A thyristor is a semiconductor device which possesses high ratings of voltage and current and also possesses the ability to handle large power. On the contrary, the transistor cannot handle large power equivalent to that handled by a thyristor. Moreover, the current and voltage rating of transistors is also quite low. Thus, power handling capacity differentiates both these devices.
Although, thyristor and transistor both are the crucial devices for switching applications but still due to differences in their characteristics they have their own area of applications.
Another difference between thyristor and transistor which is evident in its constructional feature is that thyristor is formed by four layers of P-type and N-type material arranged in an alternative manner. On the other hand, a transistor is formed by sandwiching a layer of either P-type or N-type semiconductor material between the layers of N-type and P-type material respectively.
Now, you must have got the rough idea about the differences between thyristor and transistor. But differences do not end here; there are a lot of another difference between the above mentioned four layer and three-layer device. We will discuss all those with the help of comparison chart.
But before, I indulge into comparison chart, let’s have a quick look at the roadmap of this article.
Content: Thyristor Vs Transistor
Comparison Chart
| Parameters | Thyristor | Transistor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Thyristor is a four layer semiconductor device which is used for rectification and switching. | Transistor is a three layer semiconductor device which is used mainly for amplification and switching. |
| Power Handling Capacity | More as compared to transistor. | Less as compared to thyristors. |
| Current and Voltage Rating | High Current and Voltage rating. | Low Current and Voltage rating |
| Internal Losses | Less as compared to transistors. | More in comparison to thyristors. |
| Turn-On and Turn-Off time | Requires more time to Turn-On and Turn-Off. | Takes very less time to turn-On and Turn-Off. |
| Cost | It is costly. | It is cheap and thus economical to use several applications. |
| Weight | It is bulky. | It is light in weight. |
| Triggering Procedure | It need just a single pulse to switch it to conduction state. | It needs current continuously to keep it in a conduction state. |
| High Frequency application | Not suitable. | Suitable |
| High Power Application | Suitable for high power application. | Not suitable for high power application. |
Definition
Transistor
A transistor is the semiconductor device consists of three terminals that are the emitter, base and collector. It can be used as an amplifier or switch depending upon the biasing of the transistor junction. The emitter and base terminal constitute emitter-base junction while collector and base terminal constitute collector-base junction.
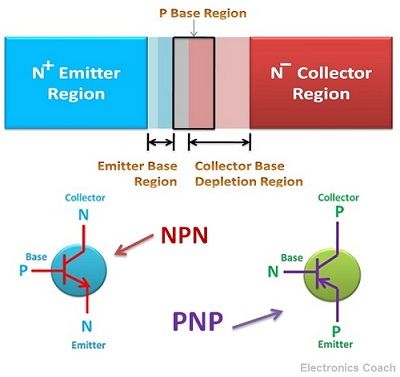
The emitter terminal is heavily doped and thus consists of a large number of charge carriers. These carriers flow towards the collector via base region and due to this current flows in the transistor. Transistor operates in three regions active region, saturation region and cut off region.
The active region characteristics of transistors are used for amplification of the weak signal while the saturation and cut off region characteristics of transistors are utilized in switching applications.
Thyristor
A thyristor is formed by four layers of semiconductor material. It consists of three terminals cathode, anode and gate terminal. The gate terminal of the thyristor is used as controlling terminal. The thyristor is switched to ON state by providing initial current to the transistor then it will remain in ON state.
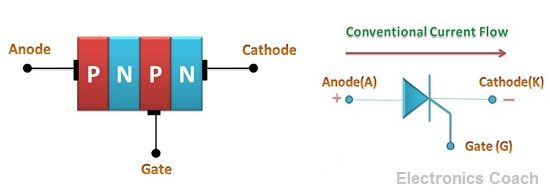
It is like two transistor PNP and NPN connected together through base-collector terminal. The collector of PNP is connected to the base of NPN, and thus NPN transistor will switch to ON state, and the collector of the NPN is connected to the base of PNP transistor. In this way, both the transistor will remain ON by just initial triggering supplied to PNP transistor.
Key Differences between Thyristor and Transistor
- High Voltage and Current Ratings: The crucial property which creates a major difference between thyristor and transistor is voltage and current ratings. The voltage and current rating of the thyristor is high due to its fabrication and design architecture while the voltage and current rating of the transistor is low in comparison to that of the thyristor.
- Power Handling Capacity: The power handling capacity of thyristor and transistor differ from each other. Thyristors possess high power handling capacity than transistors. The power ratings of thyristors are always in KW (Kilowatt) while that of the transistor, it is always in W (Watt).
- Designing: The thyristor and transistor have the different designing procedure. The thyristor is formed by four layers of semiconductor material in which P-type material and the N-type material is connected in an alternative manner while the transistor is formed by joining three layers of semiconductors.
- Terminal: Thyristor and transistor both possess three terminal, but the three terminals of transistors are the emitter, base and collector while the three terminals of thyristors are cathode, anode and gate terminal. A thyristor consists of controlling terminal, i.e. gate terminal while transistors do not require any controlling terminal.
- Internal Losses: Thyristors possess less internal loss in comparison to that of the transistor. The internal losses in a device reduce its efficiency. Thus, thyristors are considered far more efficient that transistors in case of high power applications.
- Size of the circuit: The size of thyristor and transistor circuit are also different from each other. The thyristor circuit is bulky than a transistor circuit. Thus, if you want a small circuit for high-frequency application, you need to use power transistors because power transistors are small in size.
- Cost of the circuit: The power transistors are small and cheap. Thus the circuits which use power transistor will be less costly than the circuit using thyristor.
- The requirement of Commutation Circuit: The commutation circuit is not required in case of the transistor while it is required in case of the thyristor which makes the thyristor circuit bulky.
- Turn-ON and Turn-OFF time: The transistor can be switched off immediately, but a thyristor cannot be switched off instantaneously. Thus, thyristors possess high turn-OFF time which is not suitable for high-frequency applications. Moreover, the transistor can switch ON faster in comparison to the thyristor. Therefore, the transistors are preferred over thyristors for high-frequency switching.
- High Power Application: The thyristors due to its high power handling capacity is considered best for high power applications. On the contrary, a transistor is used for low power applications.
- Triggering: The triggering required for thyristor is a single pulse and after supplying that it remains in the conduction state. On the contrary, transistors require the supply of current continuously to keep it in the conduction state.
Conclusion
Thyristor and Transistor, both are switching devices but thyristor is not suitable for the high-frequency application, and the transistor is not suitable for high power application. In high-frequency application, we should use transistor because of its small Turn-ON and Turn-OFF time. But in high power application thyristor should be used because of its high current carrying capability.
What if you will use thyristor for high-frequency application switch? It will result in poor efficiency of the resulting circuit. Therefore, we can utilize the devices in an appropriate application only when we are acquainted with the differences between them.
atom faraday says
nice article
Krati P says
Thanks for the appreciation !!!
Vipul kumar jangir says
Really this article is just like a boon for me.
Every topic is comprehensive within 5 minutes by me.
Thanks a lot for making this article.