The major difference between diode and photodiode is that a diode is a semiconductor device which conducts when it is forward biased while the photodiode conducts in reversed biased mode. The conduction in the diode is possible due to the voltage applied externally, while the conduction in the photodiode is possible only when it is illuminated by the light source.
Another important difference between diode and photodiode is that a diode cannot work when it is reversed biased, i.e. no current flows through the diode when the diode is reversed biased. On the contrary, a photodiode can work only in reversed biased. If you are thinking that the photodiode can be made to conduct by incident light on it, during forward biased mode, then you are wrong. It will conduct only in reverse biased mode.
There exist some other crucial differences between diode and photodiode, we will discuss it in the comparison chart. Before starting with the comparison chart let’s have a look at the roadmap of this article.
Content: Diode and Photodiode
| Parameters | Diode | Photodiode |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A diode is two terminal device which conducts when it is forwards biased. | A photodiode is a two terminal device which conducts when it is reversed biased. |
| Circuit symbol |  |  |
| Main Function | Diode is mainly used as a switch. | Photodiode is used for conversion of light energy into electrical energy. |
| Material Used | Germanium or silicon, any of these two can be used. | Silicon is used for manufacturing photodiode. An anti-reflective layer of Silver Nitride is used for coating. |
| Applications | Used in clippers, clampers, rectifiers etc. | Used in optoelectronic device, camera, optocouplers etc. |
Definition
Diode
A diode is a two terminal semiconductor junction formed by combining a P-type semiconductor with an N-type semiconductor. The resultant of the combination forms a junction which is depleted of mobile charge carriers, i.e. it consists of immobile charge carriers only.
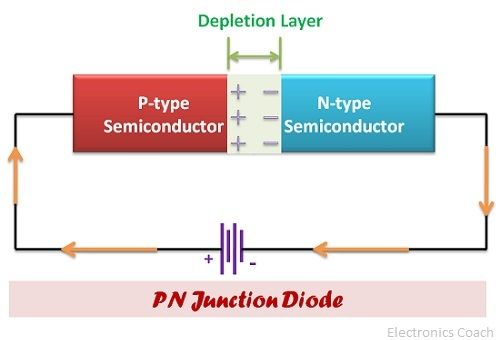
These immobile charge carriers are responsible for the existence of barrier potential between either of the semiconductor specimen. This barrier potential is nothing but a strong magnetic field created against the applied external battery potential.
When the diode is unbiased, i.e. no biasing is applied, neither forward biased nor reversed biased, then the majority charge carriers, i.e. holes in P-type semiconductor and electrons in N-type semiconductors move across the junction due to the concentration gradient of charge carriers. The concentration gradient of charge carrier means the concentration of charge carriers in both region.
Charge carriers move from higher concentration to lower concentration, the concentration of holes is more in P-side than in N-side. Therefore holes move from P-type to N-type. On the contrary, the electrons which are the majority carriers in N-type region move from N-type to P-type.
At a particular time when no majority carriers are left to cross the junction, then the conduction will stop. And the charge carriers which had been moved initially will recombine at the junction. Now, if the diode is to be switched back to the conduction state, then it must be supplied with external voltage.
But one more condition implies here, the conduction in the diode will not start until the battery potential exceeds the barrier potential or knee voltage.
Photodiode
A photodiode is a semiconductor device which can provide conduction if it is illuminated by the light source. The photodiode cannot be operated in forward biased mode; it will get destroyed if it is operated in forward biased mode.
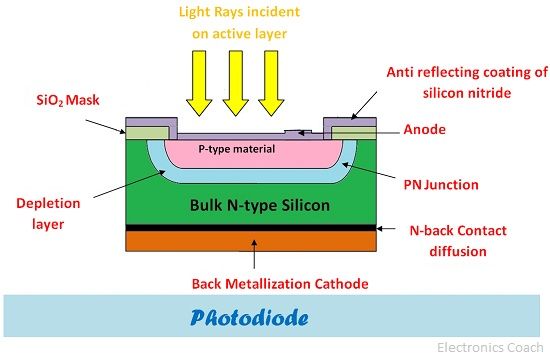
The photodiode is provided with the coating of an anti-reflective layer such as silver nitride. The function of anti-reflective layer is to prevent the light incident on photodiode from getting reflected. The presence of such layer increases the efficiency of the photodiode by trapping a significant portion of the incident light.
The incident light comprises of photons which impart their energy to electrons when collide with them. Thus, the semiconductor material is illuminated by light, the photons strike atoms of semiconductor and as a consequence of which the electrons get dislodge from the semiconductor atom. The movement of mobile electron constitutes current in the photodiode.
The small amount of current which shows its presence even in the absence of incident light is termed as dark current. The current in the photodiode can be ceased only when the positive voltage is applied to the diode.
When the terminals of the photodiode are connected with the external circuit is acts as a photovoltaic device rather than a photoconductive device. This is because reverse biasing of the device causes the minority charge carriers to get swept across the junction.
Therefore, when the photodiode is operated without reverse biased, electrons will flow from N-terminal to P-terminal through the external circuitry. In this condition, the photodiode acts a photovoltaic device. When the device is operated with the reversed biased mode, then it is said to be photoconductive.
Key Differences between Diode and Photodiode
- The key difference between the diode and photodiode is that diode is the semiconductor device which conducts when forward biased applied to it exceeds the barrier potential while the photodiode is the devices which conduct when the light is incident on it.
- The biasing mode of the diode and photodiode is also different and contradict each other; the diode operates in forward biased mode only while the photodiode operated in reversed biased mode only.
- The materials used for manufacturing diode and photodiode are also different. The diode is made up of germanium or silicon while the photodiodes are made up of only silicon.
- The anti-reflective layer is present in photodiodes while diodes do not need it.
- The reverse current which flows in photodiode varies directly with the intensity of illumination while the forward current in diodes varies directly with the forward voltage.
Conclusion
The diode is a semiconductor device which is used in various electronic devices such as clipper, clampers, and rectifier. A diode is mainly used as a switch. Photodiodes find application in optoelectronics such as optical communication equipment, camera, optocoupler etc. The diode does not convert one form of energy into another. While photodiode converts one form of energy into another, i.e., it converts light energy into electrical energy.
Sometimes we often get confused between these terms as they sound same and both are two terminal devices. The word photo with the diode changes its meaning. The key term to remember the working is the keyword photo. Photo means lights and diode is a two-terminal device.
Leave a Reply