Definition: Tuned amplifiers are used to for the amplification of a specific frequency signal or a narrowband frequency signal. Basically high frequency or radio frequency signals are amplified using tuned amplifiers. Tuning (i.e., selecting) of frequency is done by using a tuned or resonant circuit at the load.
Sometimes during amplification of the signal, it is necessary to select the desired frequency range and reject others. Thus tuned amplifiers are employed in radio receivers.
Need for Tuned amplifiers
It is already known that audio amplifiers can amplify high or radio frequency, then what is the need for a radio frequency amplifier?
An audio amplifier is unable to select a particular frequency signal. As it provides a mixture of frequency that lies in the range of 20 Hz to 20 KHz. Thus an audio amplifier is not used for radio frequency signal amplification.
Tuned circuit and resonant frequency in tuned amplifiers
As tuned circuits possess the property of resonance. Thus, it allows selection of a particular range of frequency. The resonant frequency of the tuned circuit will be the centre frequency of the selected frequency band.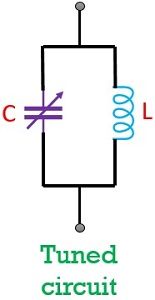
It is noteworthy here that tuned amplifiers provide high gain. This is so because employing a resonant circuit as load offers high impedance and gain of the transistor amplifier is a quantity dependent on load impedance.
Tuned amplifiers are specifically designed for narrow bandwidth frequency signal.
The resonance frequency of a tuned circuit is given as![]()
The frequency response curve for a tuned amplifier is similar to that of the resonance curve of a tuned circuit.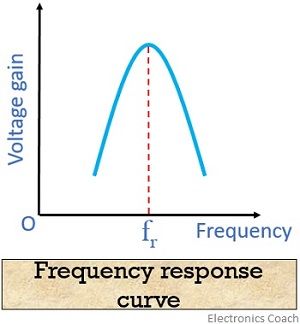
It is to be noted that the response of the tuned circuit is maximum in case of the resonant frequency. Thus, we can see the response curve is at its maximum in case of the resonant frequency. However, a sharp fall is noticed for the frequency other than the resonant frequency.
Let’s have a look at the basic circuit of a tuned amplifier: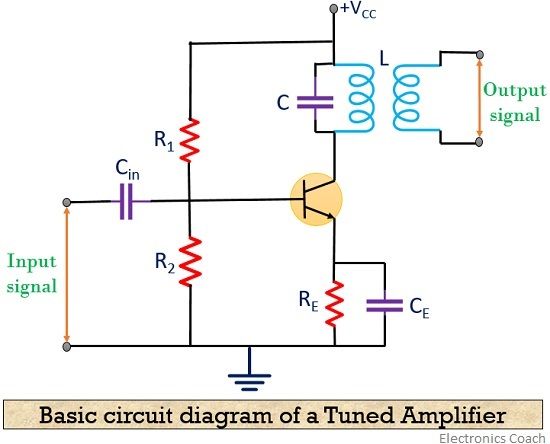
What are the resonance circuits?
The frequency at which inductive reactance becomes equal to capacitive reactance, the circuit behaves as purely resistive. The phenomenon is known as resonance and the particular frequency is known as resonant frequency.
Quality factor in Tuned Amplifiers
The quality factor is given as the ratio of coil impedance(reactance) of an inductor to its resistance. As an inductor along with inductance possesses a small amount of resistance. Thus, for a better Q factor, it is needed that the resistance must be low.
It basically measures the purity of an inductor and is a unitless quantity.
To sum up, basically, Q factor is the measure of energy storing efficiency of an inductor.
It is given by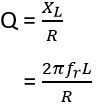
The resonance curve will show the sharper response for a higher value of Q. Thus, providing better selectivity.
Coil Losses in tuned amplifiers
The resonant circuit in a tuned amplifier contains coil. This coil is not purely inductive practically, due to losses associated with it. These losses are represented in the form of resistance.
Copper, eddy current and hysteresis losses constitute the total loss of a coil. Total loss in a coil is expressed by the series combination of inductor along with leakage resistance.
Bandwidth of tuned amplifiers
The bandwidth of a tuned amplifier is defined as that frequency range where the gain of the amplifier reduces to 70.7% of its highest value.
Let’s have a relationship between Q factor and bandwidth of a tuned amplifier.
The Q factor is given by![]()
: the frequency of resonance is given by
![]()
Classification of tuned amplifiers
The tuned amplifier is majorly classified into two categories: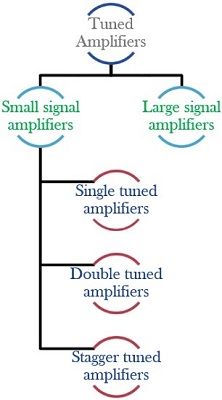
Small signal tuned amplifiers are used to amplify signals of small magnitude at radio frequency. As the power needed for its operation is small, thus operated under class A operation.
Large signal tuned amplifiers are used for amplification purpose but for the radio frequency signal having a large magnitude. As it requires large power for operation, thus operated under class B or C operation.
Further, we can classify the small signal tuned amplifier in the following categories:
Single tuned amplifier circuit employs, single parallel tuned circuit as a load per stage.
Each of the tuned circuits, in all the stage, is at the similar frequency. However, single stage tuned amplifier has a drawback known as potential instability.
- Double Tuned Amplifiers
In this type of tuned circuit, every stage consists of 2 mutually coupled tuned circuit. Both the circuit here is tuned to the similar frequency.
The double tuned circuit was basically introduced to overcome potential instability present in the single tuned amplifier. It consists of 2 inductively coupled tuned circuits. As the coupling of the 2 tuned circuit is changed, the shape of the frequency curve will also change.
- Stagger Tuned Amplifiers
This category of the tuned amplifier was basically introduced in order to overcome the disadvantages of the double tuned amplifier. As bandwidth is increased by the use of the double tuned amplifier, but due to difficulty in alignment, stagger tuning technique is used.
Stagger tuning is a technique by which, the cascaded stages are tuned to some different frequency. This provides an increase in bandwidth along with more desirable characteristics.
Advantages of Tuned amplifiers
- It possesses a good signal to noise ratio.
- Tuned amplifiers provide variable bandwidth for signal amplification.
- As it provides radio wave transmission, hence used in radio transmitter and receiver.
Disadvantages of Tuned amplifiers
- The overall circuitry is costly as well as bulky due to the presence of inductors and capacitors in tuned circuits.
- Amplification in the range of audio frequency cannot be achieved.
- Increase in bandwidth leads to complexity in the circuit.
Tuned amplifiers are used in high or radio frequency applications such as in TV and radio circuits.
Leave a Reply