Definition: Transducer is a device that holds the ability to change a form of energy into another. Transducers are of various types such as electrical transducers, mechanical transducer, thermal, optical, acoustic etc.
An electrical transducer is the cornerstone of electronics instrumentation because it converts the physical quantities which are non-electrical in nature into electrical quantities. This is because in instrumentation we need to measure the quantities and electrical quantities can be measured easily.
Significance of Transducer
Transducers are often termed as the heart of electronics instrumentation.
 This is because in instrumentation we need to measure the quantities whether it is electrical, non-electrical physical etc. But it is not so easy to measure the magnitude of physical quantity. Let’s take an example of mercury thermometer if you want to measure the body temperature, is it possible to measure it directly??
This is because in instrumentation we need to measure the quantities whether it is electrical, non-electrical physical etc. But it is not so easy to measure the magnitude of physical quantity. Let’s take an example of mercury thermometer if you want to measure the body temperature, is it possible to measure it directly??
The answer will be no. This is because we need a quantity which shows the change in the magnitude of the physical quantity. In mercury thermometer; the height of the mercury varies with the variation in the temperature. Thus, if the temperature of the measuring body increases then the height of the mercury in the thermometer also increases.
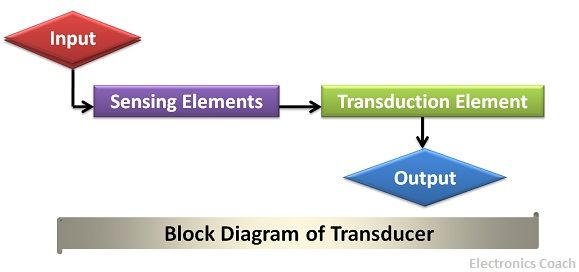
Therefore, in instrumentation when we need to measure a physical quantity we need a transducer.
Requirements for a Transducer
There are some requirements for transducers to work efficiently; these are as follows:
- Linearity: The output signal generated by the transducers and input signal given to the transducers should maintain linearity with each other.
- Ruggedness: There may be certain condition in which the device may burn due to overload. Hence, transducers should possess high electrical and mechanical strength so that it may not get deteriorated due to overload.
- Repeatability: The repeatability of the device means its ability to generate the same output when same input is given to it under same external condition. Thus, transducers should possess the feature of repeatability.
- High Signal to Noise Ratio: The signal to noise ratio describe the quality of the signal, higher the signal to noise ratio, higher will be the quality of the signal. Thus, transducers should possess high signal to noise ratio in order to provide a high-quality signal.
- Reliability: The reliability of the device is its ability to generate the output which is free from error so that it can be effectively used for a particular application. Transducers must possess high reliability as it forms the backbone of electrical instrumentation.
- No hysteresis: There should be no losses due to hysteresis in the output signal generated by the transducers.
Classification of Transducer
The Transducers can be classified into various categories according to the elements they used and according to their operational mechanism.
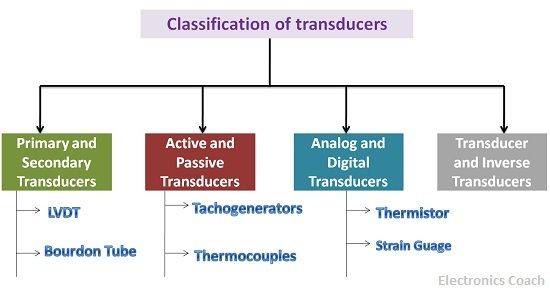
According to the sensing manner of the transducer, it can be classified into two categories, and they are as follows:-
Primary and Secondary Transducers
The primary transducer is the one which directly senses the input signal which is to be measured. While the secondary transducer is the one which involves the sensing element to sense the input signal. After this, it passes that signal to the transducer for the conversion process.
For example: Consider a pressure measurement transducer, it consists of a bourdon tube and LVDT. The pressure signal is given as input to the bourdon tube, and this bourdon tube converts the pressure into displacement.
This displacement is given as input to the LVDT which converts the displacement into voltage. Thus, in this process, the bourdon tube is considered as a primary transducer while the LVDT is considered as a secondary transducer.
On the basis of the process of energy conversion, the transducers can be classified again into two categories.
Active and Passive Transducers
The active transducer is the one which draws some part of the energy from the system which is under the measurement process of the transducer. On the contrary, the passive transducer is the one which uses the passive elements of the conversion process. The passive transducer uses resistance, capacitance, and inductance. Therefore, passive transducers require an external source of energy to perform their operations.
On the basis of the nature of the output signal generated by the transducers, it can be classified into two types.
Analog transducers and Digital transducers
Analog transducer generates the output signal in the form of analogue signal. While Digital transducers are the one which generates the output in the form of digital signal.
The output of the signal either electrical or non-electrical decides the two sub-categories of the transducer that are transducers and inverse transducers.
Transducer and Inverse Transducer
The transducers convert the non-electrical quantity into an electrical quantity. While the inverse transducers convert the electrical quantity into non-electrical quantity.
Factors essential for deciding suitability of the transducers
There are certain factors which should be kept in mind during the selection of the transducers. These points are
- Electrical Characteristics: The electrical characteristics of the transducers include frequency response; time response of the transducers, input and the output impedance of the transducers. All these electrical characteristics of the transducers should be in accordance with the electrical characteristics of the device to be measured.
- Errors: The errors obtained during conversion should be controllable and should not influence the application in which it is being used.
- Range: The range of the transducers should be high as high range devices are desirable to measure any quantity in instrumentation.
- Sensitivity: The sensitivity is the ability to produce the output even in the presence of the small input signal. Thus, highly sensitive transducers are desirable in every application of electronic instrumentation.
Thus, transducers are the crucial devices in electronics instrumentation. With the help of it we can convert one form of energy into the form which can b easily measured through electronics devices.
Leave a Reply