In the previous article, we have discussed the basics of the SCADA system. SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition system which is used for the purpose of controlling the processes that are geographically distributed.
Generally, the overall SCADA system performs under the control of centralized software and hardware combination. In this article, we will discuss the architectural design of SCADA systems.
Now a day most of the SCADA systems are based on a distributed approach but initially at the time of coming into existence central architectural approach was very common. Let us first discuss what was the concept of central architecture and further, we will discuss the present architecture of SCADA systems.
Centralized Architecture of SCADA System
We have discussed in the previous article that first-time SCADA systems came into existence in the year 1960s. And after 1960 till 1980, a large category of SCADA systems was based on centralized architecture irrespective of the type of executing process.
In the central architectural approach, a single powerful central computer was used. This central computer manages and performs the various functions of the SCADA systems like RTU polling, processing of data and information, archiving of data, as well as generating the report along with running application programs.
Due to this reason, in such architectures, the reliability of the centralized computer was the main concern. So, at that time for improvisation, with the main central computer known as a primary unit, a second computer similar to that of the main computer was used.
Although the second computer was redundant a proper connection is maintained between the two computers so that the redundant one is properly synchronized with the primary unit. The redundant computer is known as a backup unit. The main aim of using a redundant computer is to keep a backup of the functions performed by the main computer by timely transferring the updates. With this approach, the information gets secured inside the backup computer, so that when a primary unit fails then backup unit cam continue with the further operations.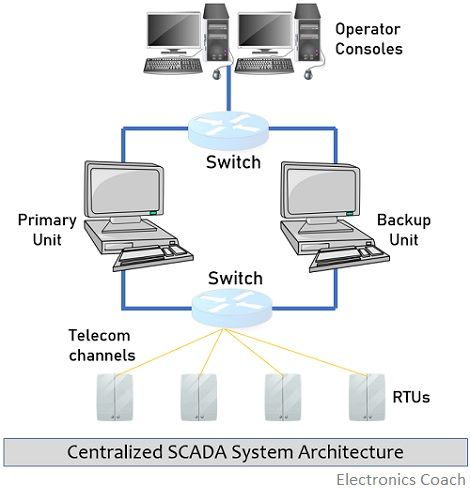
This prevents loss of data, application programs along with the loss of controlling capacity. However, due to some associated drawbacks, the successful use of redundant computer was quite challenging for SCADA system vendors.
Initially, DMA was used for quite high-speed copying of data and required resources from primary to the backup unit. However, with this approach, if there was any corruption in primary then it also gets transferred to the backup unit. Also, in the case of peripheral transferring, the complications further increase as in this case electromechanical transfer switches were needed.
Hence, due to the number of associated disadvantages, the idea of a backup unit was also suspended.
So, to deal with the disadvantages of centralized architecture SCADA systems, distributed architectures came into existence in the year 1980. The distributed architecture is majorly used by various vendors since then.
Distributed Architecture of SCADA system
In the distributed architecture, a network is formed with multiple computers, and each computer of the network is allotted a specific function and this was implemented using LAN connection.
In the initially proposed distributed architecture, the polling process of RTU was separated where a front-end dedicated computer was used for its placement. And this has removed the use of the backup unit. As in this case, the RTU polling provides data to the front-end computer which further transmits the updations to the other units of the LAN, and in this way proper synchronization is maintained.
So, in the distributed architectural approach the SCADA functions get spread to the additional computers within the network that performs the specific functions. This prevents the loss of overall system operation whenever a fault or malfunctioning occurs in any one of the computers within the network.
Further in 1990, using the 64-bit microprocessors and personal computers and with the use of a real-time operating system, SCADA systems were further improvised. These improvised systems were designed to handle the fault in a better way and also redesigns and rewrites the software that is designed to execute specific functions within the system present across multiple servers.
The figure below represents the distributed architecture of the system: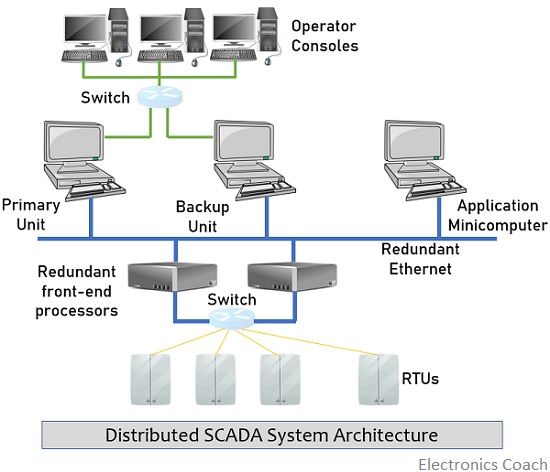
Let us now understand the generalized software architecture. The figure below represents a generalized information flow scheme within the SCADA system: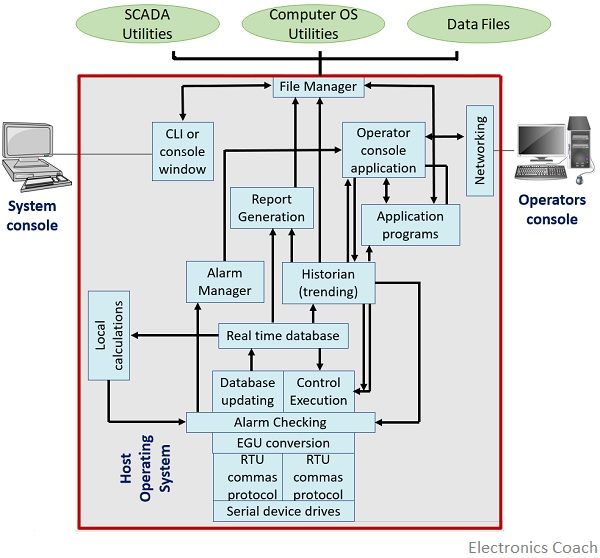
In SCADA systems, the technological upgradations in communication and computing advance the design of the system and so the performing characteristics. But this is completely associated with the hardware approach. The basic functions of the SCADA systems are as follows:
- Proper communication is maintained with the outstations present in the fields within the network so that the information of the proper ongoing process can be retrieved.
- After retrieving the data, constant updations on the database is done.
- By the use of an adequate interface, the information can be examined and displayed in real-time by the human operator.
- Also, in case of any required change to get highlighted, a proper mechanism allows a human operator to send the required control command.
Some additional, not necessary but meaningful functions must also be provided by the SCADA systems which are as follows:
- To facilitate previous as well as recent measurements calculation of new values according to the well-defined equations must be available.
- For the measurement and calculation purposes, user-defined logs and reports must be timely generated.
- A proper record on a long term basis must be maintained of the previously selected inputs.
- An adequate record of logging and alarm detection is to be made timely.
So, modern SCADA architectures necessarily include the features and functions given above. However, along with these sometimes based on industry-specific applications SCADA systems are customized with other unique requirements. Thus, the applications of the system are very much associated with the feature provided by the system.
Leave a Reply