Definition: Thyristor is a semiconductor device which comprises of four layers made up of P-type and N-type material arranges in the alternate fashion. The word Thyristor is formed from two words thyratron and transistor. Besides, the characteristics possessed by a thyristor is the combination of the properties of thyratron and transistor.
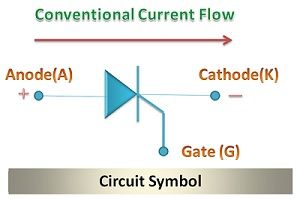
The thyratron has the property of rectification and the transistor has the property of switching. The thyristors are turned on using the control signal transferred by the transistor. Unlike the diodes, the thyristors have three terminals Anode, Cathode and Gate terminal.
The circuit symbol by which thyristors are identified in an electronic circuit is shown in the diagram below.
Construction of Thyristors
Thyristors can be understood with the help of two transistor analogy. The collector of one transistor is connected to the base of the second transistor while the collector of the second transistor is connected to the base of the first transistor.
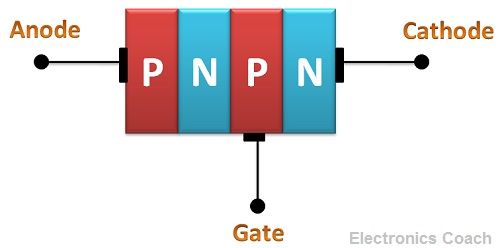
Thus, total four layers of semiconductor material are connected to each other and total three junctions are formed. In thyristors, there are three terminals that are anode, cathode and gate. Gate terminal provides the controlling voltage.
Working of Thyristor
The collector current of one transistor acts as the base current of another transistor. Thus, the collector current of one transistor will trigger another one. Without the collector current in either of the transistor, the thyristor cannot be triggered.
Now, suppose one PNP transistor is connected to the NPN transistor, then the P-terminal of the PNP transistor will be connected to one of the terminals of the battery. This will make the junction forward biased and current will start flowing in the transistor.
Due to this the collector current from PNP transistor will enter the base terminal of NPN transistor and thus the NPN transistor will also start conducting. In this way thyristor conducts.
The gate terminal when turned ON the thyristor performs rectification action but when it is turned OFF the rectification ceases. Thus, the thyristors can act as a rectifier and a switch but cannot act as an amplifier because it cannot amplify the signal.
Types of Thyristor
There are various semiconductor devices which can be classified under the thyristor family. Some of the most used devices are SCR, DIAC, TRIAC, GATT etc. We will discuss each of the devices in detail in our upcoming articles.
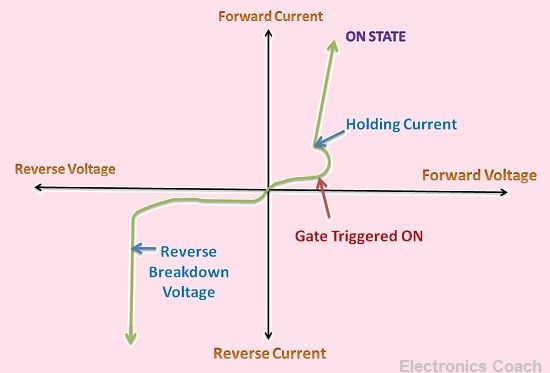
Characteristics of Thyristors
The characteristics curve of Thyristors is shown in the diagram below. With the help of characteristics curve, we can understand its working in forward biased mode and reversed biased mode in a detailed manner.
Advantages of Thyristors
- Better Efficiency: Thyristors possess better efficiency than transistors, thus it is used in various application of electronics.
- Low cost of Fabrication: The cost of fabrication of thyristors is low and thus it is economical to use in various electronics circuits for switching operation.
- Ability to be controlled: This is the robust characteristics of the thyristor as because of the gate terminal the thyristor can be controlled.
- High Reliability: The thyristor is the highly reliable device, and thus is used as a significant part in HVDC transmission.
- High Voltage and Current Ratings: The thyristor consists of four layers of semiconductor and thus the voltage and current ratings are higher in comparison to the transistor.
- Large Power Handling Capacity: The power handling capacity of the thyristor is much greater than the other semiconductor device.
- Good Trigger Sensitivity: The gate control terminal of thyristor provides the efficient controlling signal, thus it possesses good trigger sensitivity.
Applications of Thyristors
- Rectification Purpose: The thyristors are used for rectification of AC signal. Thus, when the controlled signal is given to rectifier it converts AC into DC.
- Relay Control: Thyristors are used in relay control.
- Phase Control: The phase controller used thyristors for providing phase correction in the circuit.
- HVDC transmission: They are also used in high voltage DC transmission.
- Control of temperature, level and Position: Due to its robust controlling, it can be used for controlling the temperature, level, position and illumination.
- DC and AC Motors: Thyristors are used in AC and DC motors as the speed controller.
- Transmission Lines: To improve the power factor in transmission lines, thyristors can be used.
- Cycloconverter: Thyristors play a crucial role in cycloconverters for converting AC of one frequency into AC of some other frequency.
Thyristors are the crucial power semiconductor devices. Due to its ability of rectification and switching it is used in various electronic circuits. Moreover, its four-layer architecture makes it more robust and efficient to use.
Leave a Reply