Definition: Hall Effect Sensor is the solid state device which switches to active state when it is introduced in magnetic field. The output voltage of hall effect sensor is dependent on magnetic field around it. When the magnetic field across the semiconductor slab changes the magnetic flux density also changes due to which the output voltage of hall effect sensor varies.
Principle of Hall Effect Sensor
The hall effect sensor works on the principle of hall effect.
According to hall effect when a semiconductor slab is placed in magnetic field provided that magnetic field lines are perpendicular to the axis of semiconductor specimen and current is allowed to pass along the axis of semiconductor specimen then the charges carriers of the semiconductor device experiences magnetic force.
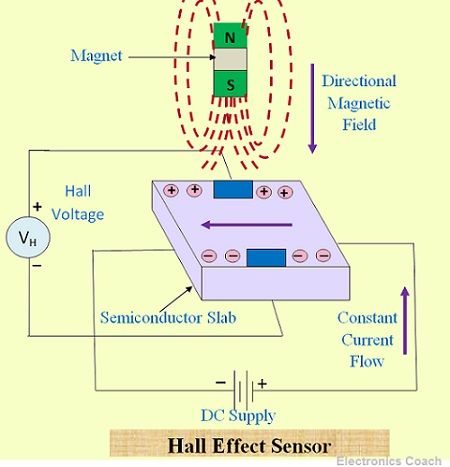
Due to this magnetic force they are pushed sidewards i.e towards the edges of the slab. As a consequence of this the electric field is created due to accumulation of charge carriers across the edges. Thus, the output voltage varies with the variation in the magnetic field. Hall effect is based on the Lorentz principle.
Hall Effect sensors uses this phenomenon of Hall effect for sensing fundamental quantities such as position, velocity, polarity etc. The two crucial term associated with magnetic field are magnetic flux density and polarity (North Pole and South Pole). The hall effect sensors uses these terms for sensing.
The output voltage generated by the sensor is directly dependent on magnetic flux density. Thus, if magnetic field across the sensor changes the output from hall effect also changes. In this way it provides sensing operation.
Hall Effect Sensor and Magnetic Sensor
You must be thinking that a magnetic sensor also does a same thing. So can we relate Hall Effect Sensor with magnetic sensor? Yes, Hall Effect sensor is a type of magnetic sensor only. Magnetic sensors also detect position, velocity with the help of variation in magnetic flux density.
Circuit Diagram of Hall Effect Switch using Hall Effect Sensor
The output voltage produced by Hall Effect Sensor is very small. Even in high magnitude of magnetic field the output voltage produced is low. Thus, DC amplifiers are used for the amplification of output voltage. Besides, regulators and switching circuits are also used in order to obtain regulated voltage.
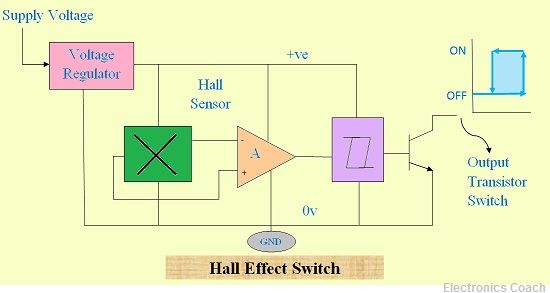
The Hall Effect sensor can provide linear output as well as non linear output i.e. digital output. The Hall voltage varies linearly with the magnetic field intensity H in case of linear output.

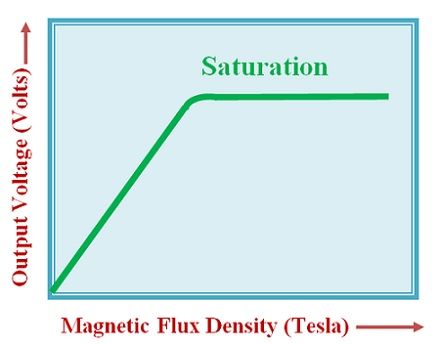
The variation of output voltage with respect to magnetic flux density is shown in the diagram below.
Linear Output and Digital Output Hall Effect Sensor
We have discussed above that linear analog sensors generate output voltage which varies with variation in magnetic flux density of the applied magnetic field. After a particular time the value of output voltage becomes constant with the value of magnetic flux density. Thus, a stage of saturation is reached.
At this stage of saturation the output voltage will not increase further with the increase in magnetic flux density. It becomes saturated. The output voltage will be low if the intensity of magnetic field is low and the output voltage will be high if the intensity of magnetic field is high.
In case of Digital output Hall Sensor the output will be comprised of two stages only i.e. ON and OFF. In digital output Hall effect Sensors, a Schmit – trigger is used in co-ordination with OP-AMP (i.e. Operational amplifier) which forms in built hysteresis. As a consequence of which there is no oscillations in output voltage.
Digital Output Hall Effect Sensors are of two types i.e Bipolar and Uni-polar. Bipolar uses positive polarity magnetic field i.e south pole for activation of sensor and negative pole i.e. north pole for deactivation of sensor. On the contrary Uni-polar digital output hall effect sensor uses only positive pole i.e South pole for activation as well as deactivation of the Hall effect sensor.
Types of Detection by Hall Effect Sensor
- Head on detection configuration: In head–on detection the magnet moves forward towards the face of the Hall sensor. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the active area of Hall Element. This configuration of Hall Effect sensors generate the output voltage according to the strength of the magnetic field.
It allow us to determine the magnetic field intensity and magnetic flux density at a particular distance from the Hall Effect Sensor. 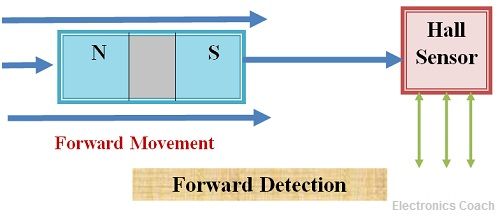
- Sideways detection configuration: In the sideway detection of hall effect sensor, it moves sideward and it is kept near the active area of Hall effect sensor.
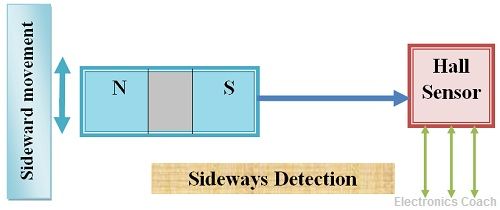
- Positional Detection: The positional detection configuration of Hall effect is shown in the below diagrams. Here LED is used, we can also use transistor if the output generated by Hall effect sensor is to be applied for switching process of higher load.
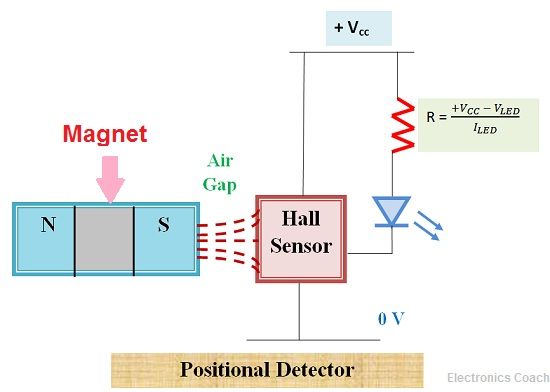
Applications of Hall Effect Sensor
Hall Effect Sensors are used for sensing positions thus, they are often used as proximity sensors. They can also be used in the application in which we use optical and light sensors. Hall effect sensors are better to use because optical and light sensors are likely to get affected by environmental conditions while Hall Effect sensors can also work efficiently in the dust, air or other external environmental factors.
Ken Willis says
Great informational site. Thank you.