Intelligent Electronic Devices abbreviated as IED is defined as devices that have single or multiple microprocessors integrated within it. Its main purpose involves the transmission or reception of data or control signals to or from an external device. The external device in consideration with the whole system can be transducers, relays, control units, etc.
IEDs are regarded as a key part of industrial control systems used for the purpose of advanced power automation. Thus, is useful in Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition systems (SCADA system), Distributed Control Systems (DCS) as a crucial component.
Introduction
In the previous content on Introduction to SCADA systems, we have discussed that it is a microprocessor-based device that establishes interaction with the external peripheral devices to communicate with the outside world regarding the transfer of data and signals.
In most simple terms, devices like microprocessor-based voltage regulators, protection relays, circuit breaker controllers, etc. that can serially communicate with other devices in the network are known as Intelligent Electronic Devices (IED). It is regarded as an important innovation to the power systems as it provides the apparent change in power monitoring as well as protection and control. Thus, it finds extensive use in power system automation for the purpose of monitoring, protecting, communicating, controlling, metering, etc.
Today’s generation IEDs offer various appreciable factors as discussed above like protection and metering with excellent computing power. Also, it can record a sequence of events that is useful in post-event analysis and fault recognition, and waveform recording along with measuring the power quality.
Thus, due to these various offered functions, it acts as a crucial component in the automation of substations and efficient monitoring in power delivery systems. More simply, power system automation seems impossible without IEDs.
Block Diagram of IED
The architectural design of intelligent electronic devices ensures certain excellent features including, flexibility, adaptability, multipurpose and modular nature along with robustness in communication capabilities.
The figure below represents the organizational block diagram representation of IED: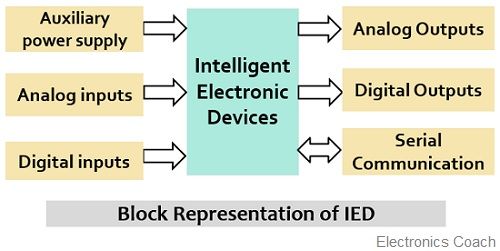 Let us now understand the operation of each building block separately in sequence.
Let us now understand the operation of each building block separately in sequence.
Auxiliary Power Supply: An auxiliary power supply or source is basically an electric power supplied by a backup alternate source other than the primary main source. IEDs always need an auxiliary power supply, unlike older protection relays where an auxiliary power supply is of not much significance. So, the acceptable power supply used by IEDs is in the range between 15 to 150 volts in the case of DC. While 110 to 140 Volts when AC.
Analog Inputs: In relays, inputs are provided by the current transformer and potential transformers. However, IEDs may have sensor inputs.
Digital Inputs: Digital inputs provided to the IEDs may be some sort of commands or any status information. Some of these need potential free contacts while some understand with the consideration of logic 0 or logic 1 as negative voltage and positive voltage respectively.
Analog Outputs: Generally, transducers are used to get the output from the IEDs which is programmable type. The output can be of active or passive nature but a passive type output requires an external power supply.
Digital Outputs: In the case of digital outputs, the potential contacts can be normally open, normally closed, or solid-state contacts. Similar to digital inputs, digital outputs are also commands or status information, and the switching capability must be properly checked as the significant differences can be noticed.
It is to be noted that IEDs offer quick real-time data transferring and receiving ability by utilizing multiple ports. The different IEDs are designed to operate on analog input, analog output, digital input, and digital output. An IED supports the integration of various individual functions into a single unit. Like an IED has electromechanical relays, wiring, control switches, and many more within it.
Some auxiliary functions are also offered by IEDs which are as follows:
- Monitoring: It monitors self and external circuits along with checking the real-time synchronization of the events that are occurring.
- Data Accessing: IEDs can access the data present locally as well as the one which is present at distant substations.
- Testing and Analysis: It has certain software tools used for the purpose of testing, reporting, and fault analysis. Also, it offers the programmable logic controller functionality.
Hardware and Software Design
Till now it is clear to us that IED offers various appreciable features for which its architectural design must be equally important. This helps in achieving proper programming, commissioning, and maintenance in a convenient way.
So, the hardware of the IED must be designed in a way that it can adapt the changes done in the future. Also, to support the maintenance of IEDs, plug-in type cards are used. The use of these cards offers ease in removing the IED from the panel without any major disconnection of the wires.
While the software of IED must support ease in analyzing the performance and configuring the desired functions individually. It offers the selection of necessary functions and hiding the ones which are not needed. And each separate function must be individually defined by the set of logical inputs, outputs, settling time, and event reporting features.
IEDs in today’s generation is emerging with various advantageous factors like waveform capturing, disturbance analyzing, metering, and programmable logic capabilities thereby eliminating the use of additional PLC.
Communication Module
The communication module is of great significance and there exist different communication protocols that are used by the manufacturers.
In today’s world, the general requirement is the IEDs that offer open communication architecture and supportable with different protocols to facilitate multiport communication with flexibility. Along with open communication protocol support, it has a serial electrical port, remote access port, optical port. The open protocols support interoperability thus is most preferable.
The communication modules support various protocols. These modules offer a replacement in the field in case of a change in communication requirement. Due to multiport communication ability, an IED is able to communicate with substation and various other IEDs in the network simultaneously.
Leave a Reply