The working principle of both Photodiode and Phototransistor is same however, various factors differentiate the two. The major difference between photodiode and phototransistor is their current gain. In other words, we can say, a phototransistor produces more current as compared to the photodiode when exposed to the same amount of light energy.
Another crucial difference between photodiode and phototransistor is that a normal PN junction diode is employed in a photodiode that produces an electric current when exposed to light. On the contrary, light energy is converted into electric current in phototransistor, that is basically a bipolar junction transistor.
Now, before discussing some other important differences between photodiode and phototransistor have a look at the contents to be discussed in this article.
Content: Photodiode vs Phototransistor
Comparison chart
| Parameter | Photodiode | Phototransistor |
|---|---|---|
| Consist of | Semiconductor diode | Junction transistor |
| Symbol | 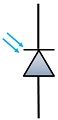 | 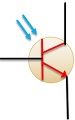 |
| Operational speed | High | Low |
| Sensitivity | Low | High |
| Noise interference | Less immune | More immune |
| Output response | Fast | Slow |
| High frequency response | Provides better results. | Provides poor results. |
Definition of Photodiode
It is a semiconductor device having 2 terminals that produce current when exposed to light. Photodiode works on the principle of photoelectric effect thus convert light energy that falls on the surface of the material into electrical energy. As the intensity of incident radiation increases, the current through the device also increases.
A photodiode is basically designed for reverse biased operation. Let us have a look at the biasing arrangement of the photodiode.
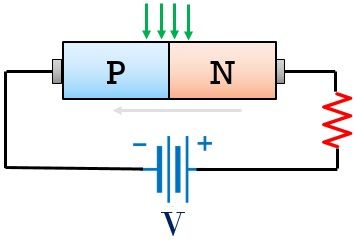
We are already aware of the fact that reverse saturation current flows through the device in reverse biased condition of a diode. Thus, in the case of photodiode also, a reverse current is the result of the thermally generated electron-hole pair by the action of light.
As the intensity of the incident radiation increases, temperature increases, resultantly current increases. The light energy that falls on the junction is responsible for charge carrier generation hence for current.
Sometimes, current is noticed in the device without any exposure to light rays, this is known as dark current.
Definition of Phototransistor
It is a device almost similar to normal junction transistor. However, the only variation that exists is a large area of the base-collector region. In phototransistor, base current is not supplied as input, instead of it, light energy is provided that is used to trigger the transistor. This supplied light energy generates an electric current through the device due to the photoelectric effect.
It can be a two or three terminal device depending on the existence of the base terminal.
The figure below shows the general construction of a phototransistor.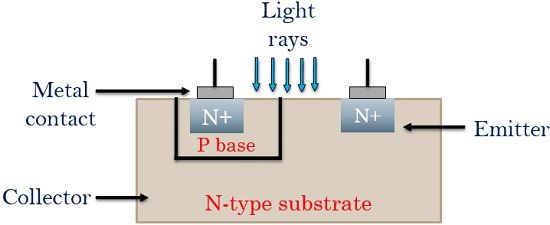
The light rays are exposed to a photosensitive base region and the output is taken through the collector terminal of the transistor.
When light energy falls on the device, electron-hole pairs are generated. These electrons after overcoming the barrier potential, move from the emitter to collector. This movement generates an electric current in the device. The intensity of emitted light determines the magnitude of the electric current.
It is noteworthy here that, the output current of a phototransistor lies in milliamps however switching occurs in microseconds.
Key Differences Between Photodiode and Phototransistor
- A photodiode consists of a semiconductor diode, that generates current when exposed to light. On the other side, phototransistor consists of a junction transistor that when exposed to light energy generates current.
- A phototransistor is more efficient as compared to a photodiode.
- When we talk about noise immunity then it is noteworthy that a photodiode is not immune to interference caused by noise. However, phototransistors are immune to such interference. This sometimes proves as a disadvantage of the photodiode.
- At a high-frequency range, phototransistor does not effectively convert light energy into electrical energy. As against this drawback is not dominant in the photodiode and thus provides good response as compared to the phototransistor.
- A phototransistor as light sensor is a less expensive device in comparison to any other light sensitive device. Thus is widely used.
- Photodiodes have the ability to generate an output at a much faster rate when light falls on its surface as compared to the phototransistor.
Applications
Photodiode
- Photodiodes are widely used in optical fibre communication.
- For high-speed operation, these are widely used in digital and logic circuits.
- Photodiode finds its applications in alarm and counter circuits.
- High computing devices make use of photodiodes.
Phototransistor
- Due to the high efficiency of a phototransistor, it is widely used as the light detectors and thus can be employed in printers, remotes etc.
- Relays and punch card also makes use of phototransistor in their circuitry.
- As the action of light controls the working of such devices thus these are widely used in counting systems as in that case power to be supplied will not be an issue.
- In a communication system, encoder circuitry widely makes use of phototransistor.
Conclusion
A photodiode performs high-speed operations very efficiently. However, due to the amplifying action of transistors, phototransistors are more sensitive and thus provides large current at the output when compared with a photodiode. At the same time, a photodiode provides the response at a rapid rate as compared to a phototransistor.
Leave a Reply