A diode is a semiconductor device which conducts in one direction only. A Zener diode is a semiconductor device which conducts in forward biased as well as reversed biased. A normal diode if operated in reversed biased will get destroyed. Thus, a normal PN junction diode is considered as a unidirectional device. On the contrary, Zener diode is designed in a way that it can conduct in a reversed biased mode without getting damaged.
The doping intensity is also one of the key features which distinguish conventional diode and Zener diode. The normal PN junction diode is moderately doped while the Zener diode is doped properly in such a way that it possesses sharp breakdown voltage.
We will discuss some other differences between diode and zener diode with the help of comparison chart.
Content: Diode Vs Zener Diode
Comparison Chart
| Parameters | Diode | Zener Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Diode is a semiconductor device which conducts only in forward biased. | Zener diode is semiconductor device which can conduct in forward as well as reversed biased. |
| Operation in Reverse Biased | It gets damaged in reverse biased. | It can operate without getting damaged. |
| Circuit Symbol |  |  |
| Doping Intensity | In normal diodes doping intensity is low. | In Zener diode doping intensity is high to achieve sharp breakdown. |
| Application | Diode is used in rectifiers, clippers, clampers etc. | Zener diode is mostly used in voltage regulator. |
Definition
Diode
A diode is formed by joining two layers of the semiconductor material, i.e. P-type layer and an N-type layer. The junction formed by joining these layers are called PN Junction. The P-type layer can also be understood as a positive layer because the majority charge carriers in a P-type layer are holes. Similarly, the N-type layer can also be considered as a Negative type layer because it consists of electrons as majority carriers.

When the diode is forward biased, it does not start conduction instantaneously, but after a particular forward voltage, it starts conduction. This forward voltage is called the knee voltage of the diode. The value of knee voltage depends on the semiconductor material, for germanium it is 0.3V, and for silicon, it is 0.7V.
When the diode is reversed biased, the depletion region becomes broader. On the contrary, the thickness of depletion region decreases with increase in forward bias voltage. Therefore, in a reversed biased condition the depletion region does not let the current to flow across it.
But the minority carriers can flow in reversed biased mode, constituting a small current in the diode. This is temperature dependent if the reverse voltage exceeds beyond a particular value the temperature increases and the minority carriers increases exponentially which can rupture the diode.
Therefore, it is recommended that normal PN junction diode should be used in only forward biased mode.
Zener Diode
A Zener diode is doped properly thus the breakdown voltage can be modified by controlling the depletion width of the diode. This is the advantage of using a zener diode in reversed biased condition.
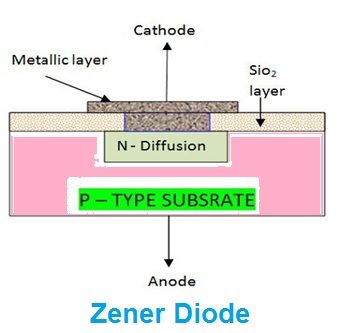
A Zener diode is constructed in the similar manner by which conventional diode is constructed the only difference is the doping characteristics. When the zener diode is forward biased, it conducts in the similar fashion by which a normal diode conducts. When it is reversed biased, it conducts, and this makes the zener diode bidirectional semiconductor device.
The zener diode can be understood by an equivalent circuit consisting of the voltage source and a resistor. The zener diode performs the same function. The higher the doping the narrow will be depletion width and the lower will be zener voltage. Thus, we can modify the width of the zener diode by appropriate doping and thus, the breakdown voltage can be modified.
Thus, we can prevent the diode from breakdown by controlling the breakdown voltage. At the breakdown voltage, the diode does not burn out suddenly because the external resistance protects the current from flowing through the diode.
Key Differences Between Diode and Zener Diode
- The direction of the current that the device allows creates a major difference between diode and zener diode. The diode conducts uni–directionally while the zener diode conducts bi–directionally in forward biased as well as in reverse biased.
- The doping characteristics of diode and zener diode are also different from each other. The zener diode is sharply doped while the conventional diode is moderately doped.
- The breakdown voltage in case of zener diode is sharp. But in normal PN junction diodes, the breakdown voltage is comparatively high
- A conventional diode cannot operate in reversed biased mode while the Zener diode can operate in reversed biased mode too.
- The Zener diode is generally used as a voltage regulator while the conventional diodes are used in the rectifier, clipper, clamper etc.
Conclusion
Diode and Zener diode, both are two terminal semiconductor device, but the crucial point which differentiates both is the ability to operate in reversed biased mode. Zener diodes are designed in a way so that they can operate in a reversed biased mode without getting damaged. On the contrary, a normal PN junction cannot be used for this purpose.
Danish says
very useful information thanks
Krati P says
Thanks for the appreciation !!
Ankit yadav says
i was reallly confused but this article cleared all by doubts,
Thank you!