier or oscillator or switch.
- Long Life: It also possesses a long life which makes it reliable for various applications as it has minimized ageing effects.
Disadvantages of using Transistors
- Low operating Frequency: It possesses operating frequency only up to certain MHz. This makes it out of the league when it comes to high-frequency applications.
- Low operating Temperature: There is a threshold limit of temperature above which if the transistor is operated it may get dilapidated. The threshold limit is 75ᵒC. Thus, we cannot operate it above this temperature range.
Everything comes with pros and cons. You must have heard this. For every advantage, a device possesses it must possess certain drawbacks although the former outweighs the latter. Transistors too have certain disadvantages.
Sai charan says
Nice one helped me a lot for my board exams of 10th std tqsm electronicscoach
Krati P says
Its a matter of immense pleasure for us that our content is helping you to understand the concept of electronics. Thanks for the appreciation !!
Makesh kurup says
Superb man helped a lot
Adnan Anam says
The explnation helped a lot, in clearing the concept. Very beautiful explanation of Transistor.
Abdullahi Danjuma Yanmaulu says
Thank you
CHANDAN GORAI says
Thank u for this notes !
it is enough to learn BJT.
Jason Lawrence says
Thank you very much for detailed information.