Definition: Superheterodyne receiver works on the principle of heterodyning which simply means mixing. It is a type of receiver which mixes the received signal frequency with the frequency of the signal generated by a local oscillator.
The output of mixer provides a lower fixed frequency also known as intermediate frequency.
These receivers are called Superheterodyne receivers as the frequency of the signal generated by the local oscillator is more than the frequency of the received signal.
Working of Superheterodyne Receiver:
Superheterodyne receiver mainly comprised of the following components:
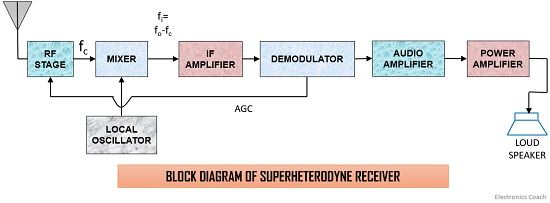
- Receiving antenna: The receiving antenna receives the signal which was sent by the transmitter. It sends the received signal for further processing.
- RF amplifier: The received signal is fed to the RF amplifier stage so as to amplify it, as the signal gets attenuated during long-distance transmission. It is tuned in such a way that it can choose the desired carrier frequency and amplify it.
- Local Oscillator: This circuit basically generates a signal with a fixed frequency and the output is then fed to the mixer. When we talk about AM broadcast system, the intermediate frequency is 455 KHz that simply means that local oscillator should select such a frequency which is 455 KHz above the incoming signal frequency.
- Mixer: A mixer simply mixes the carrier frequency with the frequency of the signal generated by the local oscillator.
Here, two different frequencies are to be mixed so as to have another frequency component of lower value. Now the thing that first comes to our mind is why the mixer produces a lower frequency value, which is the difference between the two frequencies. The summation of the carrier and local oscillator frequency at the output of the mixer will give rise to image frequency which is treated as a type of noise or distortion in the signal. This is the reason why the mixer generates a frequency difference at its output. This difference frequency is a constant value irrespective of the variations in the input, known as the intermediate frequency.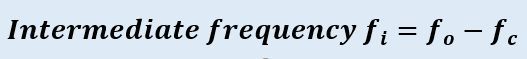 The constant frequency at its output is gained by capacitance tuning. In capacitance tuning, several capacitances are arranged together and operated by a controlling knob.It doesn’t matter what the incoming signal frequency is, the RF amplifier and local oscillator must be tuned to it.
The constant frequency at its output is gained by capacitance tuning. In capacitance tuning, several capacitances are arranged together and operated by a controlling knob.It doesn’t matter what the incoming signal frequency is, the RF amplifier and local oscillator must be tuned to it. - IF amplifier: This section basically amplifies the output of the mixer. IF amplifier provides sensitivity(gain) and selectivity (bandwidth requirement) to the receiver. As it consists of several transformers consisting of pairs of the tuned circuit.Here, the sensitivity and selectivity are uniform and does not show variations as in case of TRF receivers because IF amplifier’s characteristics are independent of that of the received signal frequency as it works on the intermediate frequency.
Due to this, the system design is quite easy so as to provide constant bandwidth along with high gain.This section has narrow bandwidth and due to its lower bandwidth, it rejects all other frequency so as to reduce the risk generated from interference.The lower bandwidth accepting nature supports Superheterodyne receivers to give much better performance than other types of receivers. - Demodulator: Demodulator is placed exactly after the IF amplifier so that the constant frequency signal is demodulated and the message signal can be extracted from it.
- Audio amplifier: The original signal is fed to the audio amplifier which does not hold distortion or noise so that it can amplify audio signal to a particular level.
- Power amplifier: Here, the signal is further amplified to a particular power level which can activate the loudspeaker. The amplified signal is finally fed to the loudspeaker circuit which converts the electrical form of the signal into an audio sound signal which can be heard by the listeners.
Receivers characteristics:
Sensitivity: In most simple words we can say it is the ability to amplify a weak or low signal. 150µV is the typical sensitivity value for small broadcast and 1µV or below is for high-quality communication.
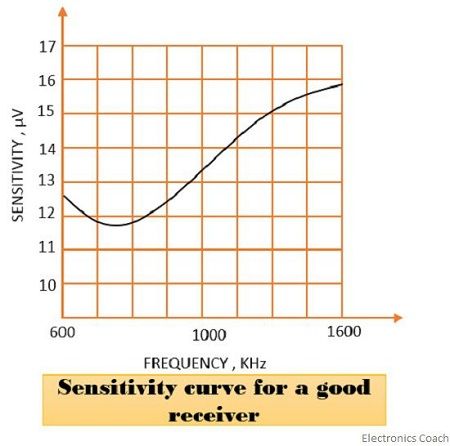
Following factors determines the sensitivity of Superheterodyne receiver:
- The gain of RF amplifier
- The gain of IF amplifier
- Noise factor of receiver
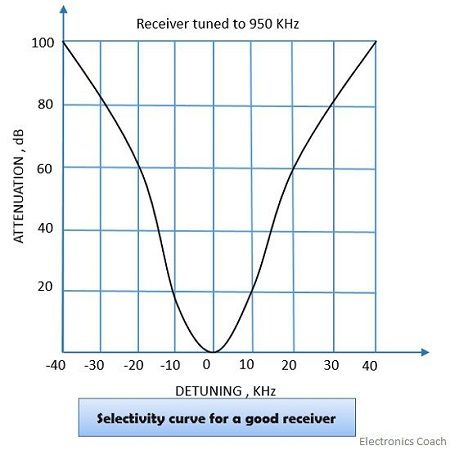
Selectivity: It is the ability of any system that decides whether the signal is desired or undesired. At high-frequency selectivity is poor, better selectivity is achieved at low frequency.
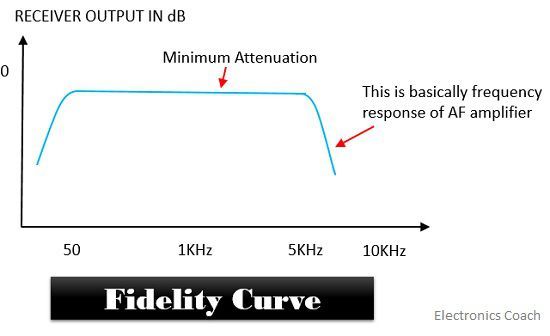
Fidelity: It is the system’s ability to produce an original signal without distortion. It is essential to produce a good quality signal. It ensures that the reproduced signal must be an exact copy of the original signal.
Advantages:
- It operates at low signal level.
- The mixer provides fixed frequency operations.
- Provides excellent selectivity and sensitivity.
Disadvantage:
- Overall system cost is increased as additional circuits are used.
Applications:
Superheterodyne receivers find its use in various places as in Television, Radio receiver, commercial radios
Prakash Mandal says
Whoever is behind this I don’t know you personally. I get to learn a lot from your website. As an electronics and communication engineering student, your notes are short simple and easy to understand. I want to thank you from the bottom of my heart.